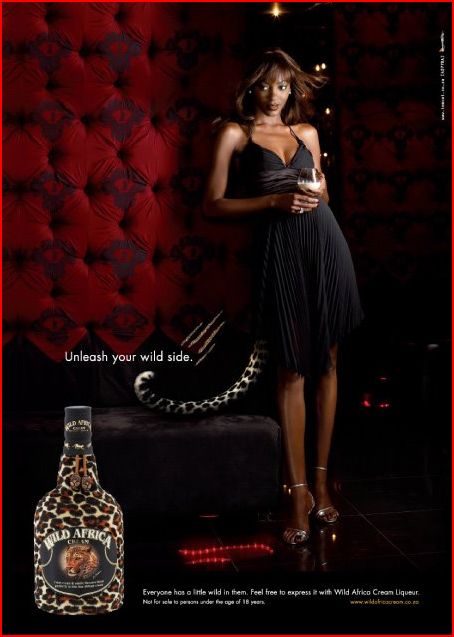
AdFreak drew my attention to a South African liqueur called Wild Africa Cream. The advertising suggests that drinking it will “unleash your wild side.”

We have posted before about the tendency to associate black people, especially black women, with animals (see here, here, here, and here), as well as the historical roots of this discourse. But, in this case, the advertising uses both black and white, male and female models.




I think what is interesting here is the association of Africa itself with animalism and primitiveness (an association that no doubt also colors our thinking about black people). (Notice that the first and only Disney film to be set in Africa, The Lion King, included only animals.) Catherine MacKinnon coined the term “anachronistic space” to refer to the idea that different parts of the globe represent different historical periods. See other examples of representing Africa in this way here, here, here, and here.
In line with this tendency to think in this way, in this advertising it’s almost as if black Africans are meant to represent white humans’ own more primitive past (ergo the drink “unleashing your wild side,” whoever you are).
I like to point out to my students that Americans are not more modern than Africans (purposefully eliding the abstract meaning of “modern” in a way that tends to surprise them out of their easy associations). It is 2009 there, also, and human evolution has progress no further from the “wild” in either place.
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.