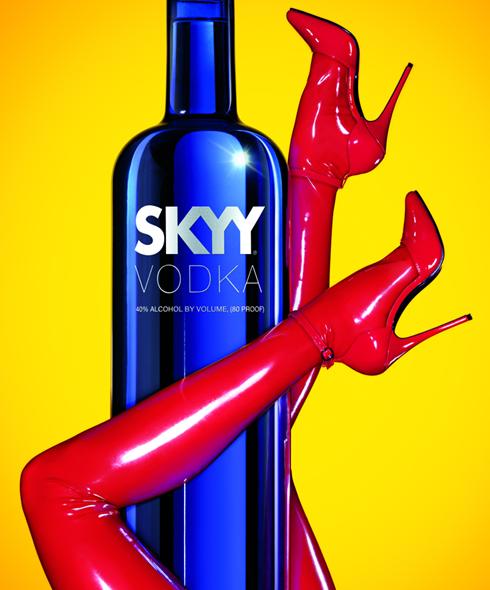
We haven’t had up any blatant phallic ad imagery in a while, so I thought I’d share with you this Skyy Vodka ad, sent in by Dmitriy T.M. (found at AdRants):
From the AdRants post:
Defending the ad, Skyy Marketing Director Maura McGinn…said, “It’s about the content of our product. We’re an adult product consumed mostly in the evening and in flirtatious situations.”
Of course, it doesn’t actually show the product ejaculating, so it’s pretty tame, really.