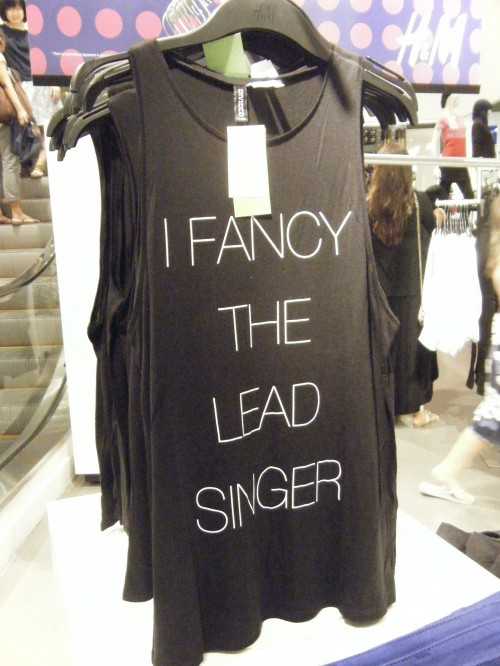For the last week of December, we’re re-posting some of our favorite posts from 2012.
In “Rock in a Hard Place: Grassroots Cultural Production in the Post-Elvis Era,” William Bielby discusses the emergence of the amateur teen rock band. The experience of teens getting together with their friends to form a band and practice in their parents’ garage is iconic in our culture now; recalling their first band or their first live show is a standard element of interviews with successful rock musicians. Bielby traces the history of this cultural form, which appeared in the 1950s. In particular, he argues that social structures largely excluded young women from full participation in the teen band phenomenon.
Though young women were involved in many other types of musical performance, the pop charts featured many successful female artists in the 1950s, and girls listened to music more than boys, rock bands emerged as a male-dominated (and predominantly White) musical form. One important reason was parents’ concern about the rock subculture and the lack of supervision. Parents might be willing to let their sons get together with friends and play loud music and travel around town or even to other cities to play in front of a crowd, but they were much less likely to let their daughters do so. Gendered parenting, and the closer regulation of girls than boys, meant that girls were less likely to be given the chance to join a band. So while boys were learning to take on the role of active producers of rock music, girls didn’t have the same opportunities.
Yunnan C. sent us photos she took of two shirts at an H&M store in Toronto that made me think about Bielby’s argument:
As Yunnan points out,
This, as fashion, enforces this idea that being in a band and playing music are for guys, limiting women to being the passive consumers and supporters of it, rather than the producers.
The shirts don’t just cast women in the role of fans; they specifically frame them as potential groupies, whose fandom is filtered through a romantic/sexual attraction to individual members of a band. Communications scholar Melissa Click argues that female fans are often dismissed because there is a “persistent cultural assumption that male-targeted texts are authentic and interesting, while female-targeted texts are schlocky and mindless—and further that men and boys are active users of media while girls are passive consumers.” While the image of the groupie is as well-known as that of the band, the groupie is usually viewed skeptically, seen as someone with a superficial, inauthentic appreciation of the music, “a particular kind of female fan assumed to be more interested in sex with rock stars than in their music.”
So the H&M shirts reflect gendered notions about who makes music (there were no shirts saying “I am the drummer”) as well as the idea that women’s appreciation for music and other forms of pop culture should be expressed through affection for a specific person, a form of fanhood that ultimately stigmatizes those who express it as superficial and inauthentic.
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.