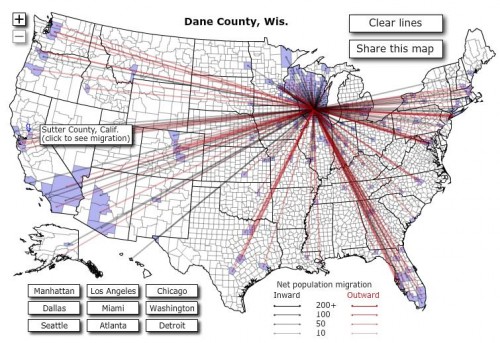
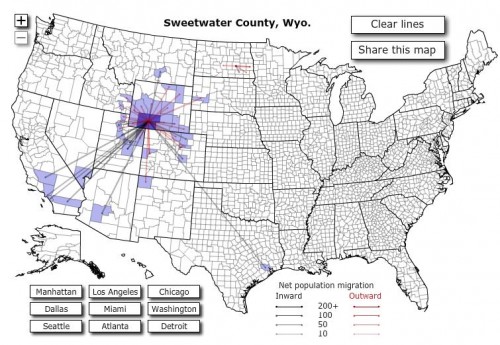
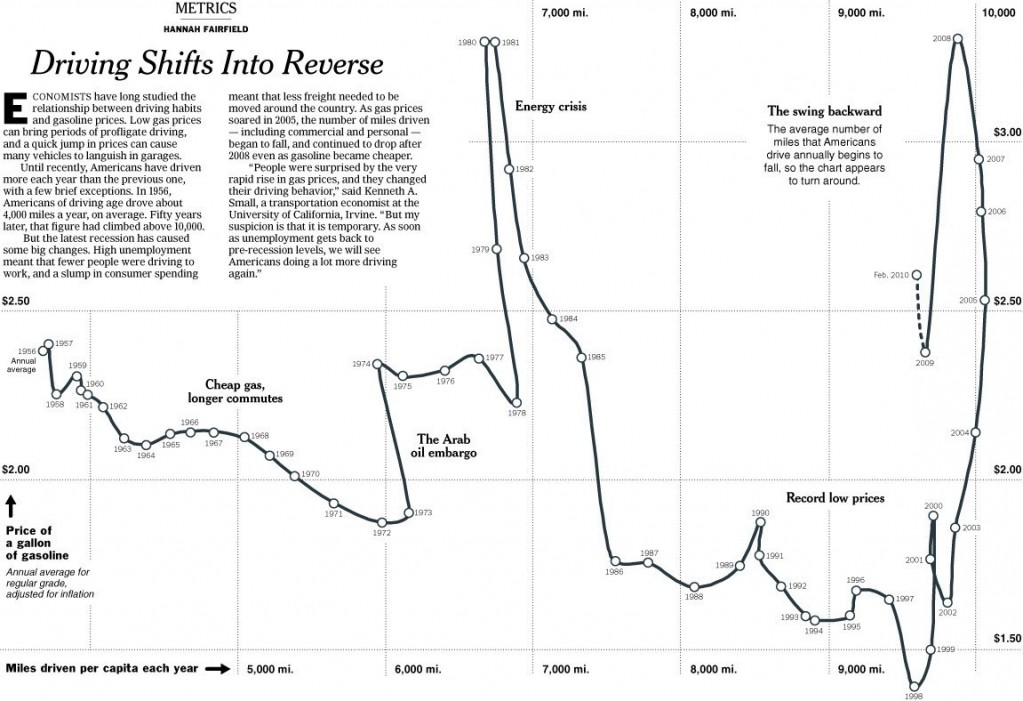
Lynne Shapiro brought our attention to the way that choices to locate bus stops can marginalize their riders, discouraging use of public transportation by those who could choose between the bus and a car and placing a burden on those who do ride the bus to complete errands. Lynne has taken photos of bus stops around Connecticut and the D.C. metro area malls and stores. She points out that they are often far from entrances, and in some cases malls didn’t allow them on the property at all.
Here are two photos, from different angles, of a bus stop at Hamden Plaza, a major shopping center in the New Haven, CT, area:
The result is to create additional burdens on those using the bus for shopping, requiring them to haul or push their purchases a significant distance to the bus stop, a process that would be particularly unpleasant in rain or snow (or, here in Vegas, when it’s 117 degrees), or for those with mobility issues.
When mass transit stops are systematically located in inconvenient or isolated areas, it disadvantages those who are dependent on public transportation and discourages others from choosing to ride rather than driving their own car, and reinforces a common perception of the bus, in particular, as an inferior form of transportation — a topic discussed more fully by Sikivu Hutchinson in Imagining Transit: Race, Gender, and Transportation Politics in Los Angeles.
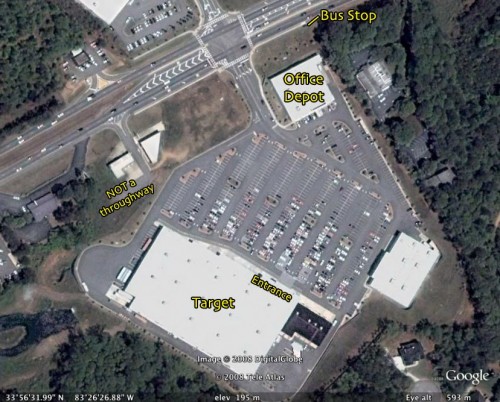
UPDATE: Reader codeman38 provided a link to an image of a Target parking lot in Athens, Georgia, which shows the lack of clear pedestrian paths from the bus stop to the store: