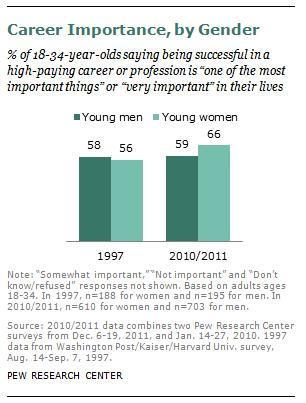
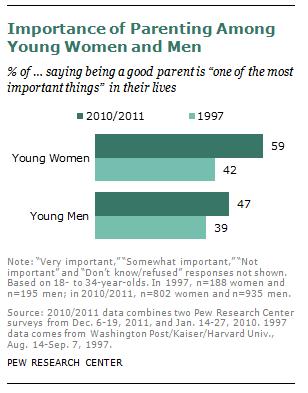
In an earlier post, Caroline Heldman offered a typology of objectification. No. 6 was a conflation of a person with a commodity. This photo of a display at the 1936 Los Angeles Electrical Exposition seems to qualify, but somehow that doesn’t make it any less charming!
Hat tip: Retronaut.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.