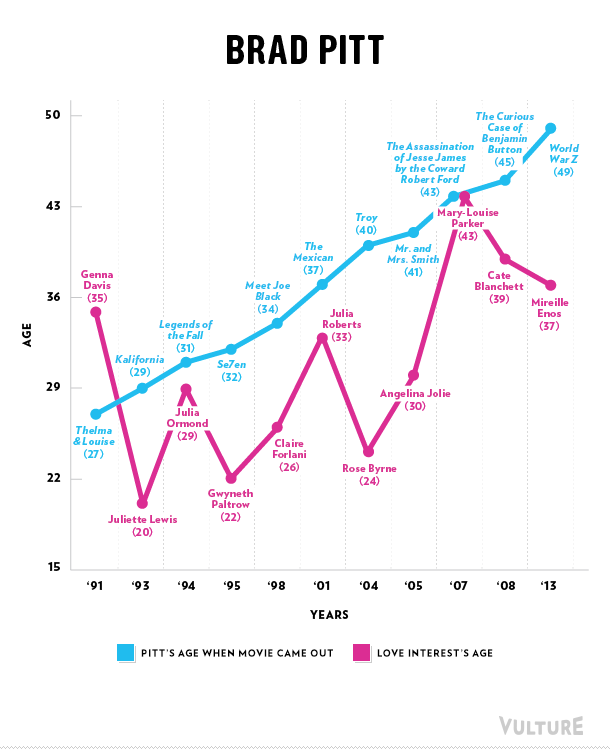
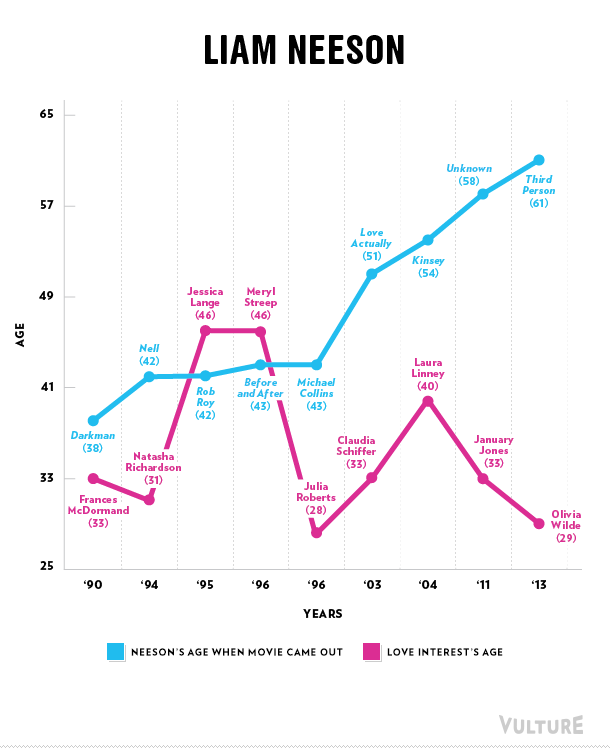
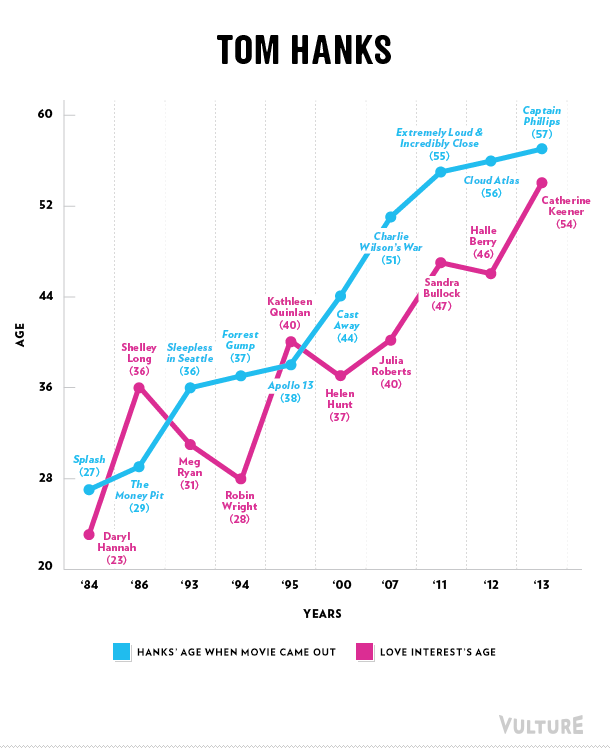
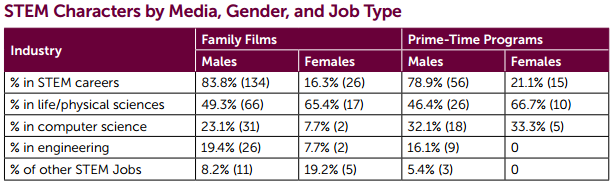Cross-posted at Family Inequality.
