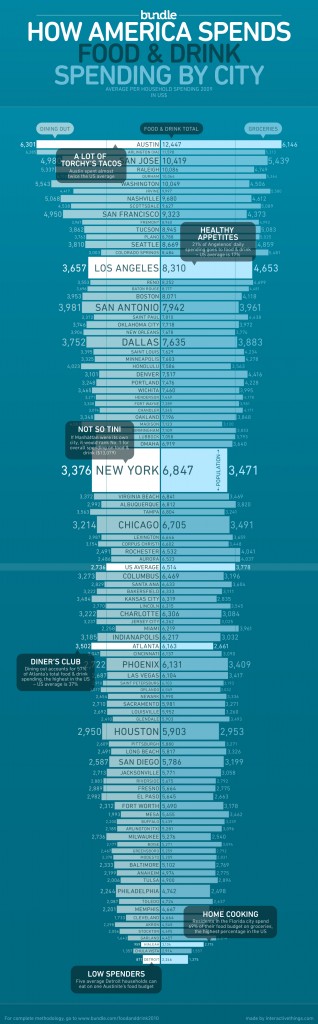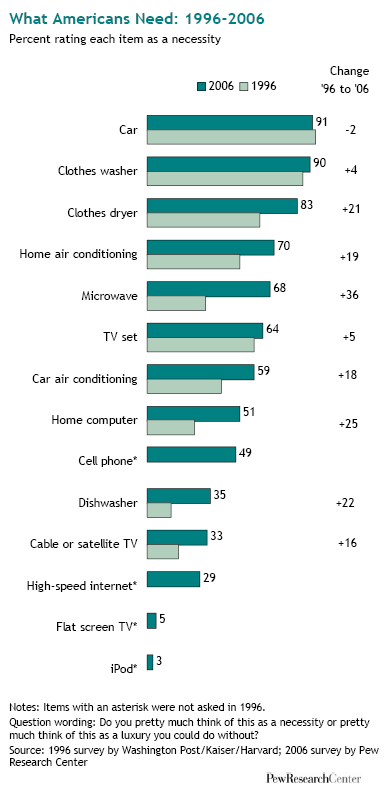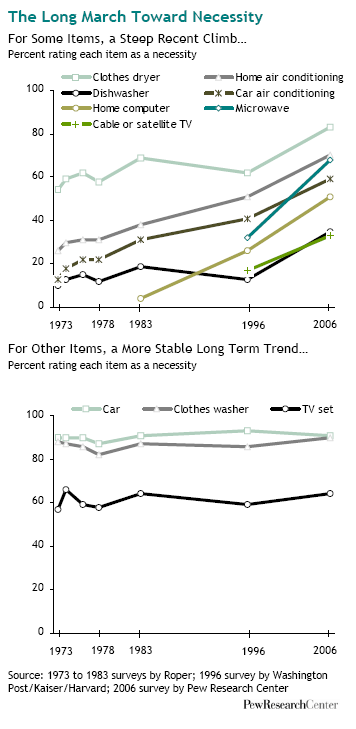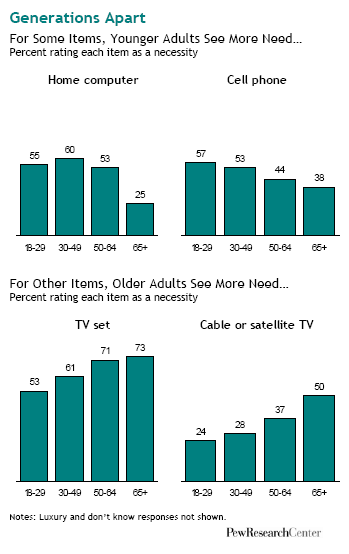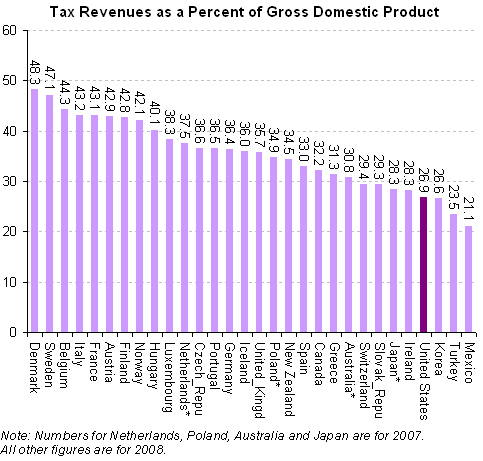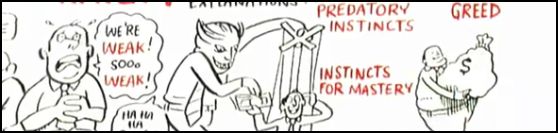
Sociologist Geographer David Harvey’s analysis of the current economic crisis is engagingly illustrated in this 11-minute video. Harvey evaluates individual, institutional, ideological, cultural, and policy explanations for the recession. He then explains Marx’s insights into the “internal contradictions of capital accumulation”: capitalists want to pay low wages, but if they’re paying low wages, then no one can buy their stuff. If both high wages and low wages translate into no profits, where does that leave capitalism?
From Cognitive Media via BoingBoing and Karl Bakeman.
Buy Harvey’s book, The Enigma of Capital and the Crises of Capitalism.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.