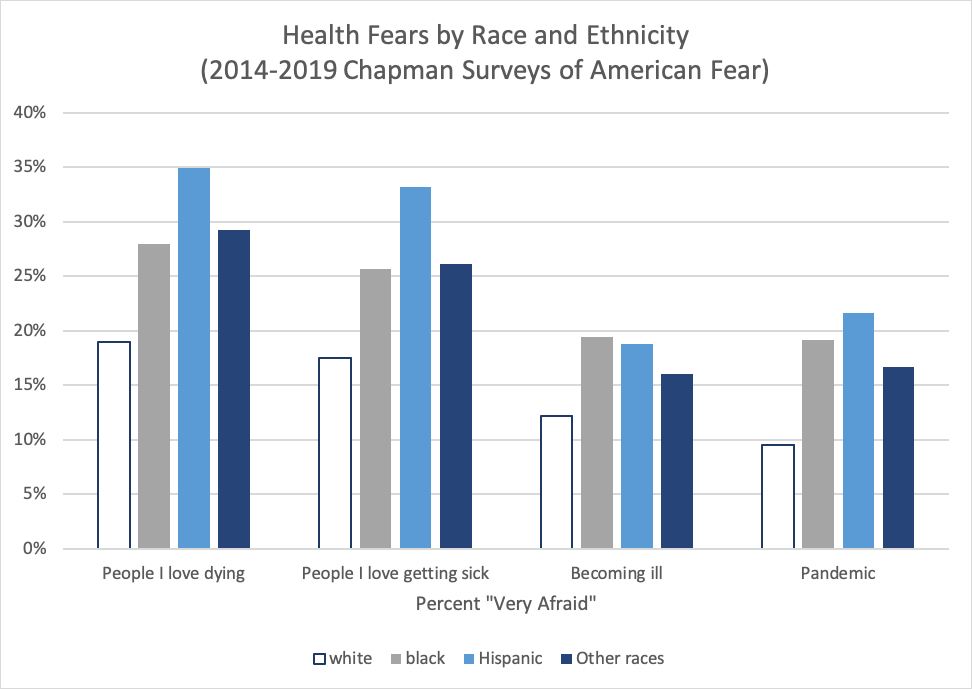
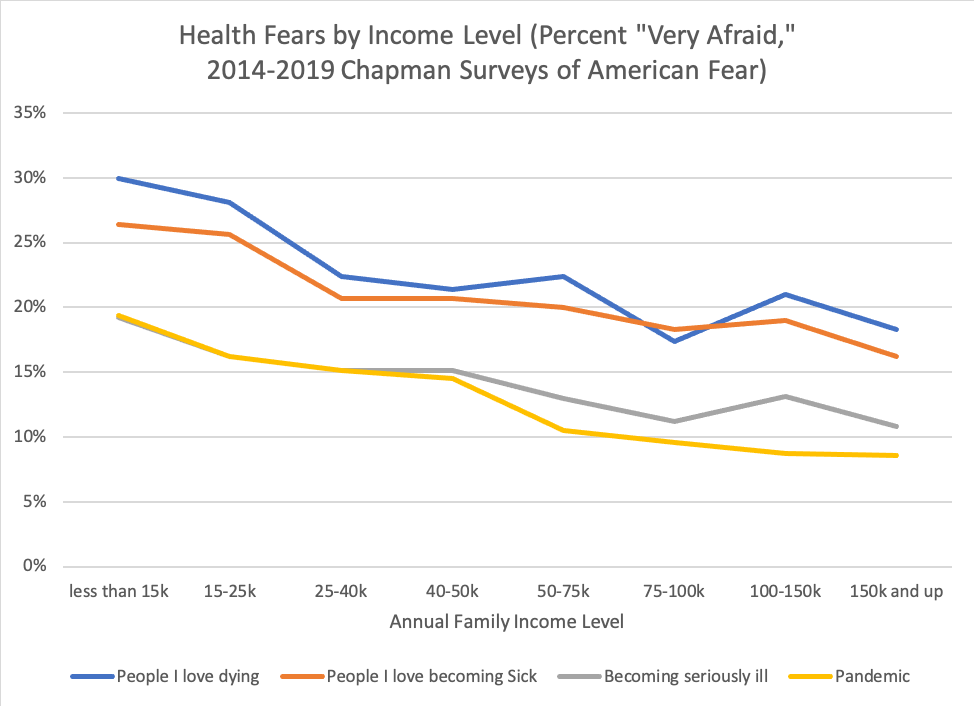
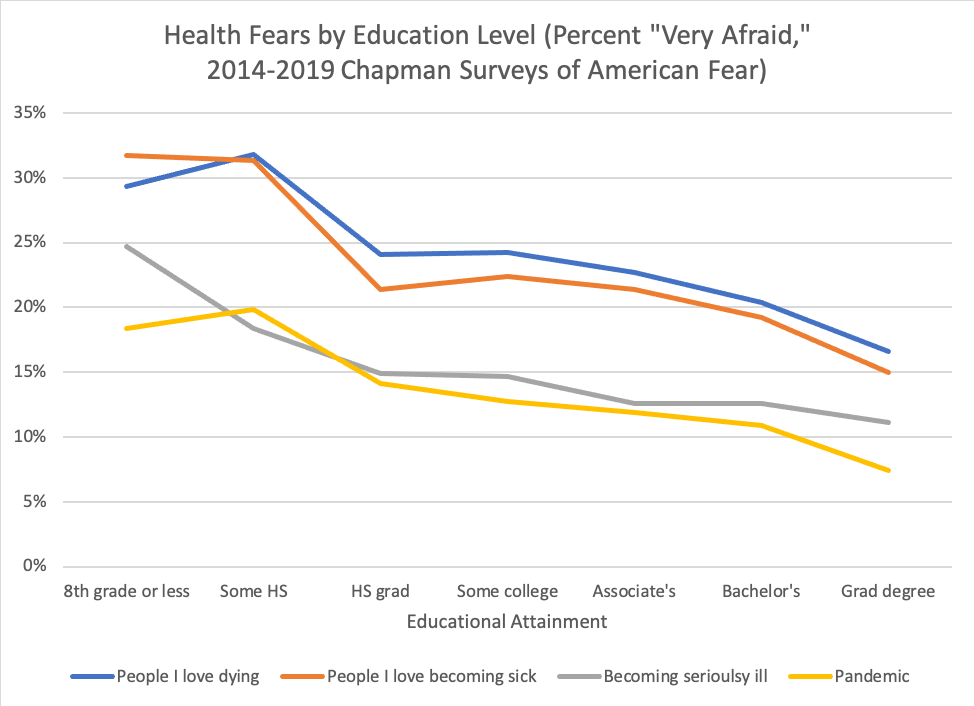
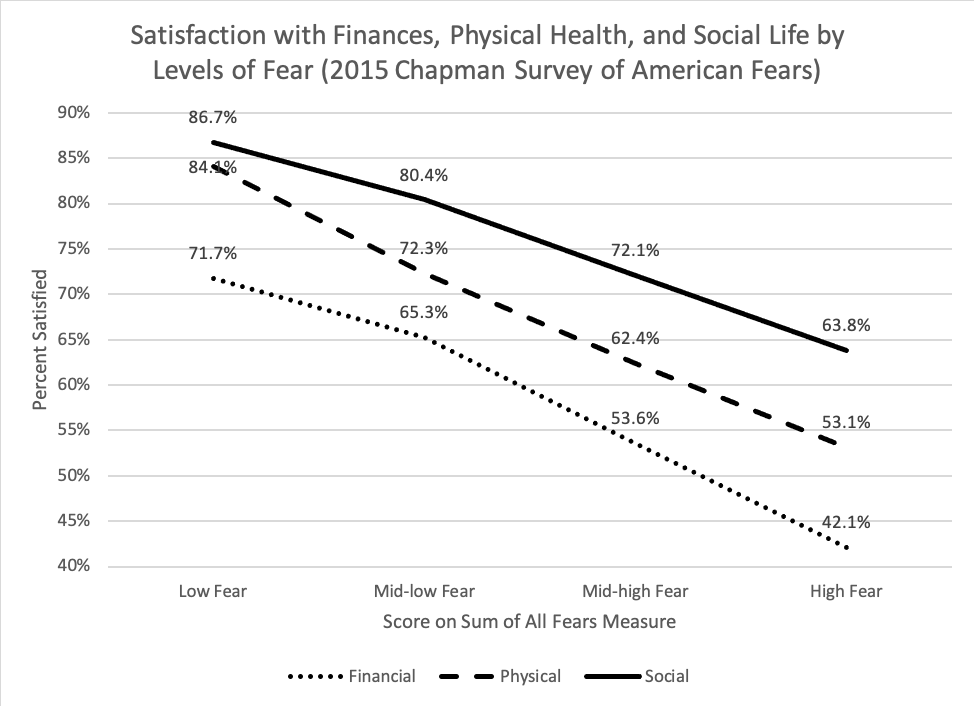
Lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic had a major impact on all kinds of social behaviors, from discrimination to civic engagement and protests. What effect has the pandemic had on more extreme behaviors, like terrorist attacks from groups like the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS)? Many armed actors, such as ISIS, threatened to use the pandemic to advance their goals. In its propaganda, ISIS even referred to COVID-19 as the “smallest soldier of Allah on the face of the earth.”

In some ways, the pandemic presented an opportunity to armed groups like ISIS. The pandemic threatened to divert resources away from fighting extremism because it overwhelmed countries’ budgets and placed demands on some countries’ security forces to deliver public health care services.
In our research, however, my colleagues and I found that the pandemic did not generally increase ISIS attacks. Instead, we found that lockdown measures adopted during the pandemic reduced attacks in Egypt, Iraq, and Syria. The effects were especially large in densely populated areas, where the population provided physical cover for ISIS’s activities, and in areas outside ISIS’s base of operations, which were harder to reach due to travel restrictions.
In taking people off the streets, the lockdowns removed the physical cover ISIS relies on for its operations, especially in urban areas, and eliminated many high-value civilian targets, such as markets. In shutting down businesses and reducing travel, the lockdowns also reduced ISIS’s revenue. However, the lockdowns were not in place long enough to significantly deplete the group’s reserves.
Even though the impact of the lockdowns on ISIS was significant, the lockdowns posed less of a challenge to ISIS than most other armed groups. ISIS has large financial reserves, operates in largely rural areas, and does not extensively target civilian populations. Most other armed groups have much smaller financial reserves than ISIS, operate in urban areas, and target civilians much more heavily. The effect of the lockdowns of these groups was likely even greater than it was on ISIS.
Our research shows us how much social context and opportunity matter to extremist violence. Despite the propaganda, even a terrorist group such as ISIS was locked down by the pandemic like everyone else.
Dr. Dawn Brancati is a senior lecturer in political science at Yale University who researches peacebuilding, especially as it relates to democracy and democratic institutions.