Emory University has a very detailed database about the Atlantic slave trade, titled Voyages: The Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade Database, which I don’t believe we’ve posted before (my apologies if we have). It includes nine maps providing information on major points of departure and destination ports for the trans-Atlantic trade; here’s a general overview:
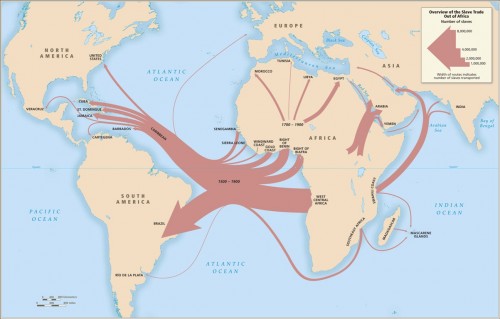
Initially the vast majority of slave voyages were organized by firms or individuals in Spain and Portugal; however, over time the slave trade was dominated by groups from northern Europe. Great Britain eventually played a major role, and over 1/3 of documented slave voyages were organized there.The description of Map 6 explains, “vessels from the largest seven ports, Rio de Janeiro, Bahia, Liverpool, London, Nantes, Bristol, and Pernambuco carried off almost three-quarters of all captives removed from Africa via the Atlantic Ocean.”
This map shows where voyages were organized, and the % of all documented African slaves that voyages from that country/area transported:
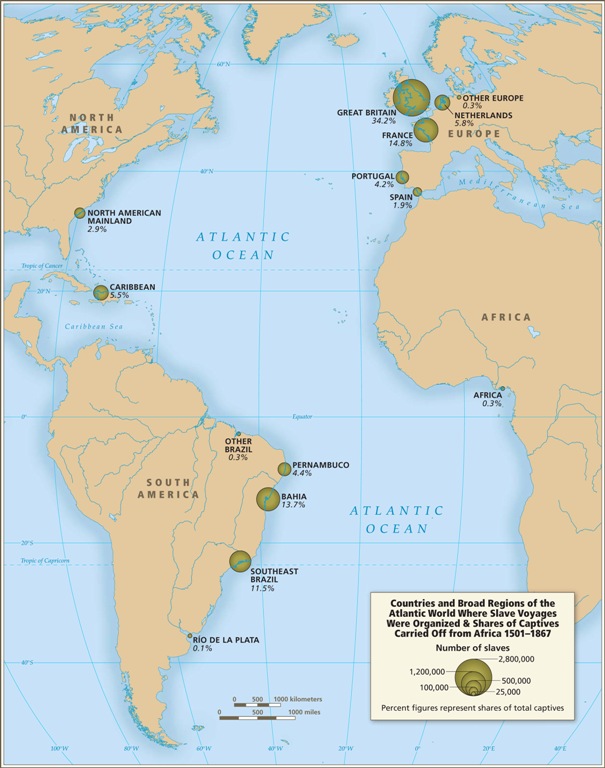
In the U.S., students generally learn about slavery in relation to cotton plantations and, to a lesser extent, tobacco. However, overall those two crops played a relatively minor role in the growth of the global slave trade. It was the growing taste for sugar, and the creation of sugar plantations, particularly in the Caribbean and South American coastal areas, that produced such an enormous demand for African slaves in the Americas. According to the Voyages website, less than 4% of all Africans captured were sold in North America.
