
Benedict Anderson coined the phrase “imagined communities” to point to the way that humans believe they are meaningfully connected, by virtue of some commonality, to people they will never know, and may have very little in common with. He applied the idea to the nation. Why do all of the citizens of China, for example, have in common with other citizens of China? In some cases little, other than their citizenship. Yet, the fact that “we are all Chinese” can motivate many people to do and feel things.
In an RSA video featuring Jeremy Rifkin, sent in by Dmitriy T.M., it is argued that the human ability to imagine a community is a neurological capacity for empathy that has evolved, both neurologically and socially, throughout human existence. First, he argues, we identified with close relatives, then with our religious community, and later with our nation-state. Our future, then, he argues, is dependent on our ability to imagine the whole world as a community. New technologies may very well enable this and Rifkin has his fingers crossed.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.

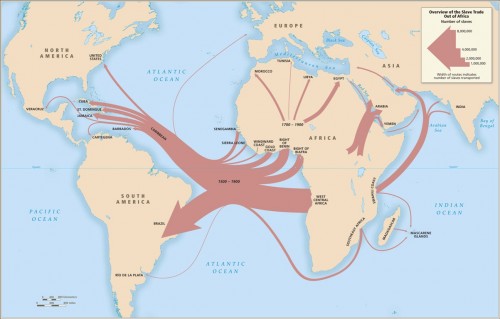
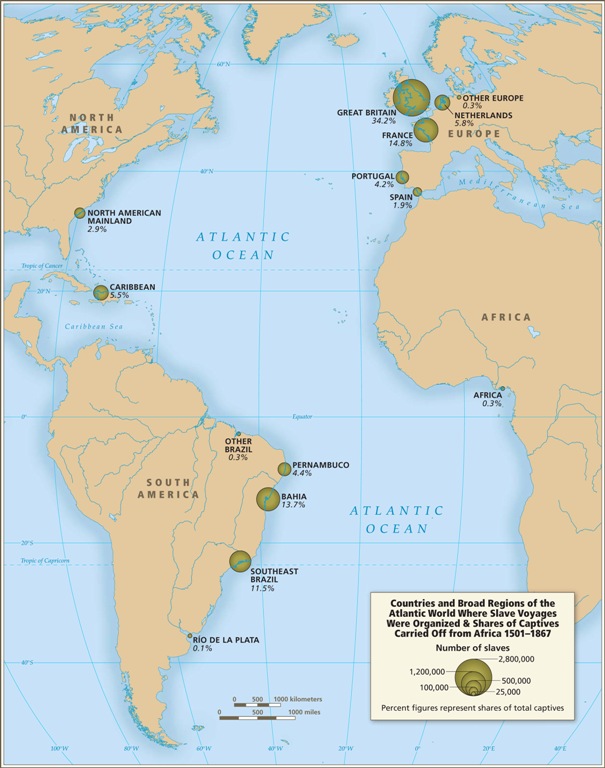
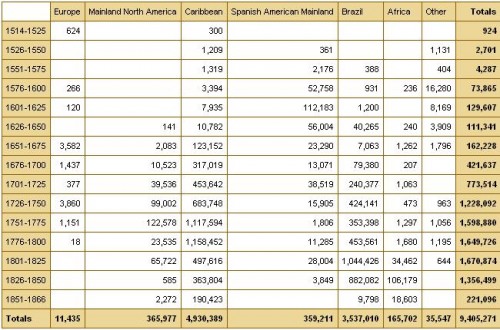
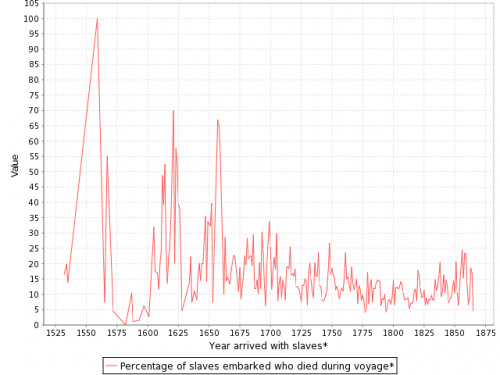
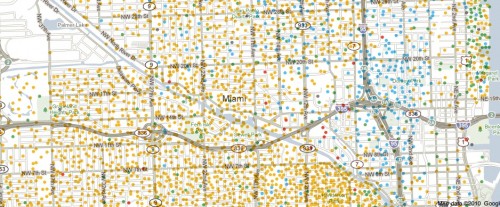
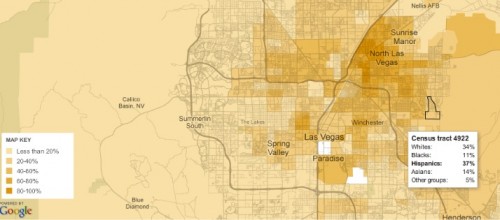
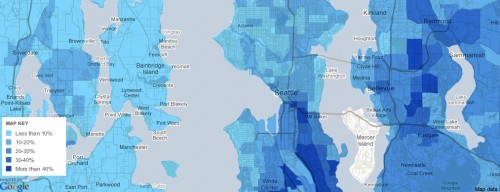
 It also fails to be true, as many anti-immigration people claim, that the U.S. accepts a uniquely large number of immigrants who need help once they arrive:
It also fails to be true, as many anti-immigration people claim, that the U.S. accepts a uniquely large number of immigrants who need help once they arrive:




