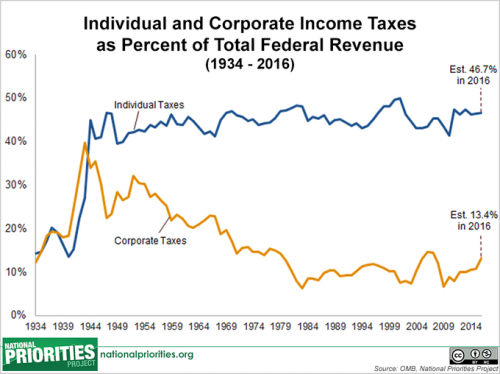
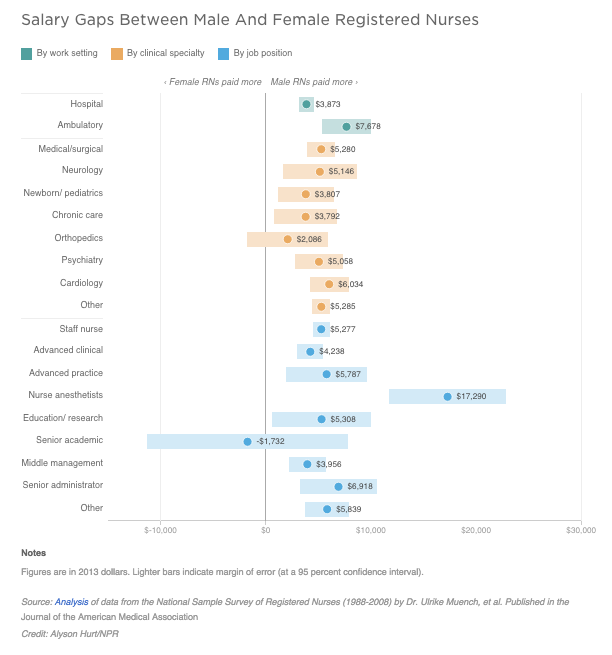
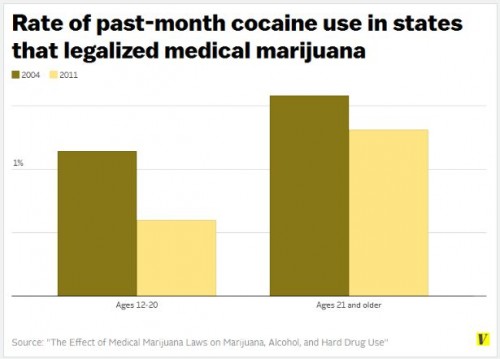
Flashback Friday.
The common sense assumption about success in sport often involves the belief that success is a result of innate talent and intensive practice. The more of both you have, the better you are. However, who is good at a particular sport is also the result of how that sport is organized. Sports have rules and those rules are made by the people who have the power to enforce their own ideas about what the rules should be over and against less powerful people with other ideas.
Long distance ski jumpers benefit from maximizing their surface area while simultaneously decreasing their weight. The less they weigh and the more drag they can produce, the farther they go. Their bodies are the primary source of weight and, as a result, there is incredible pressure for competing ski jumpers to be as thin as possible.
After criticism that the sport was creating an incentive for disordered eating, the International Ski Federation began penalizing jumpers who had a body mass index below 20. These skiers were required to jump with shorter skis, the primary source of drag. The hope was that the shorter skis would balance out the incentive for thinness, allowing jumpers to be competitive without starving themselves.
So, who wins isn’t only related to talent and practice. It is also a consequence of rules that no longer make the ability to train while starving oneself an advantage. This is a great example of the way that we write rules that shape the context for success in a sport.
—————————————
In light of this, it’s really interesting to consider the fact that ski jumping was the last Olympic event that excluded women. Women were given their first ski jumping event in 2014, though they still have one and the men have three.
The International Olympics Committee and the International Ski Federation listed a myriad of reasons for this, ranging from claims that the sport is not yet developed enough, to the idea that adding women would crowd an already overwhelmed Olympic schedule, to the assertion that the sport is not “…appropriate for ladies from a medical point of view.”
The rationales seem transparently thin, leading to the suggestion that the real reason that women weren’t allowed to compete — and still aren’t on parity with men — is because they might kick ass. If being lighter is an advantage, then women might beat men at the sport. In fact, during the time women’s future in Olympic ski jumping was being debated, the world record holder on the ski jump track at that year’s Olympics was held by a woman: Lindsey Van.
Sociologists recognize sport as a terrain on which social claims about gender are demonstrated. Not letting women play is one way that the mythology of men’s physical dominance has been maintained. Football is an excellent example. Women aren’t allowed to play football, it is asserted, because they are not big enough and would get hurt. Of course, rules that make size so critical to success in football also exclude the majority of men (who aren’t big enough to play either). If we organized football by weight classes, instead of gender, women could play football, and so could all of the men who are excluded as well. But, if we organized football by weight classes, we couldn’t claim that women were too small, weak, and fragile to play it.
It will be interesting to see how the future of women’s ski jumping plays out.
Originally posted in 2010.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.