If it were to happen that the decision as to whether the tomato was a fruit or vegetable made it to the highest court of the land — if such a strange thing were to happen — certainly the botanist’s opinion would weigh heaviest. Right?
Nope.
In fact, this decision did make it all the way to the Supreme Court. It happened in 1893. The case was brought by a tomato importing family by the last name of Nix. At the time, the law required that taxes be collected on vegetables that were imported, but not fruit.
The lawyers for the Nix family argued that the tomato is a fruit and, therefore, exempt from taxation. They were, of course, correct. Botanists define fruit according to whether it plays a reproductive role. So, any plant product with one or more seeds is a fruit, whereas vegetables don’t have seeds. Fruits are ovaries, for lack of a better term. All other plant products — stems, roots, leaves, and some seeds — are vegetables.
But the Supreme Court said, essentially, “We don’t care” and gave their gavel a good pound. Here’s some of the text of their unanimous opinion:
Botanically speaking, tomatoes are the fruit of a vine… But in the common language of the people, whether sellers or consumers of provisions, all these are vegetables which are grown in kitchen gardens, and which, whether eaten cooked or raw, are… usually served at dinner in, with, or after the soup, fish, or meats which constitute the principal part of the repast, and not, like fruits generally, as dessert.
The judges were referring to the common understanding, which has more to do with how we use the plant products than how plants use them. Your typical chef roughly divides plant products according to whether they’re sweet or savory. Fruits are sweet. Vegetables are savory and used for main courses and sides. It’s all about whether you eat them for dinner or dessert. And that’s what the Supreme Court upheld.
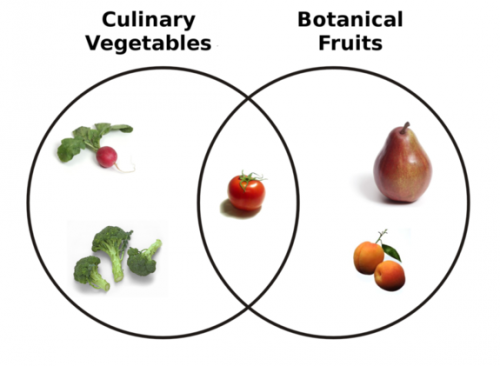
Culinary vs. botanical categorization (source):
Since the culinary scheme dominates our colloquial understanding, we mis-classify lots of other things, too. Zucchini, bell peppers, eggplants, string beans, cucumbers, avocado, and okra — all fruit. Rhubarb is a vegetable. No seeds. Pineapples are fruits. “Ah ha!” you say, “I’ve never noticed a pineapple having seeds!” That’s because commercial growers sell us seedless pineapples. Who knew. Berries are fruit, but strawberries, blackberries, and raspberries are not actually berries. Isn’t this fun?
Bruno Latour and Steve Woolgar, in Laboratory Life: The Social Construction of Scientific Facts, wrote:
If reality means anything, it is that which “resists” the pressure of a force. … That which cannot be changed at will is what counts as real.
We often think of cultural facts as somehow less real than biological ones. For the Nix family, though, biology mattered naught. They still had to pay the damn tax on their tomatoes. Culture is real, folks. Social construction is not just something we do to reality; for all intents and purposes, it is reality.
Cross-posted at Pacific Standard.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.