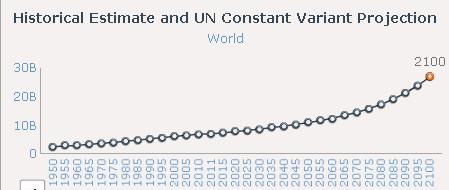
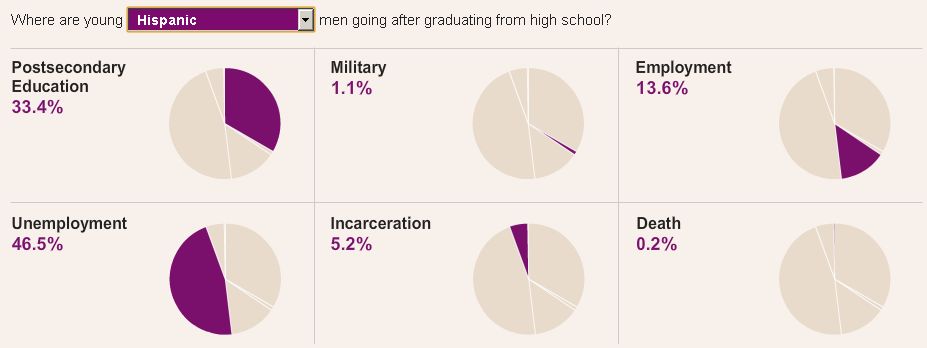
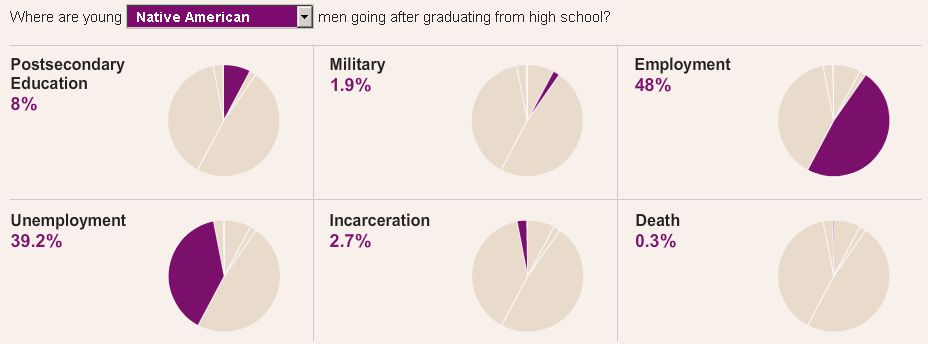
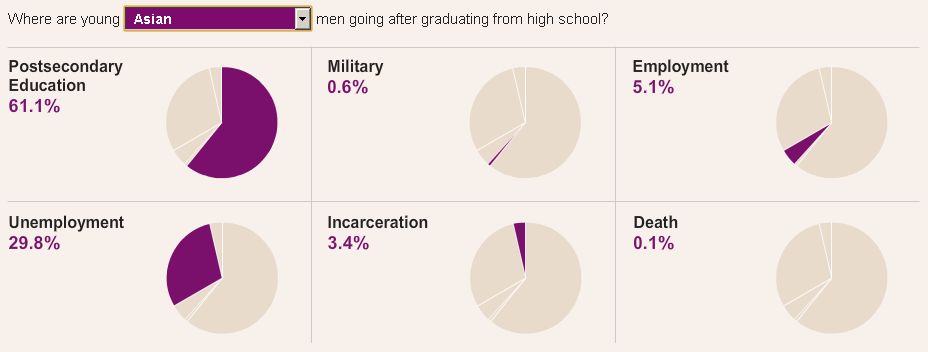
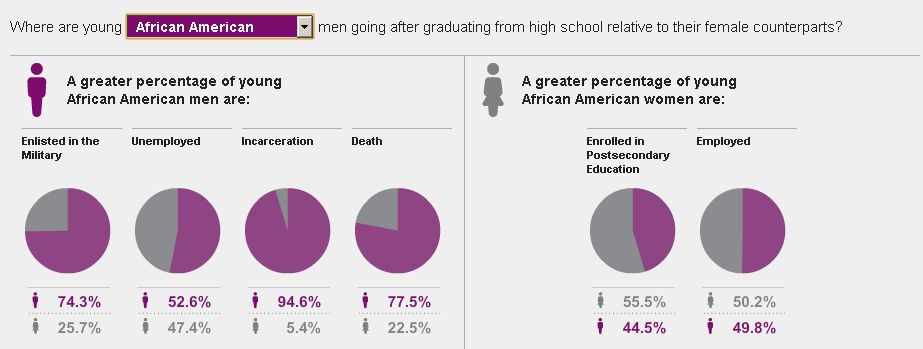
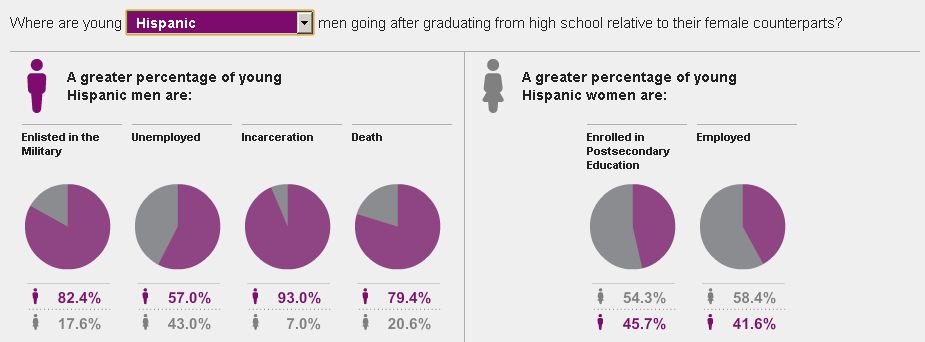
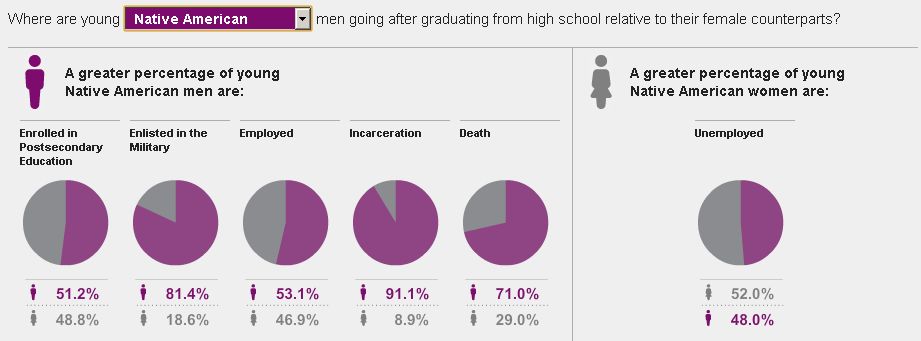
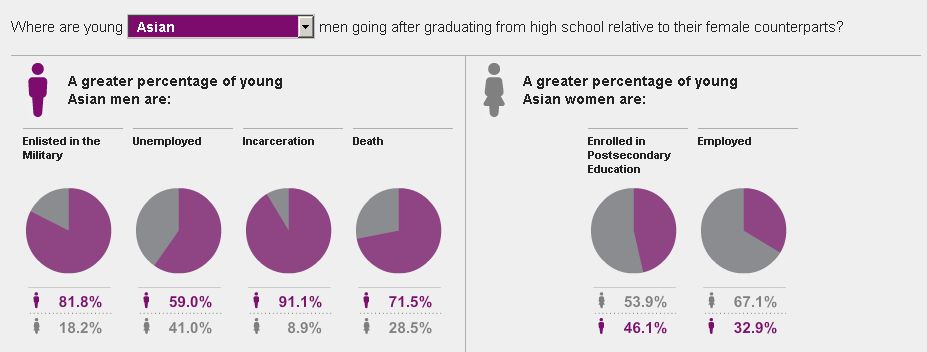
The New York Times recently ran an interesting story on prison cemeteries in Texas. For about $2,000, the state buries about 100 inmates a year. They die of lethal injection, old age, or illness, but they’re all dressed in dark pants, a white shirt, and tie, and are buried with a prayer from the prison chaplain.
When inmates die in custody, their bodies are sometimes unclaimed. This may be because they have no family at all, or their family members don’t wish to claim the body. Other times the inmate is cared for by family members who simply can’t afford to bury the person themselves. So, occasionally the family members will decline to claim the body, but show up on the day of the burial to pay their respects.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.