Cross-posted at Jezebel.
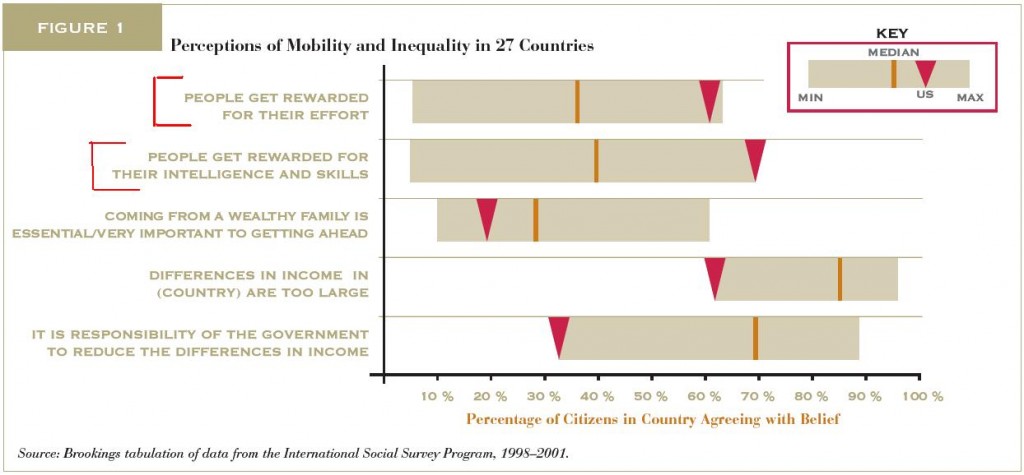
We have posted previously about how desserts, particularly chocolate ones, are often advertised to women as indulgences they can use to overcome romantic disappointments, or even as substitute sources of love. L. Ellis sent in an example of this, an ad found in Bon Appetit for Sugar in the Raw that tells women to make brownies to deal with breakup:
Indeed, you can calculate how much dessert you’re going to need by how much time you invested in the guy (“Count the years you dated. If it exceeds 5, double the recipe.”). The ad is also a great example of the contradictory messages women get to be thin but also indulge — today you can “devour that pan of chocolaty goodness,” full of butter and sugar, while you cry over your lost love, but it’s a short-lived reprieve. Inevitably, you now being single and all, the “diet starts tomorrow.”