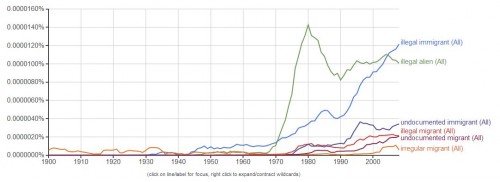
Citing the immigration scholar, Francesca Pizzutelli, Fabio Rojas explains that the phrase “illegal immigrant” wasn’t a part of the English language before the 1930s. More often, people used the phrase “irregular immigrant.” Instead of an evaluative term, it was a descriptive one referring to people who moved around and often crossed borders for work.
Rojas points out that the language began to change after anti-immigration laws were passed by Congress in the 1920s. The graph above also reveals a steep climb in both “illegal immigrant” and “illegal alien” beginning in the ’70s.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.