Larry Harnisch of the L.A. Times blog The Daily Mirror sent in some old images from the Times archives that show how photos of stars were touched up to show less skin. Here’s one of Frances Farmer (from Larry’s post about her):
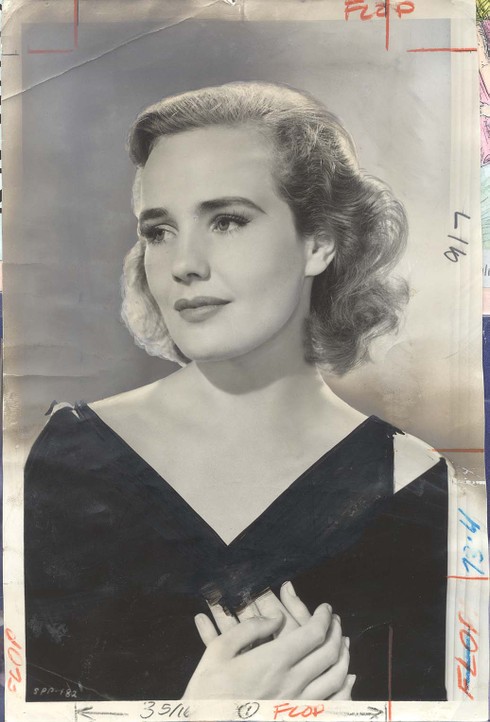

The image comes from the 1940 movie “Flowing Gold.” Apparently it was considered too revealing and the Times had someone draw in a dress above her wrap…with what appears to be a black magic marker.
Charlton Heston was also retroactively covered up. Both of the following images come from The Daily Mirror. This is a still from a 1957 episode of “Shlitz Playhouse.” Someone very obviously, and badly, drew a shirt on him:
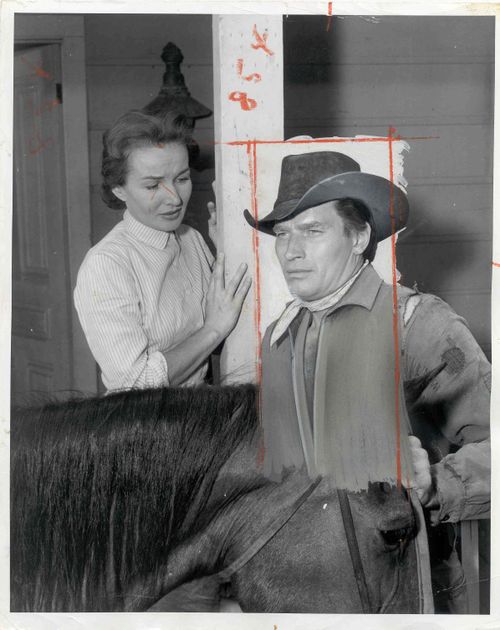

Though the photo was touched up by the L.A. Times staff, it’s not clear whether it actually appeared in the paper. This photo most definitely did, however; it accompanied a review of “The Omega Man” from August 27, 1971. They did an even better job with the shirt this time:
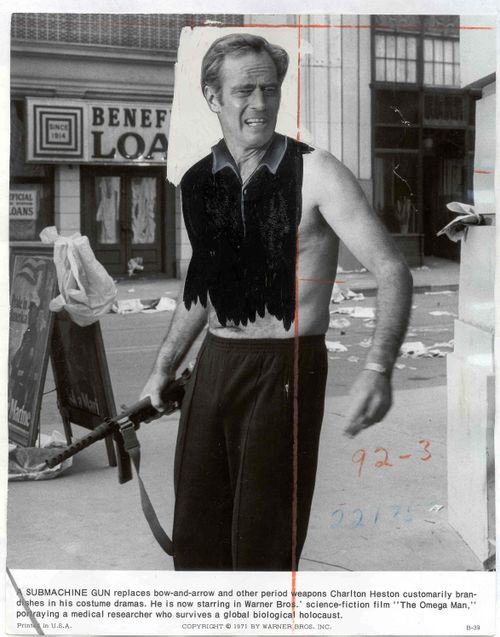

It provides some perspective on how ideas of how much uncovered skin is appropriate to run in a mainstream media outlet have changed over the years. It’s also interesting that both men’s and women’s chests were covered. But mostly they just crack me up. The last one is my favorite.
Also check out the post about Sacha Baron Cohen naked on the cover of GQ and spoofing magazine covers that have naked people on them.






![image[3] image[3]](https://thesocietypages.org/socimages/files/2009/08/image3.png)