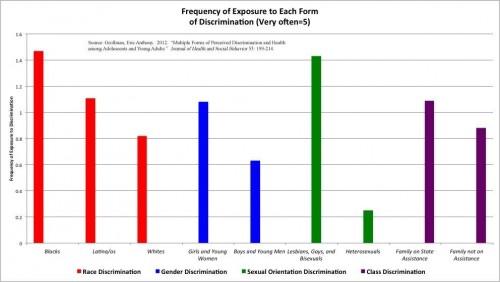
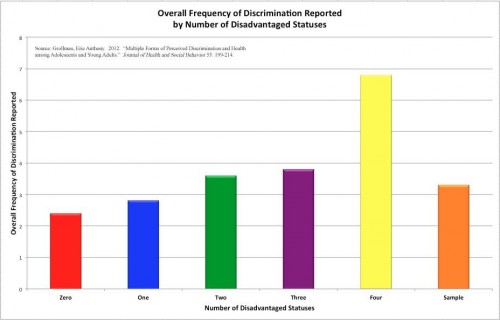
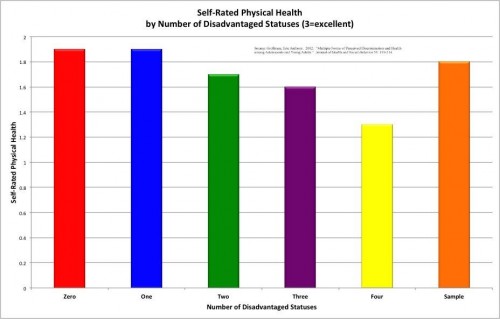
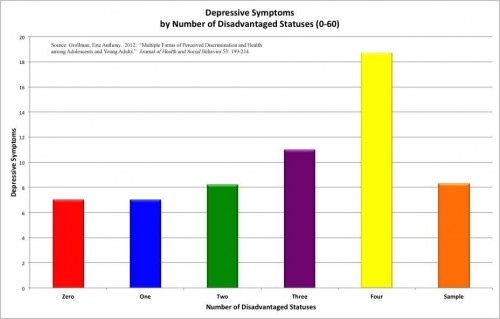
In the first half of the twentieth century, the black press solidified its role as a pillar of the community and an anchor for popular opinion. In the tumultuous period between the Great Depression and the first stirrings of the Civil Rights Movement, World War II forced black Americans to rethink their struggle for equality as well as their position in the international political arena.* Editorial cartoons became a powerful forum for airing views on the war, a lens through which the readership could view domestic race relations in the context of America’s geopolitical stature and the specter of colonialism and fascism.
Two major black newspapers with national readerships, the Chicago Defender and the New York Amsterdam News, were largely supportive of the war. Black Americans broadly supported World War II. The so-called Double-V campaign rallied black community groups and media under a banner of patriotism, with the aim of encouraging racial integration and equality. But despite the overall pro-war sentiment, the black press also featured cartoons that offered a platform for critiquing blacks’ paradoxical position in the war on a domestic and global scale.
One cartoonist, Bill Chase, reflected early isolationist sentiments among blacks. An Amsterdam News cartoon from June 8, 1940 titled “Be Careful Uncle Sam” shows a pensive Uncle Sam staring across the Atlantic at plumes of smoke. He stands upon strewn papers marked “lynching,” “lack of equal educational facilities,” “unemployment” and “no social security menials.” In a pointed reference to past wars and current national priorities, Uncle Sam says, “George Washington once said—’no entangling alliances’”:

In the June 17, 1944 Defender cartoon, Jan Jackson used a feminine metaphor to portray a double-standard in the politics of government intervention. A half-naked black woman chained to a post, arms outstretched in desperation, watches as two soldiers, labeled “liberation forces,” scurry across the Atlantic toward a mirror image of an endangered white woman on the distant shore of “enslaved Europe”; the headline is the soldiers’ empty promise, “We’ll Be Back”:

That the feminized white Europe is depicted ironically as “enslaved,” while the rescuers turn their backs on a refugee of actual slavery, reveals the absurdity of aiding a “just war” while ignoring a homegrown humanitarian crisis.
A Defender cartoon published on June 16, 1945, just before the armistice, directly aligns the U.S. with the smoldering legacy of Nazi rule. Under the headline “Blind Leading The Blind,” a haggard America steps forward from the ashes of bombed-out Europe, leading a disheveled, bloodstained Germany by the hand. Both men wear spectacles with blacked-out lenses displaying the words “race hate”:

As the war effort shifted from Europe to Asia, editorial cartoons took on an anti-colonial dimension. The Defender‘s September 8, 1945 cartoon elucidates Japan’s dual identity as both a fascist power and a non-white challenge to the global order. The inspiration for the cartoon is a report on the same page that a battleship from Mississippi docked at Tokyo Bay displaying “the Stars and Bars of the Confederacy while on deck the band played Dixie”:

