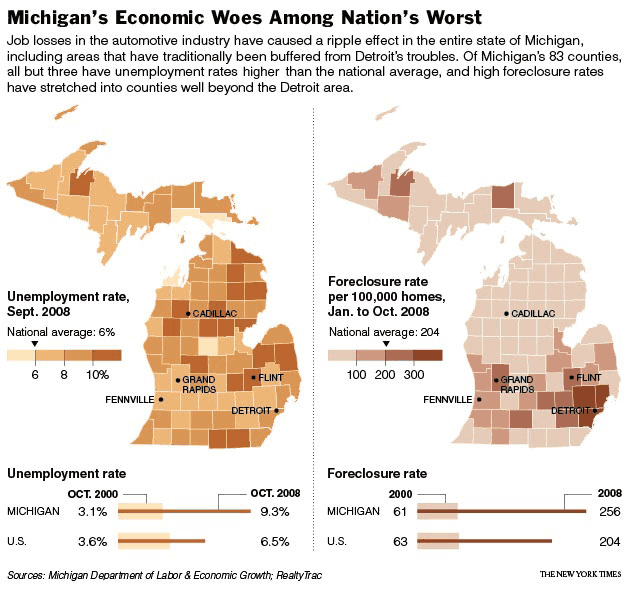
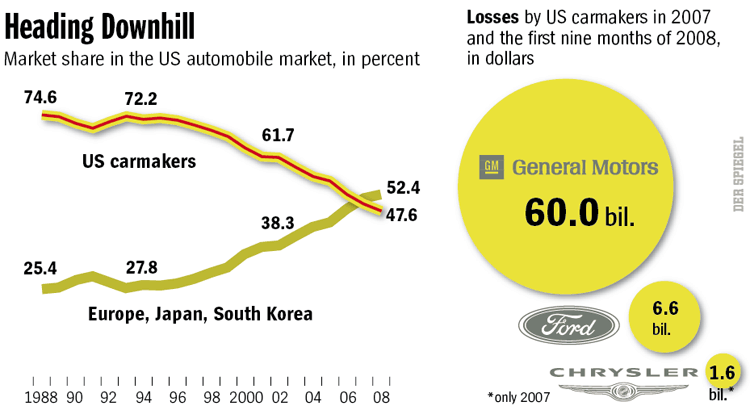
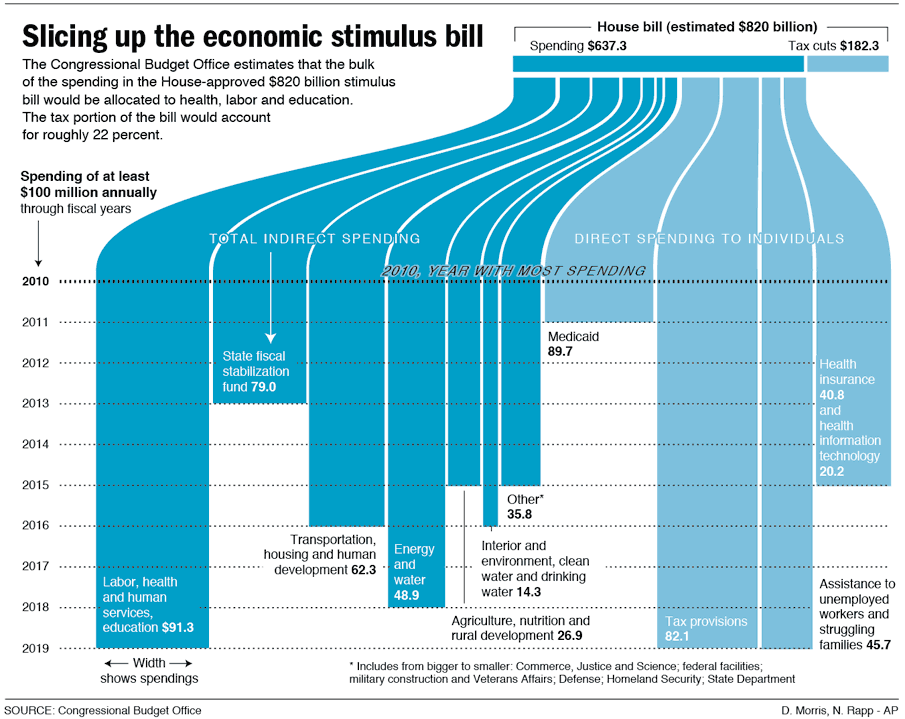
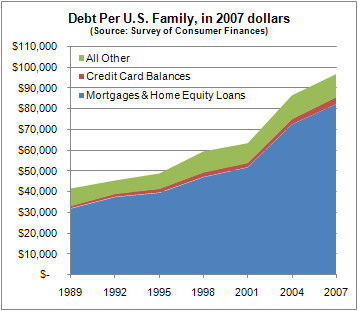
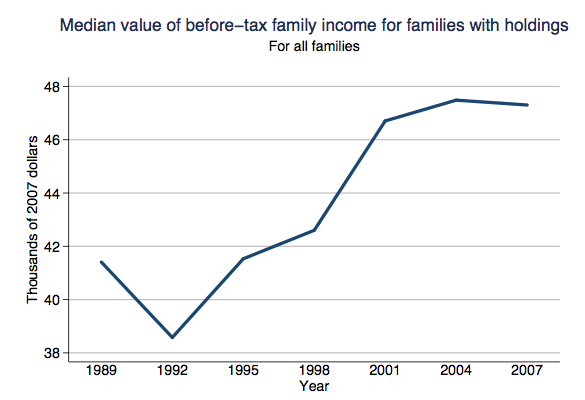
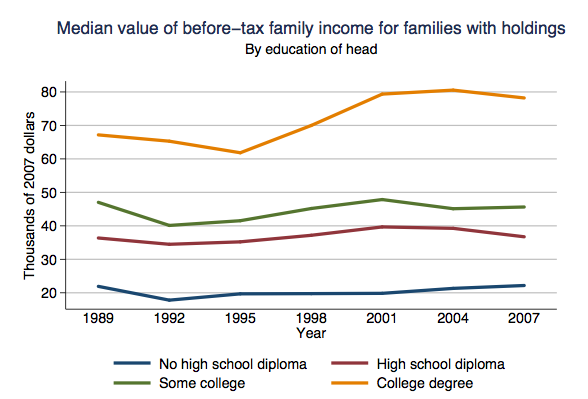
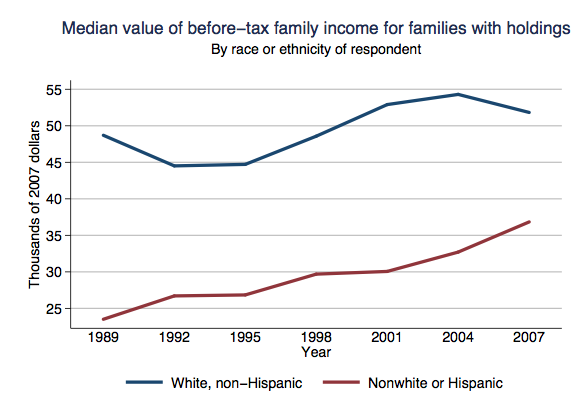
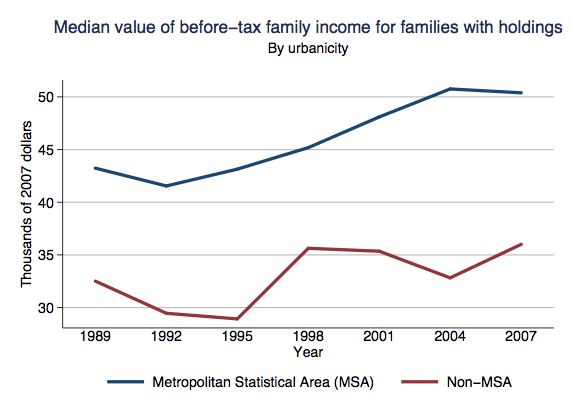
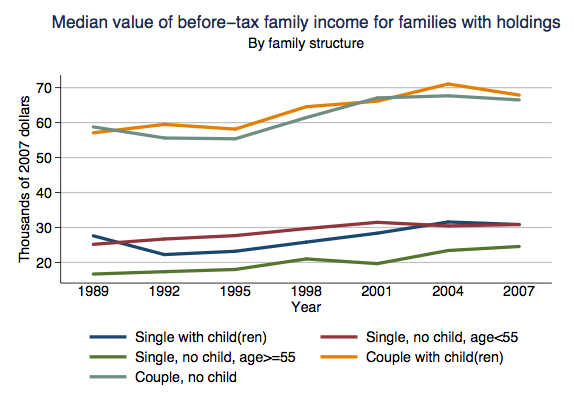Jim C. sent us this graphic designed to illustrate a proposal to reduce the lanes on Jarvis Street in Toronto from five to four (Globe and