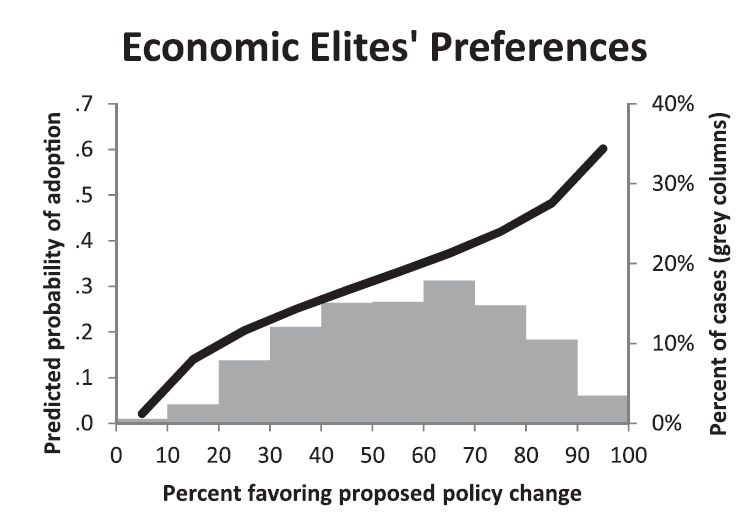
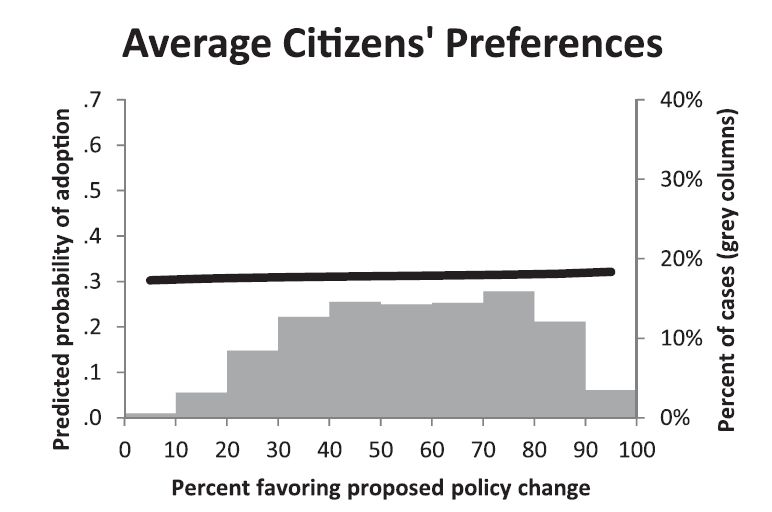
Who among us this election — except perhaps that elusive undecided voter — has not turned to a politically aligned friend and said, from their heart of hearts, “I just can’t understand how anyone could vote for Clinton/Trump”? The sheer mindbogglingness of it, the utter failure of so many Americans to even begin to fathom voting for the other candidate, is one of the most disturbing features of this election. We all seem to be asking: What could the other side be thinking!?

Perhaps what we need is a “sociology of thinking.” And we’ve got one; it’s called cognitive sociology.
One of the foundational texts in the subfield is called Social Mindscapes. In it, the sociologist Eviatar Zerubavel argues that we think as individuals (we are all alone in our brains) and we think as human beings (with the cognitive processes that humans have inherited from evolution), but we also think as members of social groups. Our thinking, then, is not only idiosyncratic (i.e., “individual”), nor universal (i.e., “human”) — though it is both those things — it’s also social. Our thinking is influenced by the groups to which we belong, what Zerubavel called “thought communities.” These are the people with whom we enjoy a meeting of the minds.
By this, Zerubavel doesn’t simply mean that our social groups shape what information we get and what arguments resonate, though that’s true. He and other cognitive sociologists argue that our thought communities shape cognition itself, that the brains of people in strongly divergent thought communities literally work differently. To Zerubavel, the idea that many Democrats can’t begin to understand Republican thinking — and vice versa — isn’t a surprise, it’s a hypothesis.
Research on sensory perception is fun evidence for their claims. Researchers have shown, for example, that our language categories influence not just how we describe the world we see, but how we see it. The Himba in Namibia, for example — who have one word for blue and some greens and another word for other greens, reds, and browns — are better than English speakers at differentiating one shade of green from another, but worse at differentiating green and blue from each other. Likewise, Russian speakers are better than English speakers at differentiating shades of blue because they have more than one word for the color and English speakers, in turn, are better than Japanese speakers at recognizing the gradations between blue and green, because the Japanese have traditionally used only one word to describe them both.
If our membership in thought communities is powerful enough to shift our very perception of color, then it must be able to influence our thinking in many other ways, too. In Social Mindscapes, Zerubavel shows that what we pay attention to, the categories we use, what we remember, and even our perception of time are all shaped by our thought communities.
Accordingly, cognitive sociology would predict that the rising polarization in politics and the fragmentation of media will make it harder and harder to understand each other, not because we don’t agree on the facts or because we have different political interests, but because our brains are actually working in divergent ways. That is, what we’re experiencing with this election is not just political disagreement, it’s a total breakdown in functional communication, which sounds about right.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.