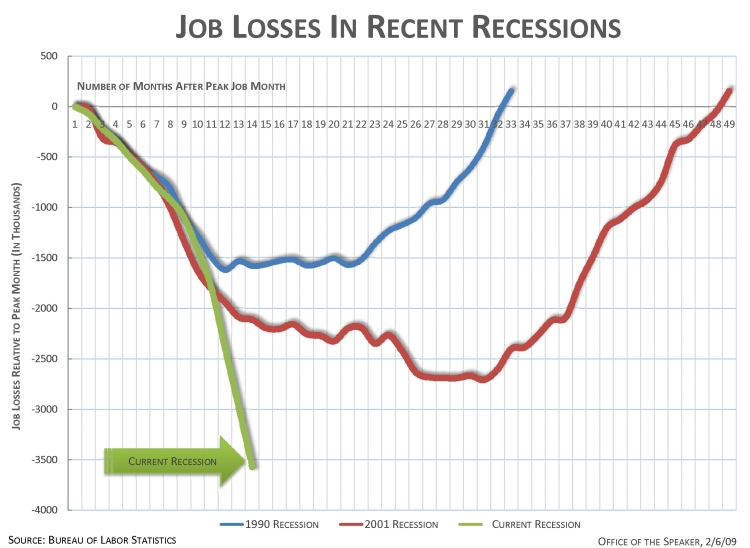
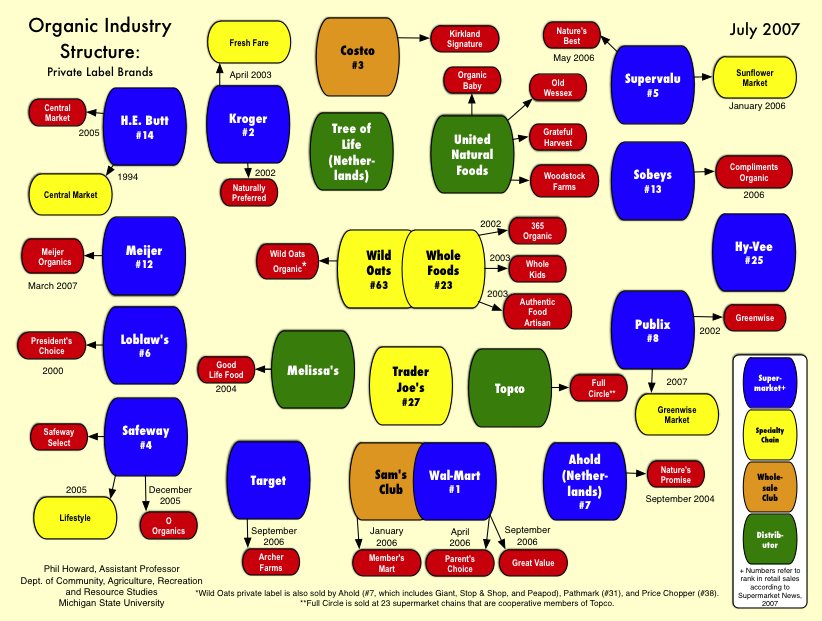
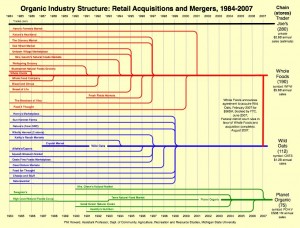
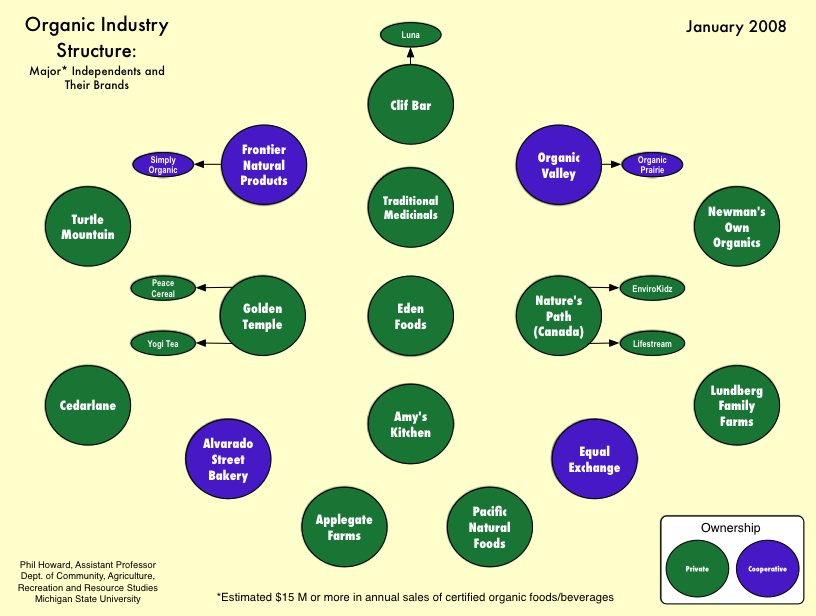
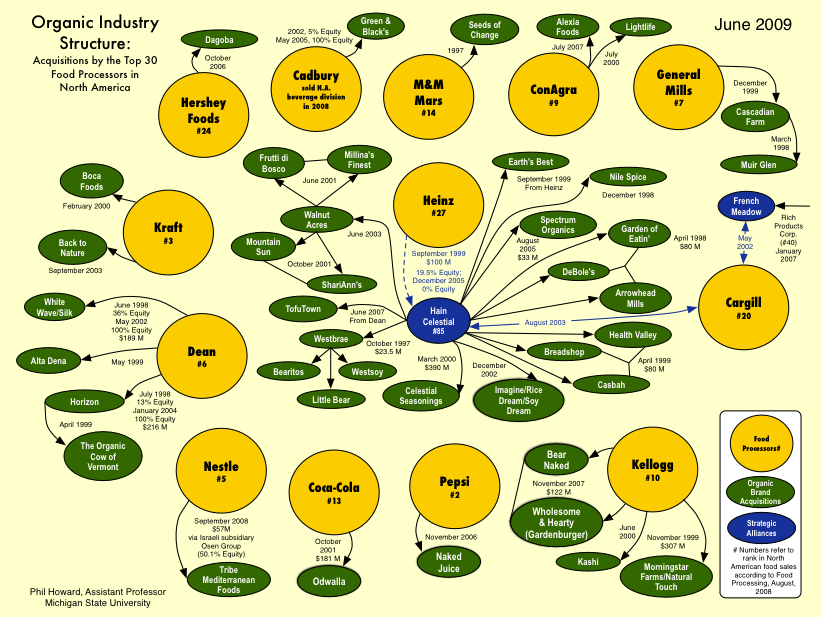
The desperate economic situation of Detroit, Michigan is in the headlines these days. From the New York Times:
In one sign of distress, in the first nine months of this year [2008], some 130,000 Michigan residents who had lost their jobs remained out of work so long that they ran out of regular unemployment benefits. By the middle of this month, 63,000 people (who had already run out of their ordinary maximum benefit — as many as 26 weeks, at as much as $362 a week) also ran out of an extension authorized by Congress.
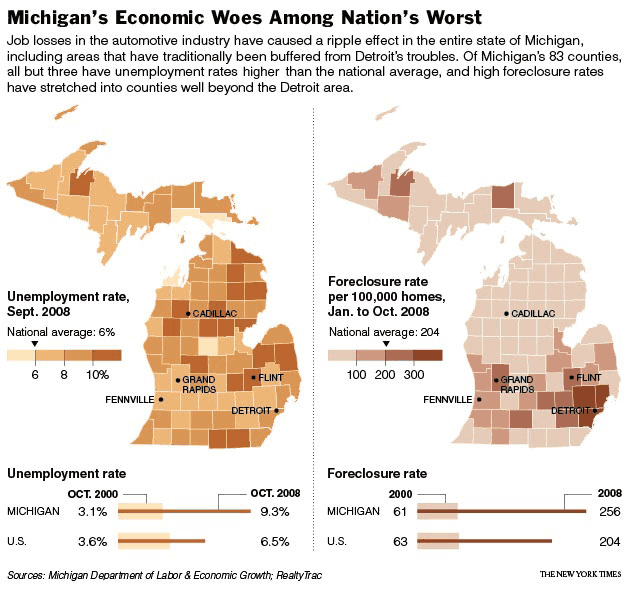
This figure shows the unemployment and forclosure rate in Michigan as of Oct. 2008. It shows that Michigan in general, and Detroit especially, is doing much worse than the national average:
