Folks at The Vagenda had the idea of asking readers to rewrite stupid/sexist headlines. Like this:
The results were fantastic. Here’s a sampling.
From @bexatrex:
From @ce_corp: 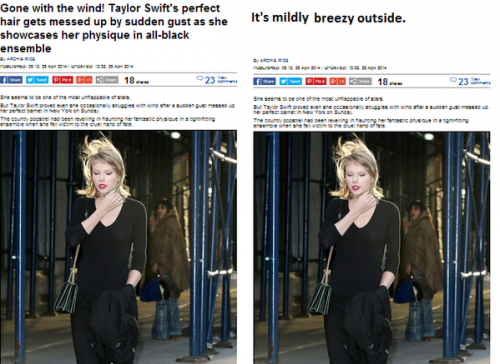 Via Buzzfeed.
Via Buzzfeed.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.