The paper quips that the commander might as well have added “another bit of ‘Mississippi culture’ to the exhibit—perhaps a lynched Negro hanging from the mast or Senator Bilbo filibustering on the poop deck.”
The cartoon displays a hodgepodge of Americana: a ship, a cowboy, a rambunctious marching band, and the offensive flag. The details expose the irony of a racist America exporting its warped civilization to a non-white country. The black soldiers walk out of a separate entryway marked “for colored.” Heading a parallel procession of white soldiers is a farcical southern vigilante holding rope and a rifle. A black soldier pats a disheveled Japanese civilian on the shoulder and says, “I know just how you’re going to feel, bub!”:

The Japanese rulers may have been fascists, but the visual satire suggests that blacks were in solidarity with Japanese civilians, who were now being invaded by another colonizer. As the cartoon headline notes, “Asiatics Are Colored Too.” Yet the black soldier’s complicity in this metaphorical lynch mob is underscored by the tool he carries: a shovel in lieu of a gun.
Despite broad support for the war in the black press, these editorial cartoons convey America’s peculiar hypocrisy through powerful imagery of suffering and anger. Yet the subtlety of the messages expresses measured, subsurface criticism—perhaps acknowledging that World War II, for all its ethical contradictions, provided a touchstone for concentrating black solidarity and political capital. In deploying these visual idioms to motivate the struggle against fascism, the images succeeded, even if the Double-V campaign itself fell short of redeeming the struggle for “victory at home.” The fight against fascism and Nazism overseas didn’t translate into enlightenment of the American body politic of race. But by mobilizing around the the Allies, black America, and its media, cast a new light on racism in the global context—a perspective later reflected in the strands of pan-Africanism and anti-colonialism in civil rights campaigns. A “white man’s war” could not serve as a real vehicle for black empowerment, but as it stretched to every corner of the globe, the trauma of modern warfare generated a new race consciousness, and new visions, that redefined blackness on the world stage.
—————
Michelle Chen is a doctoral student in history at the City University of New York Graduate Center. In her plebian life, she is a contributing editor at In These Times, a co-producer with New York’s WBAI, and an editor at CultureStrike, a project focused on the intersection of the arts, immigration and activism. Her work has appeared in The Nation, Colorlines.com, Alternet, Ms. Magazine, Newsday, and her old zine, cain.
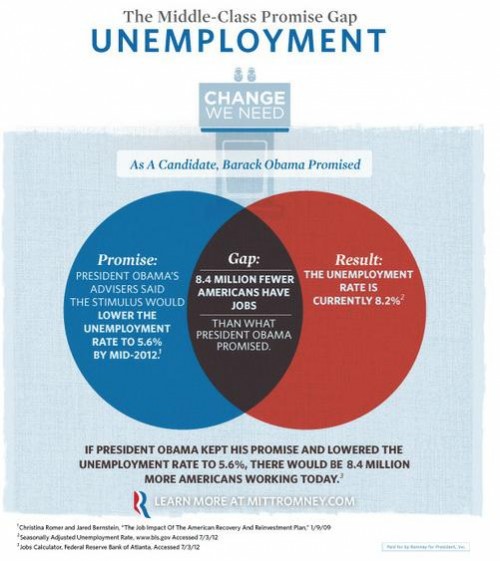
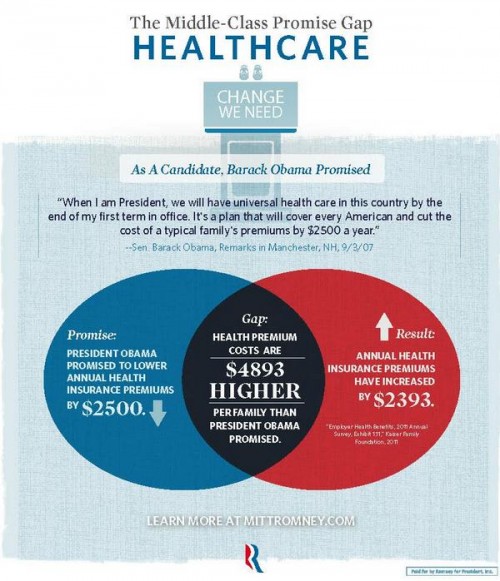

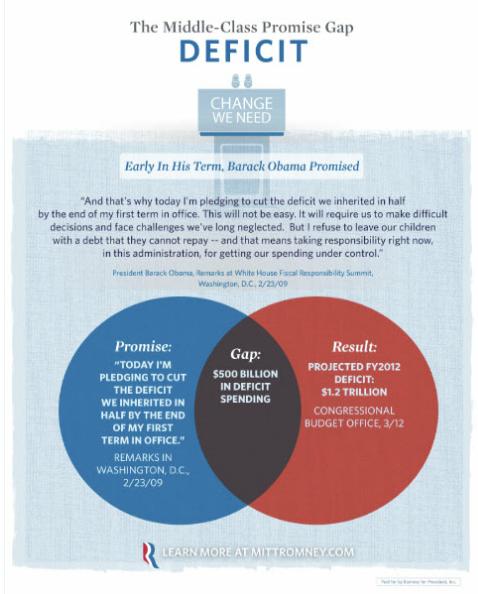 So, there you have it, an example of how not to use Venn diagrams to illustrate your data.
So, there you have it, an example of how not to use Venn diagrams to illustrate your data.