Martin Hart-Landsberg, at Reports from the Economic Front, offers a provocative hypothesis. He observes that job loss in the U.S. has been tremendous. One in 20 jobs has disappeared. Still, Congress drug its feet approving an extension of unemployment benefits. The extension has been approved, but benefits are hardly generous (on average, $309 a month week). Further, millions of unemployed people are not collecting unemployment because they’re not eligible under current policy.
Hart-Landsberg asks why there is a lack of “meaningful national efforts” to address the suffering of workers and their families?
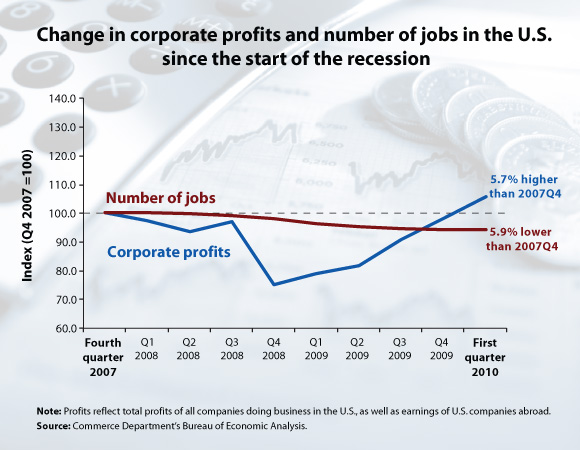
His hypothesis: Economic policy is not responsive to workers’ needs. Instead, it is heavily driven by what is best for corporations. And, it turns, out, corporations are doing swimmingly during the recession. They took a beating at first, but their profits are up. Downsizing appears to have benefited them. Consider this chart from the Economic Policy Institute (EPI):
The EPI concurs with Hart-Landsberg. Looking at this data, Lawrence Mishel concludes:
When employers are able to recover their profits many years before their employees can even hope to attain the income and employment levels they had prior to recession’s devastation, economic policy is clearly skewed in favor of corporations and not workers.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.