Today the U.S. Supreme Court has announced that the female employees of Walmart will not be allowed to bring a class action lawsuit against the company, arguing that it has not been shown that they are a class. It would have been the largest employment discrimination suit in history.
It seems timely, then, to re-post our summary of some of the evidence against Walmart. Women are, on average, paid less, are less likely to be salaried, and hold lower-ranked positions than men. This is true even though there is less turnover among women, meaning that the average female employee has been working at Walmart significantly longer than the average male employee.
——————————
The U.S. Supreme Court is hearing arguments in the Dukes v. Wal-Mart suit. Wal-Mart is accused of egregious and systematic discrimination against the 1.5 million women who have worked there since 1998. The case isn’t based on anecdotal accounts; instead, it’s backed up by reams of data. Here is some of it.
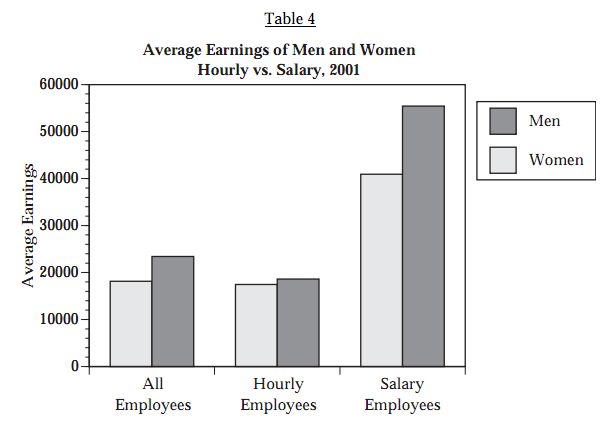
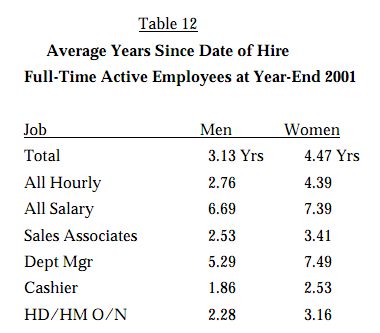
Women in hourly and especially salaried jobs make less money than men:
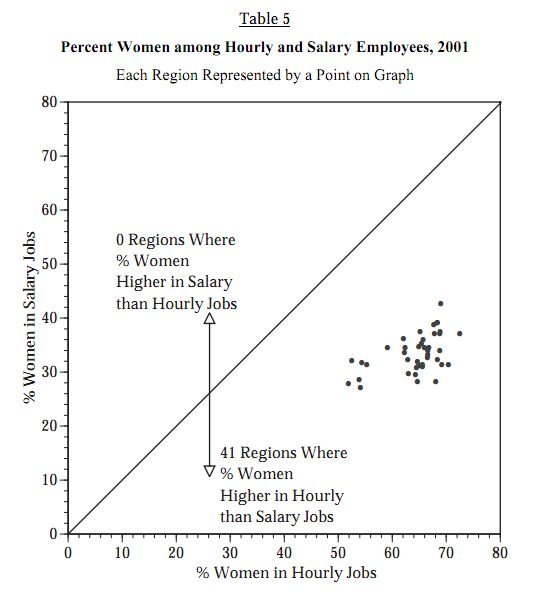
Women are disproportionately in hourly jobs (instead of salaried jobs) in every district examined:
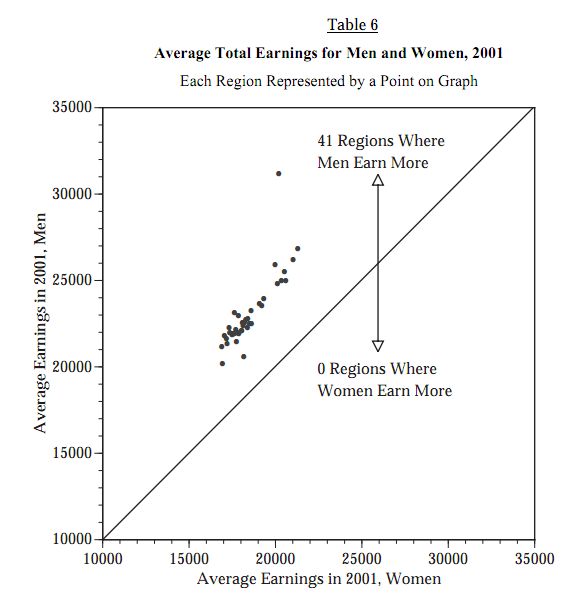
Women make less than men in every district examined:
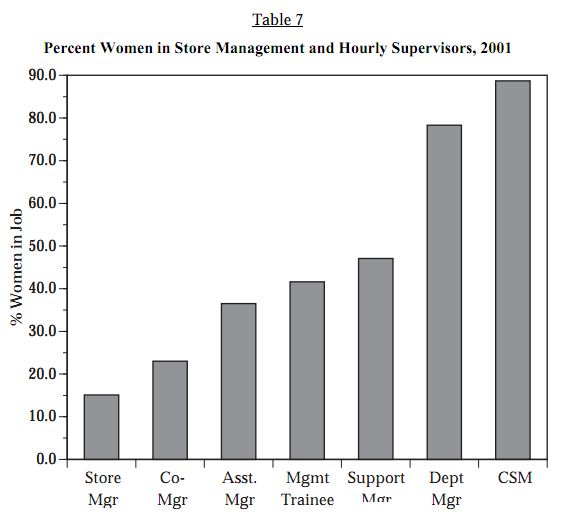
Women dominate the lowest paying, lowest ranked jobs at Walmart, and are a smaller and smaller percentages of the workforce as you go up the pay/rank hierarchy (from right to left):
And this is true despite the fact that women have lower turnover and have, on average, been working at Walmart significantly longer:
Walmart isn’t fighting the data. They’re not claiming non-discrimination. Instead, they’re arguing that compensation should be restricted to the women directly named in the suit instead of the 1.5 million women who’ve worked there. In other words, they’re hoping that the judge will not grant “class action” status to the case. If he does, it will be the largest class action lawsuit in history.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.