A reader named Caroline sent in a really nice email. “I just wanted to tell you – again,” she wrote, “how much of an impression you’ve made on my 17yo daughter Eliza.” She explains that they’d been reading SocImages together for “years (yes, years!).” We can’t express how much that means to us!
Caroline was inspired to write because Eliza had brought to her attention this image accompanying a story about a high school’s trackable ID badges:
Eliza had noted that, while the male figure was walking more-or-less directly towards the viewer, the female figure was standing with her torso contorted and her hip cocked.
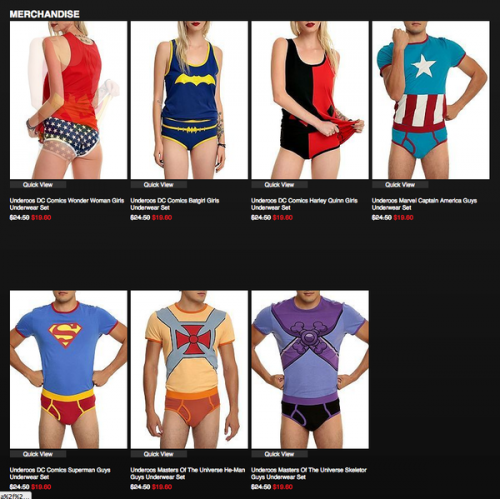
Likewise, @low_hana sent us this screenshot of DC Comics Underoos available for sale. Men are posed like, well, superheroes, but the women twist, fiddle, and turn their backs:
Now, this might seem like a small thing, and unimpressive in the singular. But, in fact, we see this kind of thing all the time, even in ostensibly objective medical textbooks and anatomy illustrations. We even see it when only faces are involved, as in this series of movie posters featuring men looking straight at the camera and women looking askance. Here’s one example:
As these types of images add up in our subconscious, they tell us a story about masculinity and femininity. It’s a complicated one, but might include lessons like this: men face things head on, while women are uncertain; women pose and men take action; men are straightforward, women sly.
Thanks Caroline, for sending in another example of such an insidious and largely invisible cultural pattern. And great job, Eliza, for spotting it!
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.