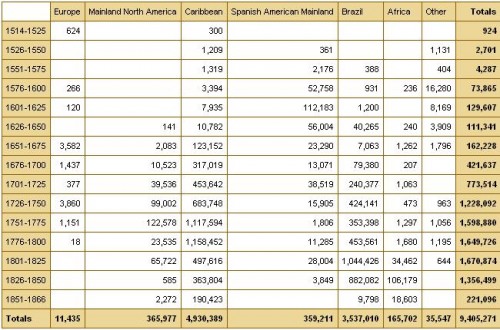
The website also has a database of thousands of documented trips in the trans-Atlantic slave trade, including everything from point of origin, destination, number of slaves, % who died during voyage, length of trip, and so on. Some include many more details than others, as you’d expect. You can also create tables to display the variables you’re interested in. Here’s the table showing the slave trade, broken into 25-year intervals and by destination. We can clearly see that the slave trade made one big jump in the late 1500s (going from 4,287 in the 1551-1575 interval to 73,865 between 1576 and the end of the century) and another huge jump in the late 1600s, with the height of the slave trade occuring in the 1700s through the mid-1800s:
You can also create various graphs and charts. Here is a graph of the % of slaves who died during the trip, by year:
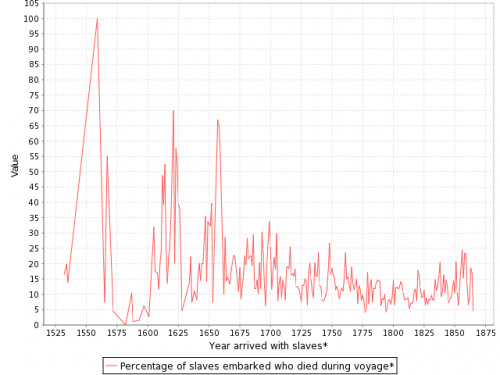
I presume the extremely high numbers in the 1550s must be skewed by some ships that sank or met some other disaster that led to the death of everyone aboard.
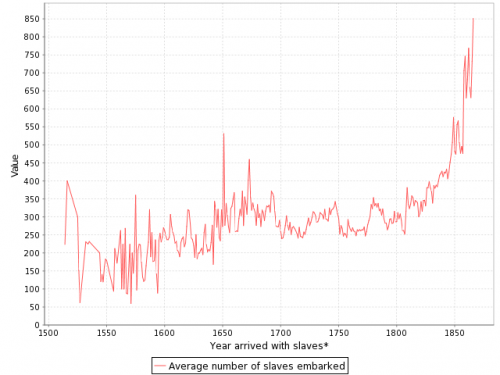
Over time, ships carried larger numbers of individuals per trip:
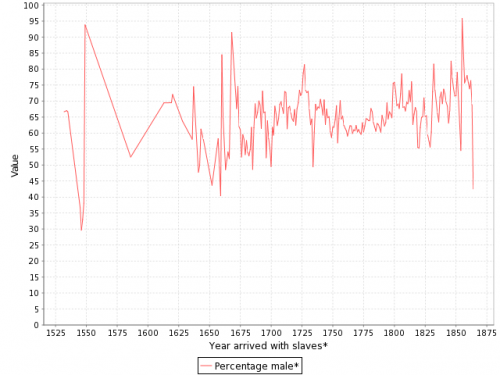
The individuals taken as part of the slave trade were predominantly male:
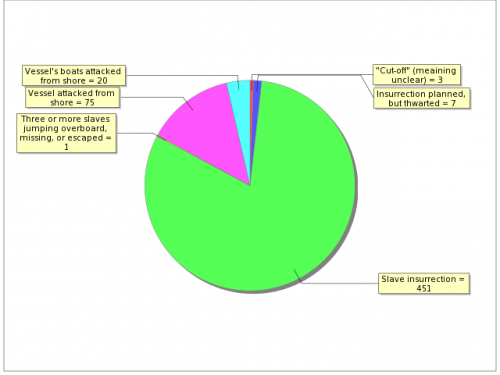
Documented types of resistance from captives or from Africans trying to free them:
You can spend quite a bit of time on this, I warn you — creating timelines, graphs, and so on. It’s taken me an hour to write this post because I keep getting distracted creating charts and tables. Overall, the site is a fantastic resource for both specific information and for helping illuminate the enormity of the Atlantic slave trade. Thanks to Shamus Khan for the tip.





















