Click here for a nice gender and race analysis of a range of Halloween costumes for adults and kids by our blogger, Wendy. We’ve also highlighted two costumes in particular: the Sexy Scholar and Anna-Rexia. And, of course, just a few days ago, we posted about the Halloween display that includes a lynched Sarah Palin and a screenshot of an Obama mask found by searching for “terrorist costume.” And don’t miss our jack-o’-lantern tribute to Max Weber. See also, if you like, my Huffington Post about the race, class, and gender politics of Halloween.
To our newest Halloween material:
Andrea G. scanned in an entire Halloween costume catalog and offers some global observations about the breadth of costumes made available. You can check out her flickr account here or scroll down for the images and some of Andrea’s commentary.
The Cover and Back:
Boys’ costumes:

Boys’ costumes (continued) and girls’ costumes:

Girls’ costumes (continued):

Women’s costumes:
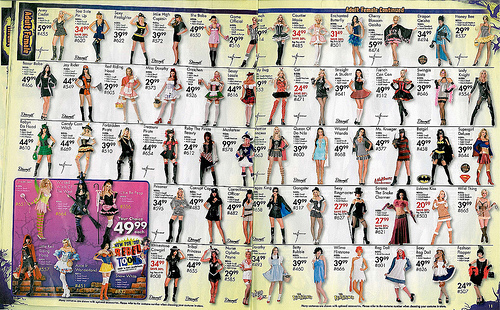

Plus women’s costumes:


Plus women’s costumes (continued) and adult men’s costumes:

Plus men’s costumes:
First, Andrea notes how gendered the costumes are. Women overwhelmingly are supposed to look sexy, while men are supposed to look funny or scary. Note that this doesn’t vary much by age. The costumes for adults and children are strikingly similar.
Second, Andrea points to how often men’s faces are covered by masks and how infrequently women’s are. She writes that “5 out of the 198 costumes categorized under “female” or “girls” were masked (2.5%)” and “96 of the 180 costumes categorized under “male” or “boys” were masked (53.3%).” Andrea thinks: “I think this touches on the double standard American society holds for females/girls to be attractive and beautiful, while males/boys do not have to cater to this social rule, for the most part.”
Third, Andrea notes that there are costumes designed to make men look fat, but not women. For example, this “Freshman 15” costume:

Thanks Andrea!














