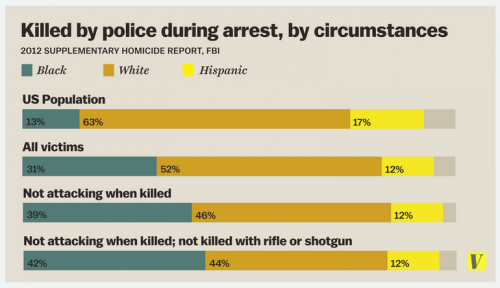
Flashback Friday.
In August of 2010, NPR reported on a scale developed by a forensic psychologist, Michael Stone, on which murderers could be placed according to how evil they are (from slightly evil to really, really really evil). To illustrate the scale, NPR developed this graphic:
Let’s say, for the sake of argument, that the artists designing this graphic did not purposefully associate darker skin-like colors with more evil and lighter skin-like colors with less evil. I think this is a fair assumption, though I don’t know for sure that this is true. But let’s give them the benefit of the doubt.
If they didn’t do this on purpose, then race never consciously entered their minds. Once you notice that the colors are skin-like colors, and if you are a member of a society that discriminates against darker-skinned people, you immediately see that this graphic reproduces those stereotypes… AND YOU CHANGE THE COLORS. Any color, going from light to dark, will illustrate intensity. How about red? In Western societies, red is associated with anger. If you insist on using black because black signifies evil in our culture, how about using a true black (that is very rarely if ever seen on people) and a gray scale? How about any color other than brown?
I think this is likely a case in which the producers of the image did not think. And not thinking is one of the most insidious ways that racism and other bigotries get reproduced. People who don’t think about race are the most likely to endorse racial stereotypes. When people who think about race are distracted — with another task, or loud music, or some other intervening stimulus — they are more likely to think stereotypically than when they are not distracted. We can’t be colorblind. Our unconscious is steeped in racial meanings. Consciously fighting those associations is the only way to be less racist.
Not thinking about race is a cousin to thinking racist thoughts. Only thinking hard about race helps alleviate racism. And this graphic is an excellent example of why.
Originally posted in 2010.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.