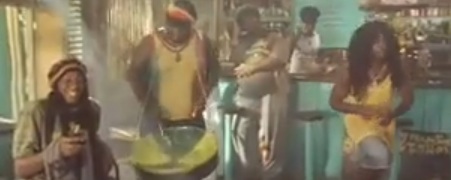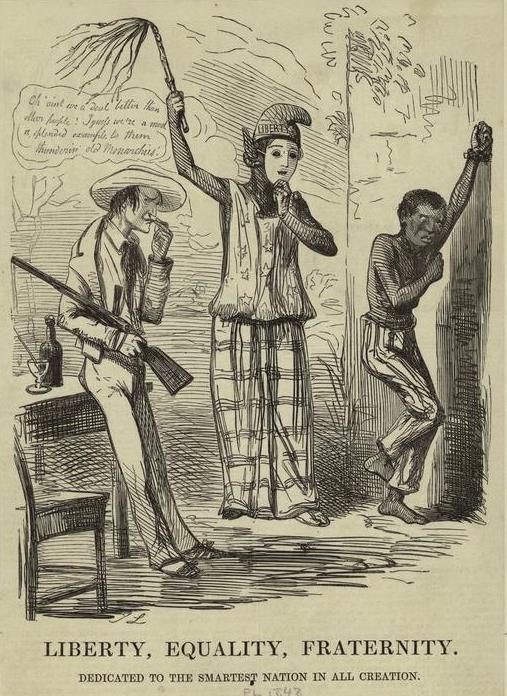In response to my post yesterday about tourism ads presenting local (often, though not always, non-White) residents of vacation hotspots as tourist attractions and amenities for relatively privileged travelers to enjoy, Lauren J. sent in a Heineken ad that pokes fun at the expectations visitors to Jamaica often have about how Jamaicans would act, and how local residents may feel obliged to play along and give tourists (with their cash) the “authentic” experience they desire:
Search results for white privilege
We have posted in the past about non-Whites being used as props in tourism and travel ads, there for the enjoyment and convenience of tourists, like other tourist attractions. Rhiannon J. sent in another excellent example of the residents of vacation areas being treated like just another amenity. In this ad for Travelocity, a White family enthuses about the many pleasures of their vacation spot — including the sun, the sand…and “the Rodrigo”:
As Rhiannon pointed out, the family discusses Rodrigo, who apparently loves carrying fruits for White tourists, the way you might discuss a stray dog.
UPDATE: Reader Chorda correctly points out that, while my use of race as the dividing point made sense when viewing these ads as a group, in this particular case “ethnicity” would probably be a more appropriate term to use.
The U.S. is not a very race-literate society. We aren’t taught much about the history of race relations or racial inequality in school and almost nothing about how to think about race or how to talk to one another about these theoretically and emotionally challenging issues. Many Americans, then, don’t have a very sophisticated understanding of race dynamics, even as most of them want racial equality and would be horrified to be called “racist.”
In teaching Race and Ethnicity, then, I notice that some of the more naive students will cling to color-blindness. “Race doesn’t matter,” they say, “I don’t even see color.” Being colorblind seems like the right thing to be when you’ve grown up being told that (1) all races are or should be equal and (2) you should never judge a book by its cover. It is the logical outcome of the messages we give many young people about race.
But, of course, color blindness fails because race, despite being a social invention, still matters in our society. Enter the ongoing scandal about the Cadbury candy bar ad featuring Naomi Campbell, sent in by Dolores R., Jack M., and Terri. The ad compares the Dairy Milk Bliss Bar to Campbell. It reads: “Move over Naomi, there’s a new Diva in town.”
The ad has been called racist because it compares Campbell to a chocolate bar; chocolate is a term sometimes used to describe black people’s skin color or overall sexual “deliciousness.” The ad, then, is argued to be foregrounding skin color and even playing on stereotypes of black women’s sexuality.
So what happened here? One the one hand, I see the critics’ point. On the other, I can also imagine the advertising people behind this ad thinking that they want to link the candy bar with the idea of a diva (rich, indulgent, etc.), and choosing Campbell because she is a notorious diva, not because she’s a black, female supermodel. They could argue that they were being colorblind and that race was not at all a consideration in designing this ad.
The problem is that being colorblind in a society where race still colors our perceptions simply doesn’t work. The truth is that race may not have been a consideration in designing the Cadbury ad, but it should have been. Not because it’s fun or functional to play with race stereotypes, but because racial meaning is something that must be managed, whether you like it or not. This is where Cadbury failed.
In my classes, I ask my earnestly-anti-racist students to replace color-blindness with color-consciousness. We need to be thoughtful and smart about race, racial meaning, and racial inequality. Racism is bad, but color-blindess is a just form of denial; being conscious about color — seeing it for what it is and isn’t, both really and socially — is a much better way to bring about a just society.
Cadbury, for what it’s worth, has apologized.
See also the Oreo Barbie, the Black Lil’ Monkey Doll, the Obama Sock Monkey, Disparate Pricing for Black and White Dolls, and Accidentally Illustrating Evil with Skin Color.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.

I invite you to spend seven minutes listening to Baratunde Thurston explaining what, exactly, is wrong with the fact that Barack Obama was hounded into releasing his long form birth certificate. He does a wonderful job of historicizing the requirement that Obama prove that he is an American (to a man such as Donald Trump), at the same time that he explains why this questioning of Obama’s citizenship is deeply hurtful to all Black Americans and their allies.
Via BoingBoing. Transcript after the jump (via Racialicious).
Jamal Spencer, a student in Naomi Glogower’s sociology class at Michigan State University, sent in the following promotion for Black History Month, courtesy of the Los Angeles Clippers (source):
Spencer makes two interesting points. First, Black History Month is in February. Oops. Second, and more importantly, notice that the promotion includes admitting “1,000 underprivileged children free.” It is assuming that “Black” is coterminous with “underprivileged,” erasing middle and upper class Blacks and poor Whites. In fact, about half of poor people are White and about 75% of Black people are not poor. This promotion, however, strengthens the conception that the poor are Black, a conception that contributes to the (racist) maligning of and restriction of benefits for the poor. Happy Black History Month indeed.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
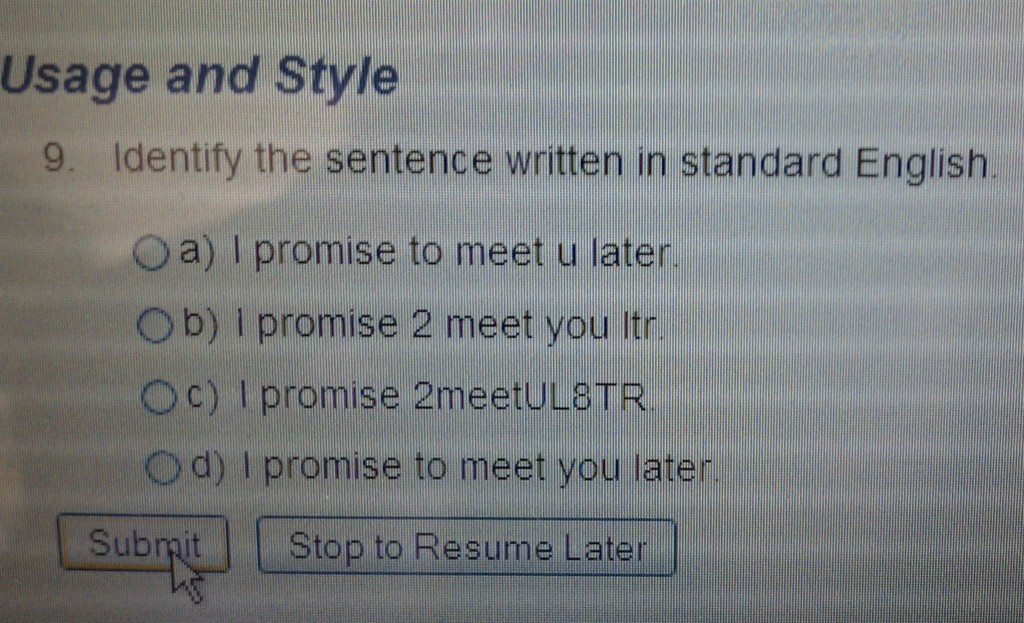
Malia Green, taking a writing diagnostic test while enrolled in Junior College, came across the following question:
The question was part of Pearson’s MyWritingLab, self-described as “a complete online learning program [that] provides better practice exercises to developing writers.”
I have heard rumor that young people have been adopting shorthand tweet-type language as “standard English,” using it in communications with professors and in their academic papers. The inclusion of this question in Pearson’s test suggests that this may, indeed, be a widespread phenomenon and that young adults may not necessarily know the difference between the English most of their parents grew up with and the English they have encountered in this brave new world.
Despite the fact that each of the answers will make sense to anyone familiar with text-ese, the correct answer on the Pearon’s test is clearly d). So, are the answers a) through c) actually wrong? Who gets to decide what “standard English” is anyway?
The whole thing reminds me of the controversies over African American Vernacular English, better known as “ebonics,” in the 1990s. The idea that some people “talk right” and some people do not is an excellent way to justify prejudice. Perhaps an employer largely chooses not to hire black people, not because they’re black, of course, but because they don’t “talk right.” Is the outcome significantly different? And who decides what “talking right” sounds like anyway? Well, the people who have the power to do so… and they typically side with themselves.
So, is text-ese wrong? Only according to those who are making the rules (and Pearson’s tests). And what do you want to bet that those young people who are taught to differentiate between the kind of English they are allowed to use in texts and the kind they are allowed to use in “proper” communication are class privileged, on average? And disproportionately white, accordingly?
So, who decides the future of English? And will “2” and “u” be words in it, or not?
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
A while back Kale let us know that the New York Public Library had made their images collection available online.The collection has images on a huge array of topics, from fashion to the military to slavery to insects to a whole category for stilts, and including political cartoons, illustrations from publications, photographs, and so on.
Kale found the collection particularly interesting as a way to look at historical racism and rhetoric about race relations in publications aimed at White readers. This 1875 cartoon, titled “A Privilege?”, presents segregation as actually protecting African Americans from the scourge of alcohol:
Text:
A PRIVILEGE?
Wife, “I wish you were not allowed in here.”
It’s a fascinating example of the use of institutionalized racial inequalities that hurt African Americans to, instead, garner sympathy for White women and children and present African Americans as, really, better off.
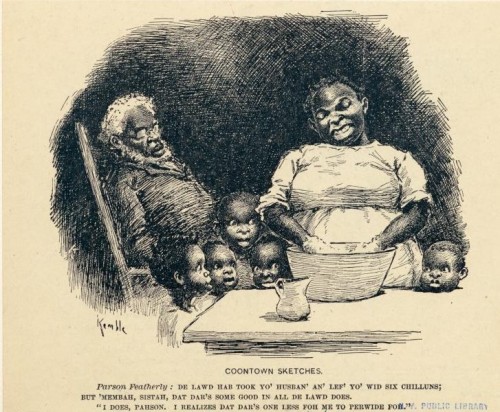
Another, published in Life in 1899, implies African American men are burdens on their families, making their wives take on the role of providing for everyone:
Text:
Parson Featherly: De Lawd hab took yo’ husban’ an’ lef’ yo’ wid six chilluns; but ‘membah, Sistah, dat dar’s some good in all de Lawd does.
“I does, Parson. I realizes dat dar’s one less for me to perwide foh.”
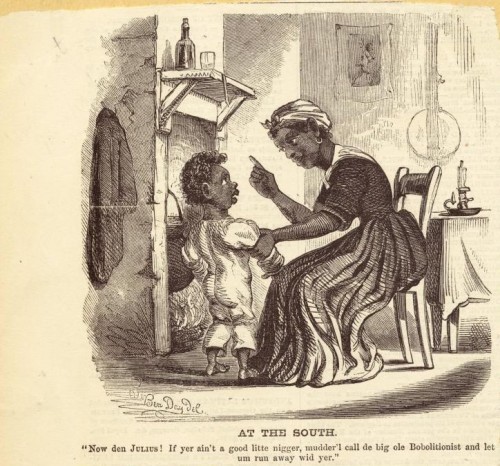
This 1860 cartoon from Harper’s Weekly shows an African American woman (presumably a slave) in the South using the “Bobolitionists” — that is, abolitionists, who wanted to outlaw slavery — as a threat, a type of monster that will come steal him if he’s not good:
Text:
“Now den Julius! If yer ain’t a good litte nigger, mudder’l call de big old Bobolitionist and let um run away wid yer.”
I’m sure it must have been very comforting to some readers to think of slaves viewing abolitionists as threats rather than potential allies.
Other cartoons mock African Americans’ physical attributes, marking them as laughable or even grotesque:
Text:
“Would de gemman in front oblige by removing de hat?”
“Would de same gemman oblige by puttin’ de hat on agin?”
(Details.)
Text:
“Now we’ll see ef dat sawed off Peterson man kin escape de issue dis time.”
(Details.)
There are also examples that criticized U.S. race relations, such as this 1848 cartoon from Punch [Note: a reader thinks this might be about France, which banned slavery in 1848, but the NYPL has it listed as relevant to U.S. slavery, so there may be so lost context here]:
Enjoy!
