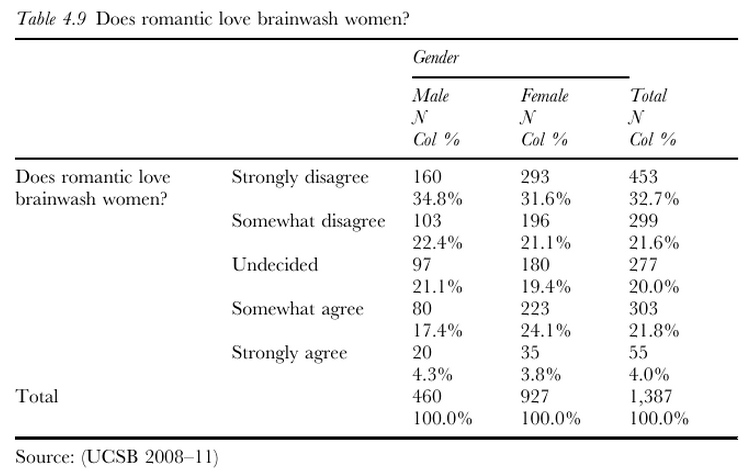
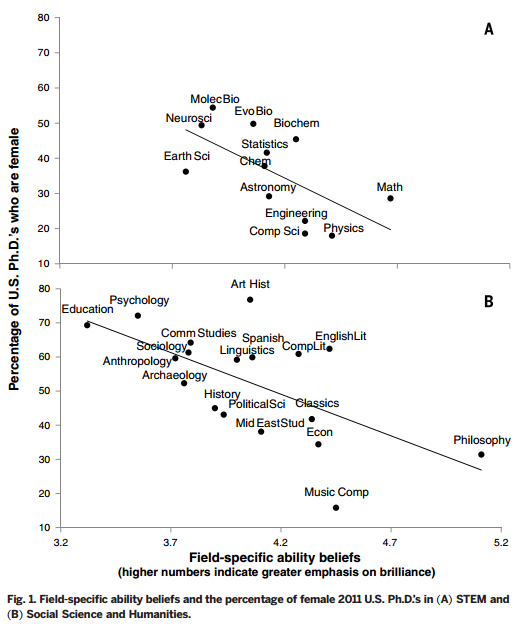
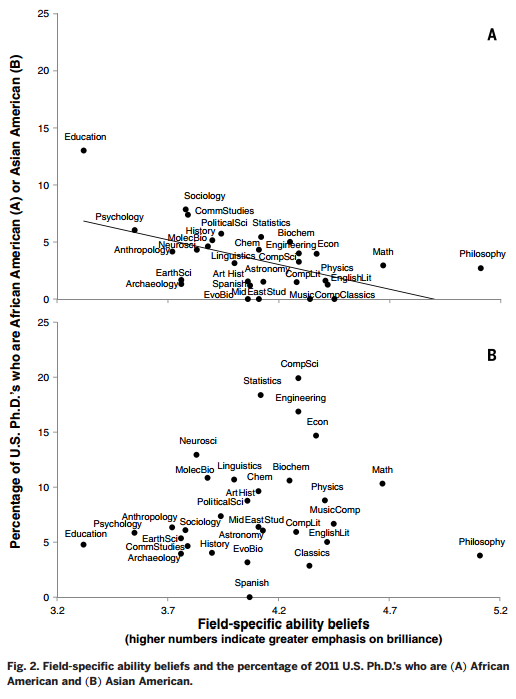
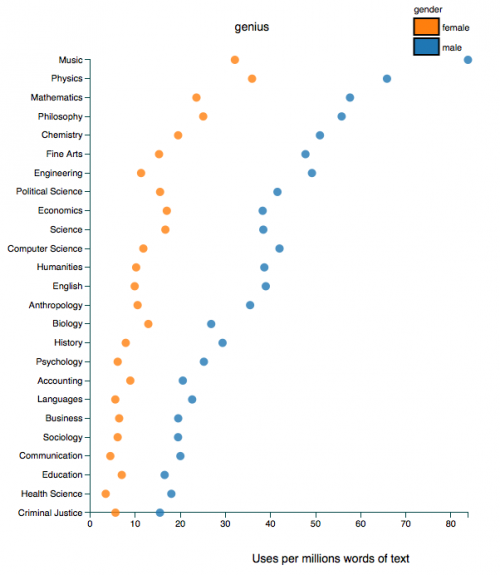
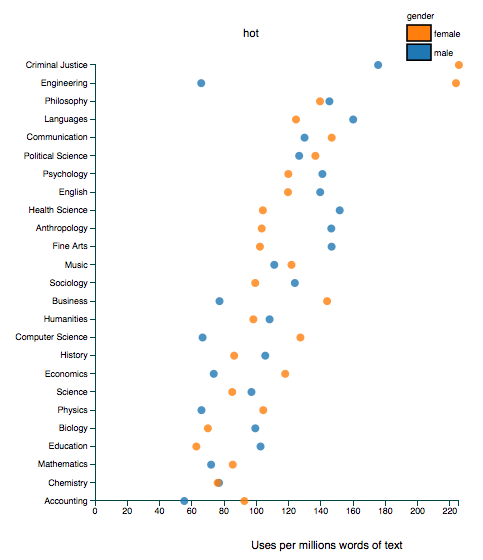
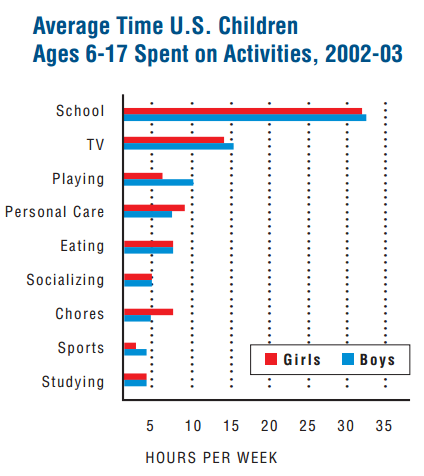
Sociologists are interested in the workings of power. How is inequality produced and sustained? What discursive and institutional forces uphold it? How are obvious injustices made invisible or legitimized? Why is it so hard to change hearts, minds, and societies?