The other day when the Pew report on mothers who are breadwinners came out, I complained about calling wives “breadwinners” if they earn $1 more than their husbands:
A wife who earns $1 more than her husband for one year is not the “breadwinner” of the family. That’s not what made “traditional” men the breadwinners of their families — that image is of a long-term pattern in which the husband/father earns all or almost all of the money, which implies a more entrenched economic domination.
To elaborate a little, there are two issues here. One is empirical: today’s female breadwinners are much less economically dominant than the classical male breadwinner — and even than the contemporary male breadwinner, as I will show. And second, conceptually breadwinner not a majority-share concept determined by a fixed percentage of income, but an ideologically specific construction of family provision.
Let’s go back to the Pew data setup: heterogamously married couples with children under age 18 in the year 2011 (from Census data provided by IPUMS). In 23% of those couples the wife’s personal income is greater than her husband’s — that’s the big news, since it’s an increase from 4% half a century ago. This, to the Pew authors and media everywhere, makes her the “primary breadwinner,” or, in shortened form (as in their title), “breadwinner moms.” (That’s completely reasonable with single mothers, by the way; I’m just working on the married-couple side of the issue — just a short chasm away.)
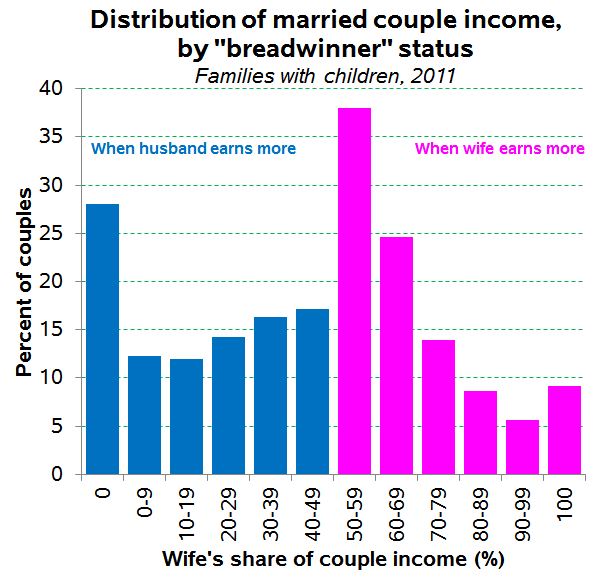
The 50%+1 standard conceals that these male “breadwinners” are winning a greater share of the bread than are their female counterparts. Specifically, the average father-earning-more-than-his-wife earns 81% of the couple’s income; the average mother-earning-more-than-her-husband earns 69% of the couple’s income. Here is the distribution in more detail:
This shows that by far the most common situation for a female “breadwinner” is to be earning between 50% and 60% of the couple’s income — the case for 38% of such women. For the father “breadwinners,” though, the most common situation — for 28% of them — is to be earning all of the income, a situation that is three-times more common than the reverse.
Collapsing data into categories is essential for understanding the world. But putting these two groups into the same category and speaking as if they are equal is misleading.
This is especially problematic, I think, because of the historical connotation of the term breadwinner. The term dates back to 1821, says the Oxford English Dictionary. That’s from the heyday of America’s separate spheres ideology, which elevated to reverential status the woman-home/man-work ideal. Breadwinners in that Industrial Revolution era were not defined by earning 1% more than their wives. They earned all of the money, ideally (meaning, if their earnings were sufficient) but, just as importantly, they were the only one permanently working for pay outside the home. (JSTOR has references going back to the 1860s which confirm this usage.)
Modifying “breadwinner” with “primary” is better than not, but that subtlety has been completely lost in the media coverage. Consider these headlines from a Google news search just now:
- Huffington Post: All-Male Fox Panel Freaks Out About Female Breadwinners
- New York Times: U.S. Women on the Rise as Family Breadwinner
- ABC News: Record Number of Female Breadwinners, According to Pew
Further down there are some references to “primary breadwinners,” but that’s rare.
Maybe we should call those 100%ers breadwinners, and call the ones closer to 50% breadsharers.
Philip N. Cohen is a professor of sociology at the University of Maryland, College Park, and writes the blog Family Inequality. You can follow him on Twitter or Facebook.