[Note: A commenter has expressed concern that I ended this post with “Enjoy!” I apologize for my insensitivity. I meant it in terms of “Enjoy browsing this fascinating archive,” of which racist imagery is only a small part, not, I hope it would be clear, “Enjoy looking at racist cartoons!” I wasn’t thinking about how it might appear immediately after those set of images, and I should have been more careful.]
Justin A. B. drew our attention to a Marie Claire fashion slide show titled “Nude is the New Black.” By “nude” (ironically) they mean, “white-person-color.” Every single picture featured a tan or cream item. Every. Single. One.
We’ve been covering this phenomenon. See our posts on “flesh-colored,” Michelle Obama’s “nude” colored dress, the new in-color, lotion for “normal to darker skin,” and color-assisted medical diagnosis.
NEW! (July ’10): Anna sent in another example, this time an article about Givenchy’s Fall 2010 collection. According to the article (at style.com), “everything was white, flesh-colored, or gold, with a salon dedicated to each shade.” On the Givenchy website, they use the term “nude.” An example of a “flesh-colored/nude” dress:
A group photo that shows the range of colors; the two in the middle are the “nude” dresses:
Also NEW! (July ’10): Juliana B. pointed out that in the May 2010 issue of Esquire an article on haircuts completely ignored Black men, who might not be able to use the suggestions on their hair…but in the June issue, the editor responded to a letter from a reader by acknowledging “he’s right.” They then included a segment on haircuts for Black men:
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
We have posted in the past about non-Whites being used as props in tourism and travel ads, there for the enjoyment and convenience of tourists, like other tourist attractions. Rhiannon J. sent in another excellent example of the residents of vacation areas being treated like just another amenity. In this ad for Travelocity, a White family enthuses about the many pleasures of their vacation spot — including the sun, the sand…and “the Rodrigo”:
As Rhiannon pointed out, the family discusses Rodrigo, who apparently loves carrying fruits for White tourists, the way you might discuss a stray dog.
UPDATE: Reader Chorda correctly points out that, while my use of race as the dividing point made sense when viewing these ads as a group, in this particular case “ethnicity” would probably be a more appropriate term to use.
The U.S. is not a very race-literate society. We aren’t taught much about the history of race relations or racial inequality in school and almost nothing about how to think about race or how to talk to one another about these theoretically and emotionally challenging issues. Many Americans, then, don’t have a very sophisticated understanding of race dynamics, even as most of them want racial equality and would be horrified to be called “racist.”
In teaching Race and Ethnicity, then, I notice that some of the more naive students will cling to color-blindness. “Race doesn’t matter,” they say, “I don’t even see color.” Being colorblind seems like the right thing to be when you’ve grown up being told that (1) all races are or should be equal and (2) you should never judge a book by its cover. It is the logical outcome of the messages we give many young people about race.
But, of course, color blindness fails because race, despite being a social invention, still matters in our society. Enter the ongoing scandal about the Cadbury candy bar ad featuring Naomi Campbell, sent in by Dolores R., Jack M., and Terri. The ad compares the Dairy Milk Bliss Bar to Campbell. It reads: “Move over Naomi, there’s a new Diva in town.”
The ad has been called racist because it compares Campbell to a chocolate bar; chocolate is a term sometimes used to describe black people’s skin color or overall sexual “deliciousness.” The ad, then, is argued to be foregrounding skin color and even playing on stereotypes of black women’s sexuality.
So what happened here? One the one hand, I see the critics’ point. On the other, I can also imagine the advertising people behind this ad thinking that they want to link the candy bar with the idea of a diva (rich, indulgent, etc.), and choosing Campbell because she is a notorious diva, not because she’s a black, female supermodel. They could argue that they were being colorblind and that race was not at all a consideration in designing this ad.
The problem is that being colorblind in a society where race still colors our perceptions simply doesn’t work. The truth is that race may not have been a consideration in designing the Cadbury ad, but it should have been. Not because it’s fun or functional to play with race stereotypes, but because racial meaning is something that must be managed, whether you like it or not. This is where Cadbury failed.
In my classes, I ask my earnestly-anti-racist students to replace color-blindness with color-consciousness. We need to be thoughtful and smart about race, racial meaning, and racial inequality. Racism is bad, but color-blindess is a just form of denial; being conscious about color — seeing it for what it is and isn’t, both really and socially — is a much better way to bring about a just society.
Cadbury, for what it’s worth, has apologized.
See also the Oreo Barbie, the Black Lil’ Monkey Doll, the Obama Sock Monkey, Disparate Pricing for Black and White Dolls, and Accidentally Illustrating Evil with Skin Color.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.

