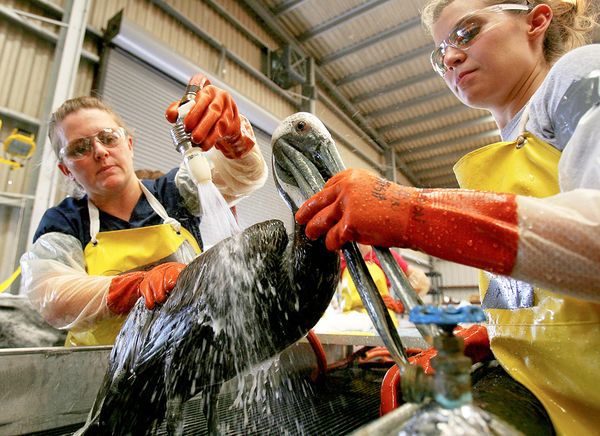
Crossposted at Jezebel.
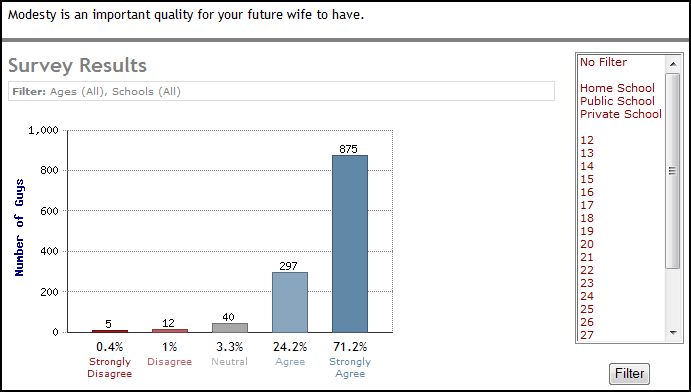
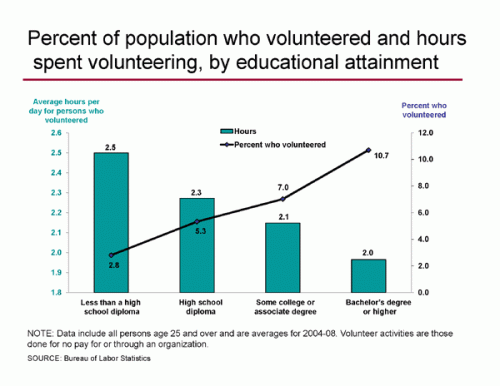
Robin E. sent us to a downright fascinating set of survey results. Administered by a Christian website, the survey questions were submitted by “Christian girls” who wanted to know what “Christian guys” think is modest. 1,600 guys then answered the survey, offering both quantitative and qualitative answers. Why would girls care what guys, as opposed to God, think? Because Christian guys, their future husbands, are judging them on their modesty. Ninety-five percent of them say that modesty is an important quality in their future wife (see the question in the upper left corner):
So, how do these “guys” define immodesty? The most common theme was dressing to draw attention to the body instead of the heart or spirit.
Something that is immodest is something that is designed to arouse lust within me (male, age 24).
Something that is immodest is something that is unnaturally revealing (male, age 20).
Something immodest draws attention to a girl’s body (male, age 28).
Many of the guys stressed that they really wanted to interact with girls as people. Borrowing language from feminism, they expressed a desire to think of a girl as a whole person, not just a hot body.
Something attractive draws you toward them. It makes you respect the person. Something immodest is usually unattractive. It makes you think less of that person, thinking of them as an object… (male, age 16).
My responsibility is to not treat women as objects for my satisfaction, even if they dress and act like it. It devalues them, and makes me a user of people… (male, age 26).
In a move that is in contrast to (most) feminist values, however, girls are supposed to help men treat them like people by not dressing like an object. That is, by not dressing immodestly.
So what rules for girls did guys identify?
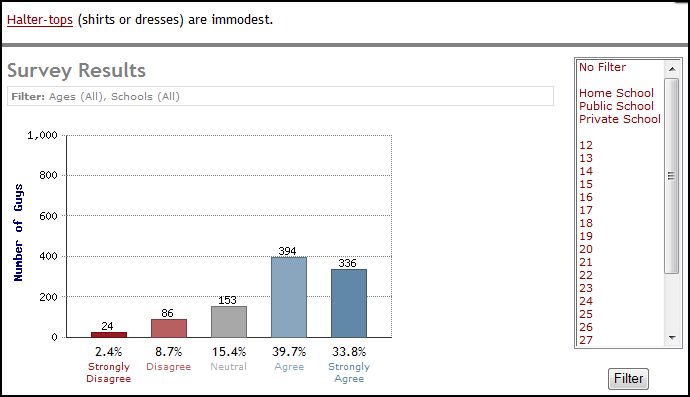
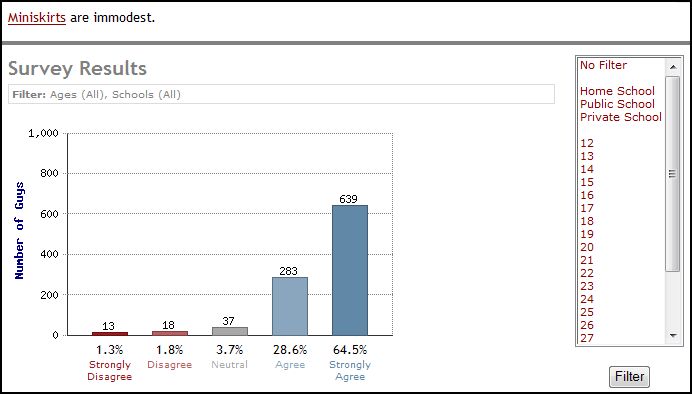
Well, first, guys largely agreed that revealing clothes were immodest (again, see the question in the upper left corner):
Halter tops and mini skirts, I suppose, are obvious candidates for immodesty. There were lots more subtle rules, too, though with less agreement.
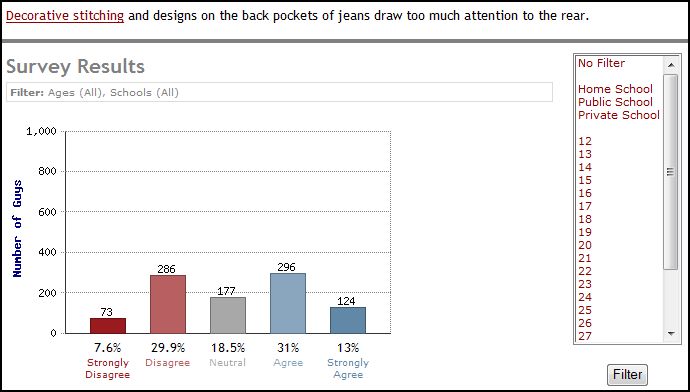
Forty-four percent of guys think that designs on the back pockets of jeans are immodest (19% aren’t sure):
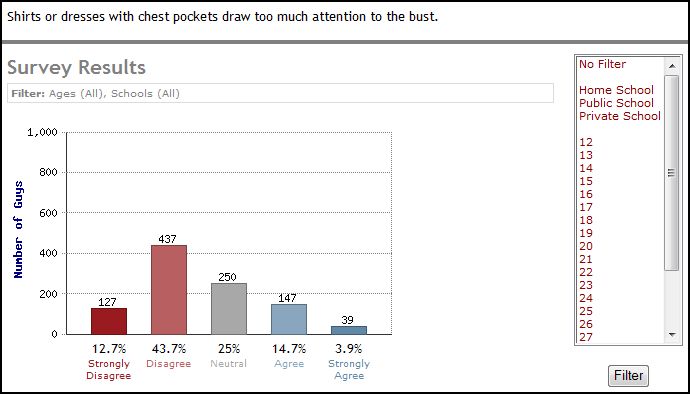
A minority, 19 percent, think that shirts with pockets are immodest (25% aren’t sure):
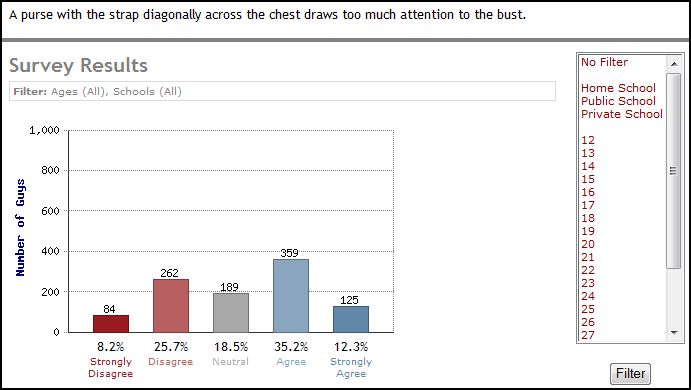
Forty-eight percent think that purses should not be worn across the body (19% aren’t sure):
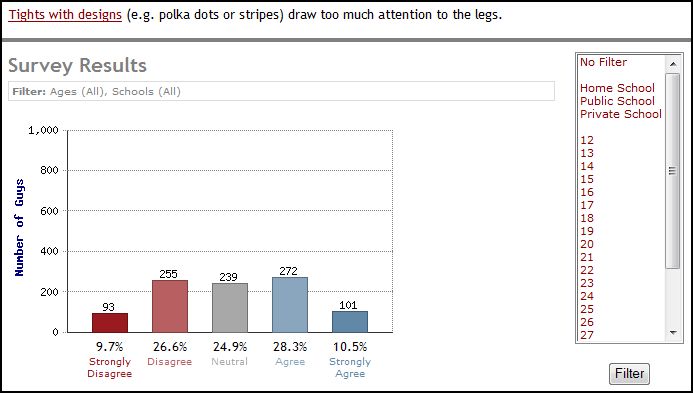
Thirty-nine percent oppose tights with designs (25% aren’t sure):
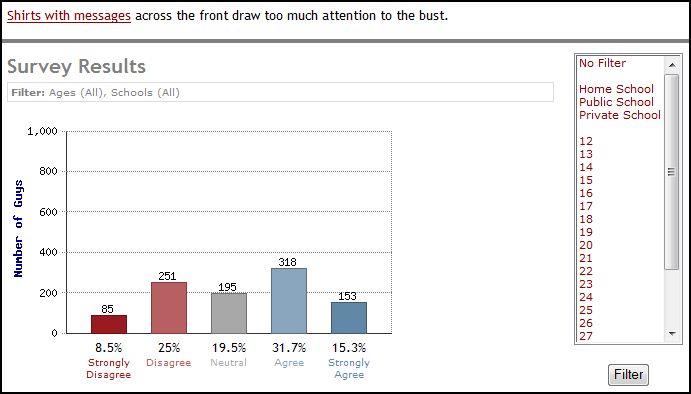
Forty-seven think that t-shirts with messages across the front improperly draw attention to breasts:
But being modest wasn’t simply a matter of clothes. Guys defined immodesty, also, as an “attitude” or a “carelessness.” Attaining modesty was also about how you use your body and the way you act, “sexually or otherwise.”
An immodest lady is loud, proud, and dresses in a way that communicates such an attitude (male, age 24).
Something becomes immodest when the person wearing it has an attitude of carelessness (male, age 17).
As one guy said:
If you are dressing to get attention from a guy, then anything you wear can be immodest (male, age 13; my emphasis).
Some examples of behavior the guys mostly agreed was immodest:
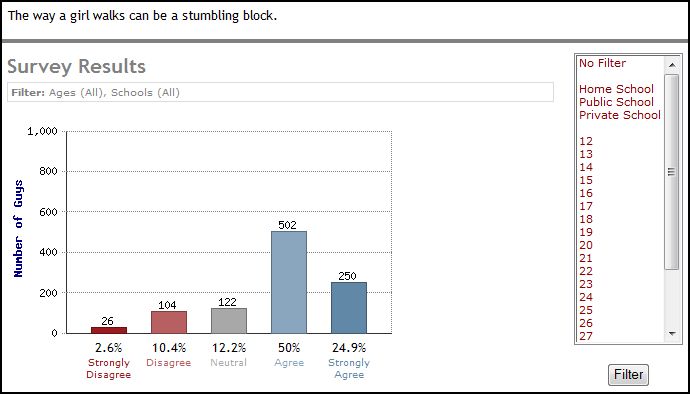
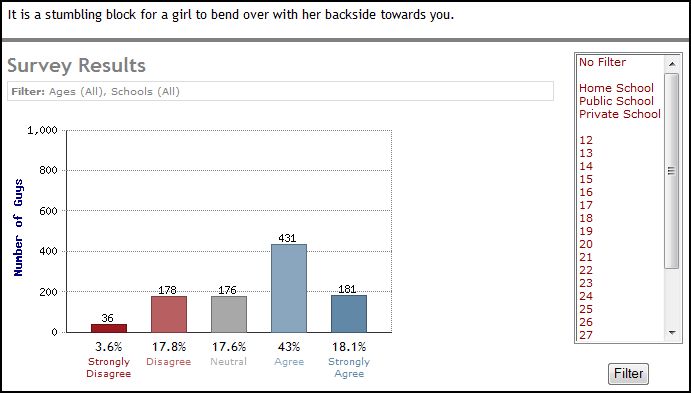
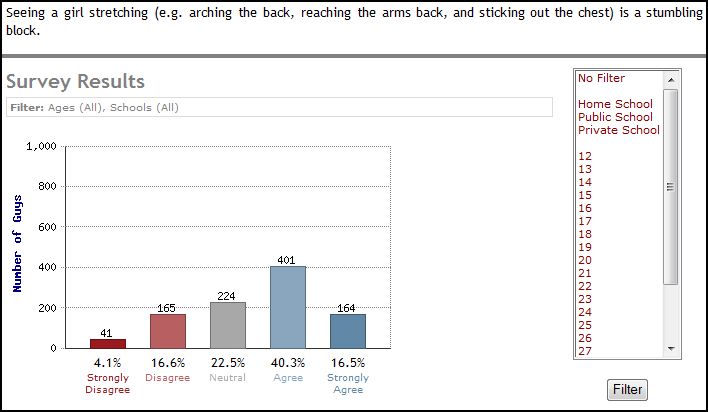
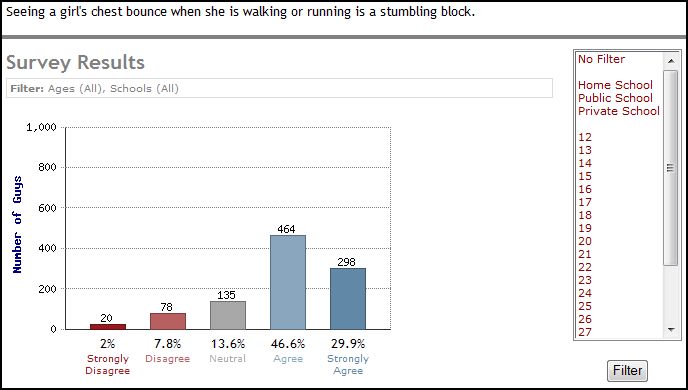
Immodesty, then, is not simply about being vigilant about your clothing (don’t wear a purse that falls diagonally across your body, don’t show your arms or your thighs), it’s a constant vigilance about how you display your body (don’t stretch, bend, or bounce). “Clothing plays a part in modesty, but it is only a part,” an 18 year old male explains, “Any item of clothing can be immodest” (his emphasis).
