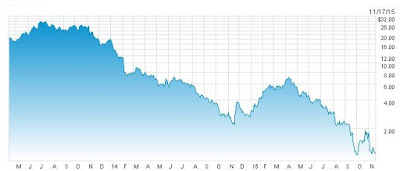
Americans have a low opinion of Congress. Less than 10% of the voters think that Congress is doing a good job. But their own Representative . . . not so bad. A third of us think that our own rep deserves re-election (Rasmussen). Even that is low. Until recently, a majority of people approved of their own representative while disapproving of Congress in general. It’s been the same with crime. People feel safer in their own neighborhoods than elsewhere, even when those other neighborhoods have less crime.
Race relations too are bad . . . elsewhere. In the last year, the percent of Americans saying that race relations in the country are “bad” doubled (roughly from 30% to 60%). That’s understandable given the media coverage of Ferguson and other conflicts centered on race. But people take a far more sanguine view of things in their own community. Eighty percent rate local race relations as “good,” and that number has remained unchanged throughout this century. (See this post from last summer.)
Not surprising then that the problem with marriage in the US turns out to be about other people’s marriages. A recent survey asked people about the direction of their own marriage and marriage in the US generally.
Only a handful of people (5%) see marriage generally as getting stronger. More than eight times that say that their own marriages have strengthened. The results for “weaker” are just the reverse. Only 6% say that their own marriage has weakened, but 43% see marriage in the US as losing ground.
Why the “elsewhere effect”? One suspect is the media bias towards trouble. Good news is no news. News editors don’t give us many stories about good race relations, or about the 25-year drop in crime, or about the decrease in divorce. Instead, we get crime and conflict and a variety of other problems. Add to this the perpetual political campaign with opposition candidates tirelessly telling us what’s wrong. Given this balance of information, we can easily picture the larger society as a world in decline, a perilous world so different from the one we walk through every day.
At first glance, people seeing their own relationships as good, others’ relationships as more strained seems like the opposite of the pluralistic ignorance on college campuses. There, students often believe that things are better elsewhere, or at least better for other students. They think that most other students are having more sex, partying more heartily, and generally having a better time than they are themselves. But whether we see others as having fun or more problems, the cause of the discrepancy is the same – the information we have. We know our own lives first hand. We know about those generalized others mostly from the stories we hear. And the people – whether news editors or students on campus – select the stories that are interesting, not those that are typical.
Originally posted at Montclair SocioBlog.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.