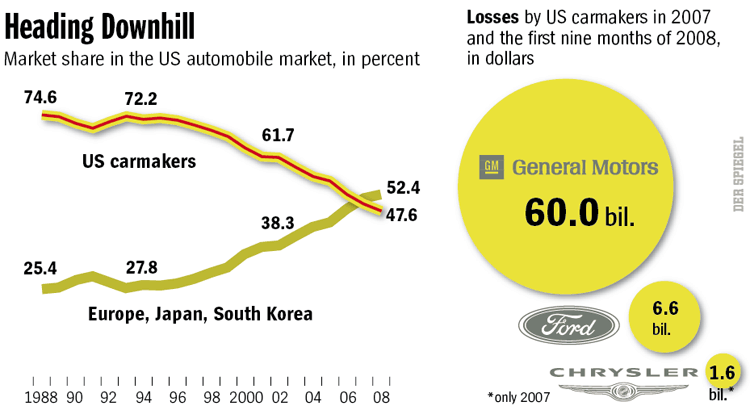
Today’s numbers reflect not just the current recession, but 30 years of decline. A figure from Spiegel reveals that the marketshare of U.S. automakers have been steadily dwindling:
Spiegel reports that the city has lost more than half its inhabitants since the 1950s (from close to 2 million, to 917,000 in 2009). The tax base has plummeted and city services, in turn, have been cut.
The conditions in Detroit are dire, and they contrast greatly with the city in the late 1800s and early 1900s. Then, Detroit’s shipping and manufacturing economy, innovative for its time, made it a rich and vibrant city. Today, the ruins of that vibrancy still occupy the city.
Detroit’s main train station, opened in 1913 has not been used since 1988:

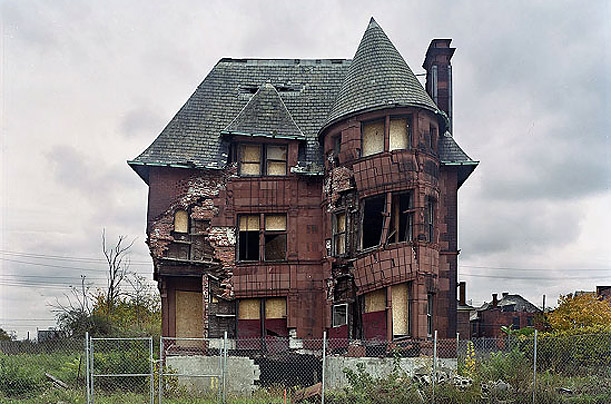
Constructed in 1893 in the once-elegant Brush Park neighborhood, this home, designed by architect Albert Kahn, was moved from its original location several years ago by preservationists who hoped to preserve it. It was demolished last year:

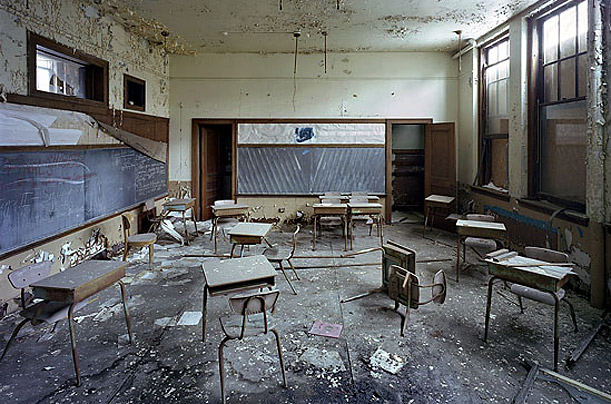
Many of the city’s Catholic schools have been closed, though the churches they are affiliated with remain active:

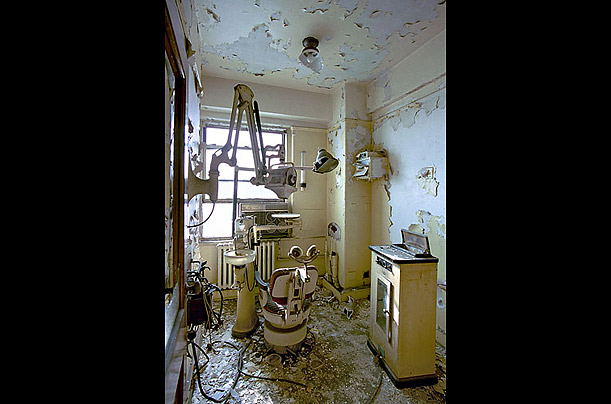
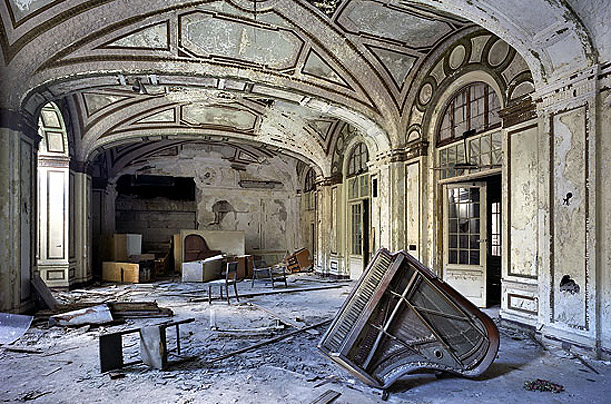
One of the city’s most prominent skyscrapers, this 35-story tower once housed the offices of many doctors, lawyers and dentists. It has been virtually empty since the 1980s. Developers hope to convert the building to residential units by 2010:

This spectacular Spanish Gothic theater, built in 1928, was closed in the 1970s:
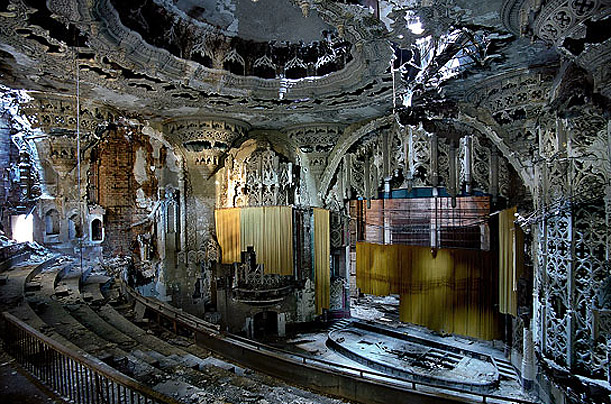

Once one of the most luxurious residential hotels in Detroit, Lee Plaza closed in the 1990s:

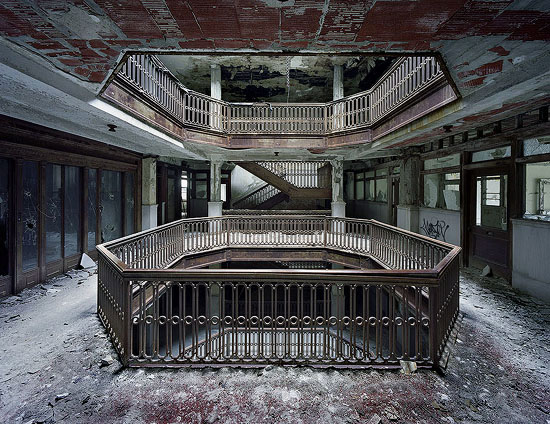
The Farwell Building:

Photographers Yves Marchand and Romain Meffre write: Detroit’s “splendid decaying monuments are, no less than the Pyramids of Egypt, the Coliseum of Rome, or the Acropolis in Athens, remnants of the passing of a great civilization.”
Images first found here.


 It’s fascinating that a magazine well-known for objectifying women also participates (at least in running this ad) in encouraging men to self-objectify. Without suggesting that women and men are equally objectified in American culture, I think it might be interesting to talk about the extent to which we live in an objectifying culture, period, and learn to self-objectify whether we are men or women.
It’s fascinating that a magazine well-known for objectifying women also participates (at least in running this ad) in encouraging men to self-objectify. Without suggesting that women and men are equally objectified in American culture, I think it might be interesting to talk about the extent to which we live in an objectifying culture, period, and learn to self-objectify whether we are men or women.