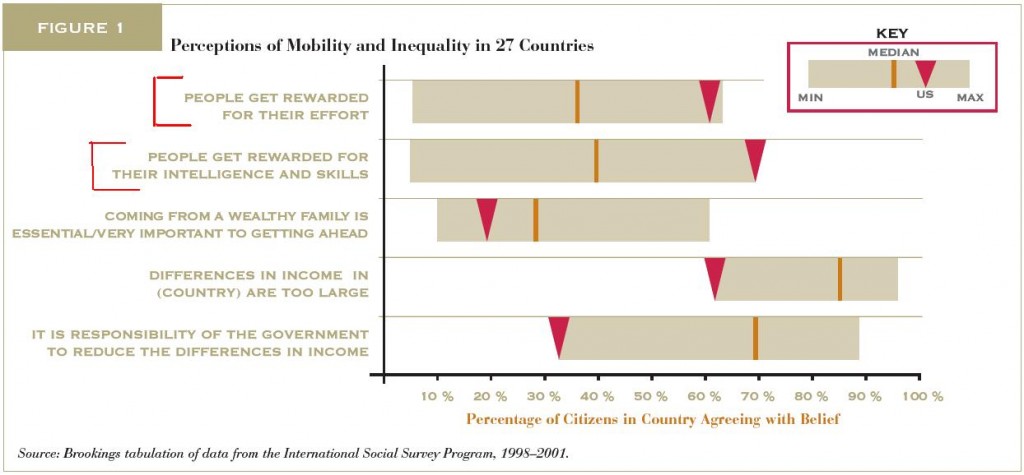
Malia Green, taking a writing diagnostic test while enrolled in Junior College, came across the following question:
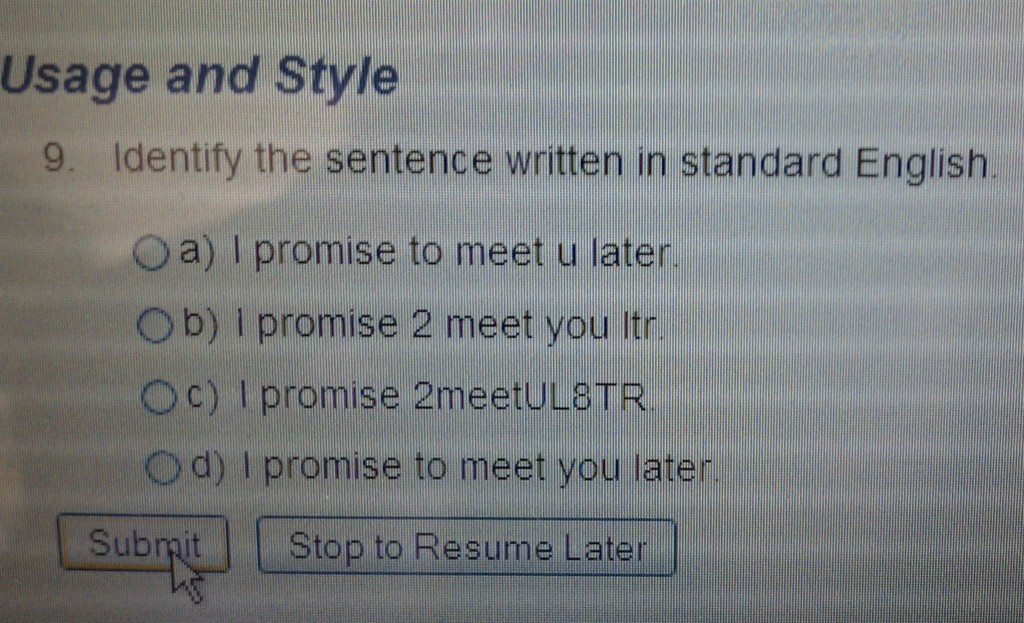
The question was part of Pearson’s MyWritingLab, self-described as “a complete online learning program [that] provides better practice exercises to developing writers.”
I have heard rumor that young people have been adopting shorthand tweet-type language as “standard English,” using it in communications with professors and in their academic papers. The inclusion of this question in Pearson’s test suggests that this may, indeed, be a widespread phenomenon and that young adults may not necessarily know the difference between the English most of their parents grew up with and the English they have encountered in this brave new world.
Despite the fact that each of the answers will make sense to anyone familiar with text-ese, the correct answer on the Pearon’s test is clearly d). So, are the answers a) through c) actually wrong? Who gets to decide what “standard English” is anyway?
The whole thing reminds me of the controversies over African American Vernacular English, better known as “ebonics,” in the 1990s. The idea that some people “talk right” and some people do not is an excellent way to justify prejudice. Perhaps an employer largely chooses not to hire black people, not because they’re black, of course, but because they don’t “talk right.” Is the outcome significantly different? And who decides what “talking right” sounds like anyway? Well, the people who have the power to do so… and they typically side with themselves.
So, is text-ese wrong? Only according to those who are making the rules (and Pearson’s tests). And what do you want to bet that those young people who are taught to differentiate between the kind of English they are allowed to use in texts and the kind they are allowed to use in “proper” communication are class privileged, on average? And disproportionately white, accordingly?
So, who decides the future of English? And will “2” and “u” be words in it, or not?
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.