How does all this work?
Earlier this month, a sliver of insight was posted. It’s a clip of a speech by Anita Sarkeesian in which she reveals what it’s like for one person to be the target of sustained, online harassment.
In 2009, Sarkeesian launched Feminist Frequency, a series of web logs in which she made feminist arguments about representation of women in pop culture. In 2012, she launched a kickstarter to fund an ambitious plan to analyze the representation of women in video games. This drew the attention of gamers who opposed her project on principle and thus began an onslaught of abuse: daily insults and threats of rape and murder, photoshop harassment, bomb threats, and a video game in which her face can be beaten bloody, just to mention a few examples. Last fall she canceled a speech at Utah State University because someone threatened to commit “the deadliest school shooting in American history” if she went on. It’s been brutal and it’s never stopped.
So, is this power at work? Has she been silenced? And has her larger project – awareness of sexism and misogyny in video games – been harmed?
I’m not sure.
As an individual, Sarkeesian has continued to speak out about the issue, but how she does so and with what frequency has been aggressively curtailed by the harassment. In the four-and-a-half minute clip, with the theme “What I Couldn’t Say,” she talks about how the harassment has changed how she engages with the public. I offer some tidbits below, but here’s the full clip:
She explains:
I rarely feel comfortable speaking spontaneously in public spaces, I’m intentional and careful about the media interviews I do, I decline most invitations to be on podcasts or web shows, I carefully consider the wording of every tweet to make sure it is clear and can’t be misconstrued. Over the last several years, I’ve become hypervigilant. My life, my words, and my actions are placed under a magnifying glass. Every day I see my words scrutinized, twisted, and distorted by thousands of men hell bent on destroying and silencing me.
How she gets her message across has been affected as well:
[I cant’ say] anything funny… I almost never make jokes anymore on YouTube… I don’t do it because viewers often interpret humor and sarcasm as ignorance… You would not believe how often jokes are taken as proof that I don’t know what I’m talking about… even when those jokes rely on a deep knowledge of the source material.
And she feels that, above all, she’s not allowed to talk about the harm that her harassers are doing:
I don’t’ get to publicly express sadness, or rage, or exhaustion, or anxiety, or depression… I don’t get to express feelings of fear or how tiring it is to be constantly vigilant of my physical and digital surroundings… In our society, women are not allowed to express feelings without being characterized as hysterical, erratic bitchy, highly emotional, or overly sensitive. Our experiences of insecurity, doubt, anger, or sadness are all policed and often used against us.
A youtube search for the video reveals a slew of anti-Sarkeesian responses were published within days.
——————–
Sarkeesian’s revelations put an inspiring human face on the sacrifice individuals make to fight-the-good-fight, but also reveal that, in some ways, her harassers are winning.
That said, their grotesque display of misogyny has raised Sarkeesian’s profile and drawn attention to and legitimized her project and her message. That original kickstarter? The original call was for $6,000. Her supporters donated almost $159,000. The feminist backlash to the misogynist backlash was swift and monied.
Ever since, the abuse she’s suffered as an individual has made the issue of both sexism in video games and online harassment more visible. Her pain may have been good for the visibility of the movement. I wonder, though, what message it sends to other women and men who want to pursue similar social justice initiatives. It is a cautionary tale that may dampen others’ willingness to fight.
The battle is real. The gamers who oppose Sarkeesian and what she stands for have succeeded in quieting, if not silencing her and have probably discouraged others from entering the fray. But Sarkeesian’s cause and the problem of gamer misogyny is more visible than ever. The fight goes on.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.