Mail, May 22, 2009, p. A12). As Jim points out, the text of the graphic describes the proposal accurately, and even points out that the graphic misrepresents the change, but the graphic itself still gives the impression that the reduction will be to two, not four lanes.
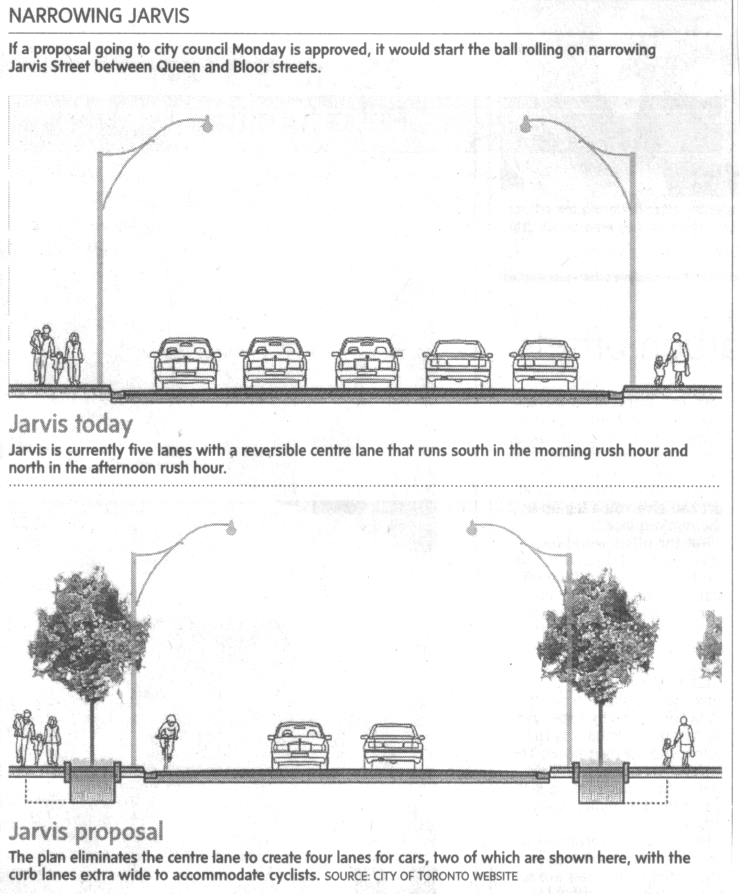
It is a good example of how much graphics matter. Even with the text, it is potentially misleading. Such misrepresentation can also be purposeful and political. Jim speculates that this is the case here:
As is often the case whenever there are modest efforts to make space on city streets for pedestrians and cyclists, right-wing councillors (and affluent commuters) raised the spectre of traffic chaos and a ‘war on the car’.
If you’re interested in comparing the representation of this proposal by the Globe with its representation in the proposal itself, check out the final page of the proposal. Thanks to Nick J. B. in the comments for the link.
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.