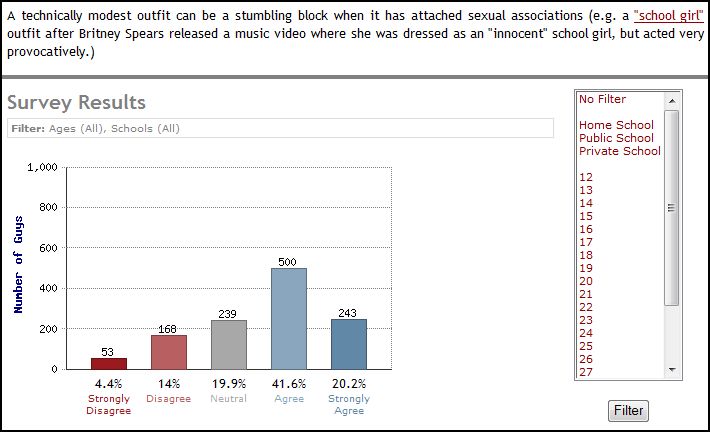
In addition, these rules are potentially changing all the time. A “technically modest” outfit, such as a school uniform, can suddenly have immodest connotations (so watch MTV, girls, to stay on top of these shifting meanings):
This is a great deal of self-monitoring for girls. Not just when they shop, but when they get dressed, and all day as they move, and with constant re-evaluation of their clothes and how they fit. But, the rationale is, they must be vigilant and obey these rules in order to protect guys from the power of all bodies (both their own sexiness, and men’s biological response to it). Guys are burdened with lust, they insist.
A lot of the guys in this survey talked about temptation. In some cases, the men would use very powerful words, such as this guy defining immodest:
Immodest: Screams that her body is different than mine. Attempts to manipulate me. Forcefully offers to trade what I want (in the flesh) for what she wants: attention (male, age 30).
This language — suggesting that women’s bodies “scream” at him, attempt to control him, and “forcefully” tempt him — is reminiscent of Tim Beneke’s interviews with men about sexual violence in Men on Rape. Michael Kimmel (summarizing Beneke in Guyland) discusses how lots of the terms used to describe a beautiful, sexy woman are metaphors for danger and violence: “ravishing,” “stunning,” bombshell,” “knockout,” “dressed to kill,” and “femme fatale.” “Women’s beauty,” Kimmel surmises, “is perceived as violence to men” (p. 229).
This is very much like the rationale for the burqa. Women’s bodies incite men’s sexual desires, sometimes to violence; they must be kept hidden.
These Christian guys, however, did claim responsibility for their own thoughts, feelings, and actions. When asked about their role in avoiding lust, many were adamant that it was their own responsibility. Many felt that innocent, shameless, platonic interaction between men and women was a team effort:
Sisters in Christ, you really have no concept of the struggles that guys face on a daily basis. Please, please, please take a higher standard in the ways you dress. True, we men are responsible for our thoughts and actions before the Lord, but it is such a blessing when we know that we can spend time with our sisters in Christ, enjoying their fellowship without having to constantly be on guard against ungodly thoughts brought about by the inappropriate ways they sometimes dress. In 1 Corinthians 12 the apostle Paul presents believers as the members of one body – we have to work together. Every Christian has a special role to play in the body of Christ. That goal is to bring glory to the Savior through an obedient, unified body of believers – please don’t hurt that unity by dressing in ways that may tempt your brothers in Christ to stumble (male, age 24).
The asymmetry of this project, however, is striking. The lust is men’s; the bodies are women’s. It’s an asymmetry built right into the survey design. Modesty is something pertains to only girls and immodesty is something that guys get to define. This may be even more pernicious than women’s constant self-monitoring. It erases women’s own desires and the sex appeal of men’s bodies, leading women to spend all of their time thinking about what men want. By the time they do have sex, and most of them will, they may be so alienated from their own sexual feelings that they won’t even be able to recognize them.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.