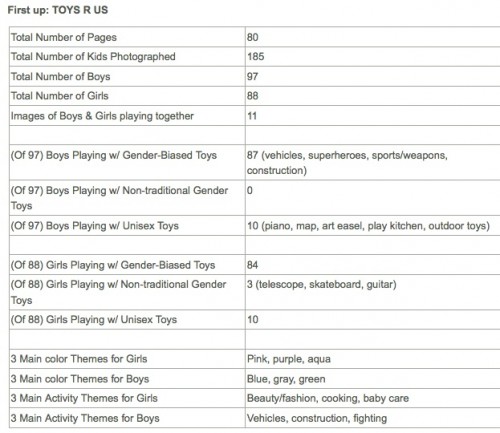
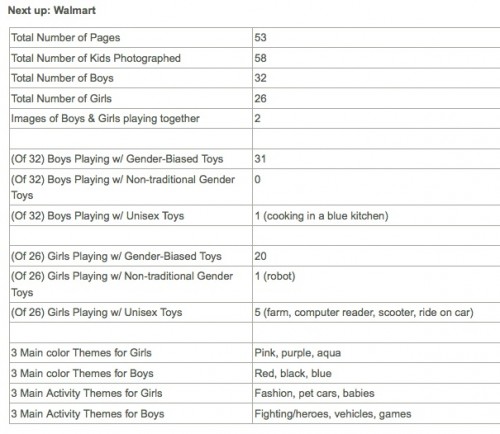
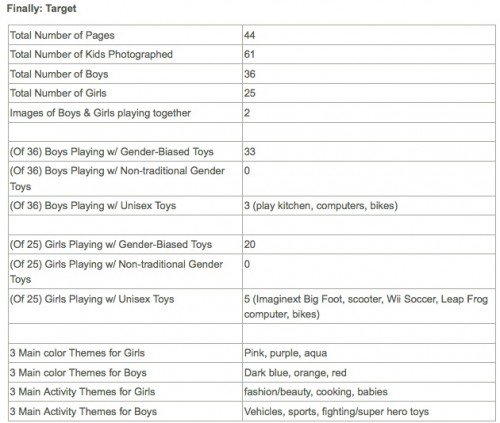
Some nice news has come out lately that the occasional toy store is taking the words boy and girl off of their aisle signs — mostly in Sweden, I say half-jokingly — but Google ngrams suggests that we’re nowhere near backing off of separating children’s toys by sex.
Sociologist Philip Cohen graphed the frequency of “toys for boys” and “toys for girls” relative to “toys for children.” This is just language, and it’s just American English, but it’s one indication that the consciousness raising efforts of organizations like Let Toys Be Toys is still on the margins of mainstream society.
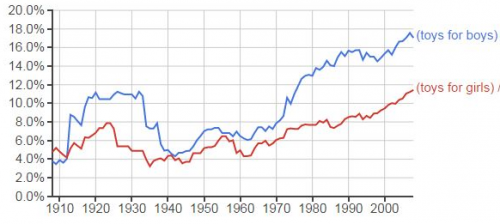
As you can see from the graph, the extent to which children are actively talked about as gendered subjects varies over time.
One explanation for why companies resist androgynous toys and clothes for children — an arguably adults, too — has to do with money. If parents with a boy and a girl could get away with one set of toys, they wouldn’t need to buy a second. And if they could hand down clothes from girls to boys and vice versa, they would buy less clothes. The same could be said for borrowing and trading between family members and friends.
It would really cut into the profits of these companies if we believed that all items for children were interchangeable. They work hard to sustain the lie that they are not.
Cross-posted at Pacific Standard.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.