I invite you to spend seven minutes listening to Baratunde Thurston explaining what, exactly, is wrong with the fact that Barack Obama was hounded into releasing his long form birth certificate. He does a wonderful job of historicizing the requirement that Obama prove that he is an American (to a man such as Donald Trump), at the same time that he explains why this questioning of Obama’s citizenship is deeply hurtful to all Black Americans and their allies.
Via BoingBoing. Transcript after the jump (via Racialicious).
Jamal Spencer, a student in Naomi Glogower’s sociology class at Michigan State University, sent in the following promotion for Black History Month, courtesy of the Los Angeles Clippers (source):
Spencer makes two interesting points. First, Black History Month is in February. Oops. Second, and more importantly, notice that the promotion includes admitting “1,000 underprivileged children free.” It is assuming that “Black” is coterminous with “underprivileged,” erasing middle and upper class Blacks and poor Whites. In fact, about half of poor people are White and about 75% of Black people are not poor. This promotion, however, strengthens the conception that the poor are Black, a conception that contributes to the (racist) maligning of and restriction of benefits for the poor. Happy Black History Month indeed.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
Malia Green, taking a writing diagnostic test while enrolled in Junior College, came across the following question:
The question was part of Pearson’s MyWritingLab, self-described as “a complete online learning program [that] provides better practice exercises to developing writers.”
I have heard rumor that young people have been adopting shorthand tweet-type language as “standard English,” using it in communications with professors and in their academic papers. The inclusion of this question in Pearson’s test suggests that this may, indeed, be a widespread phenomenon and that young adults may not necessarily know the difference between the English most of their parents grew up with and the English they have encountered in this brave new world.
Despite the fact that each of the answers will make sense to anyone familiar with text-ese, the correct answer on the Pearon’s test is clearly d). So, are the answers a) through c) actually wrong? Who gets to decide what “standard English” is anyway?
The whole thing reminds me of the controversies over African American Vernacular English, better known as “ebonics,” in the 1990s. The idea that some people “talk right” and some people do not is an excellent way to justify prejudice. Perhaps an employer largely chooses not to hire black people, not because they’re black, of course, but because they don’t “talk right.” Is the outcome significantly different? And who decides what “talking right” sounds like anyway? Well, the people who have the power to do so… and they typically side with themselves.
So, is text-ese wrong? Only according to those who are making the rules (and Pearson’s tests). And what do you want to bet that those young people who are taught to differentiate between the kind of English they are allowed to use in texts and the kind they are allowed to use in “proper” communication are class privileged, on average? And disproportionately white, accordingly?
So, who decides the future of English? And will “2” and “u” be words in it, or not?
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
A while back Kale let us know that the New York Public Library had made their images collection available online.The collection has images on a huge array of topics, from fashion to the military to slavery to insects to a whole category for stilts, and including political cartoons, illustrations from publications, photographs, and so on.
Kale found the collection particularly interesting as a way to look at historical racism and rhetoric about race relations in publications aimed at White readers. This 1875 cartoon, titled “A Privilege?”, presents segregation as actually protecting African Americans from the scourge of alcohol:
Text:
A PRIVILEGE?
Wife, “I wish you were not allowed in here.”
It’s a fascinating example of the use of institutionalized racial inequalities that hurt African Americans to, instead, garner sympathy for White women and children and present African Americans as, really, better off.
Another, published in Life in 1899, implies African American men are burdens on their families, making their wives take on the role of providing for everyone:
Text:
Parson Featherly: De Lawd hab took yo’ husban’ an’ lef’ yo’ wid six chilluns; but ‘membah, Sistah, dat dar’s some good in all de Lawd does.
“I does, Parson. I realizes dat dar’s one less for me to perwide foh.”
This 1860 cartoon from Harper’s Weekly shows an African American woman (presumably a slave) in the South using the “Bobolitionists” — that is, abolitionists, who wanted to outlaw slavery — as a threat, a type of monster that will come steal him if he’s not good:
Text:
“Now den Julius! If yer ain’t a good litte nigger, mudder’l call de big old Bobolitionist and let um run away wid yer.”
I’m sure it must have been very comforting to some readers to think of slaves viewing abolitionists as threats rather than potential allies.
Other cartoons mock African Americans’ physical attributes, marking them as laughable or even grotesque:
Text:
“Would de gemman in front oblige by removing de hat?”
“Would de same gemman oblige by puttin’ de hat on agin?”
(Details.)
Text:
“Now we’ll see ef dat sawed off Peterson man kin escape de issue dis time.”
(Details.)
There are also examples that criticized U.S. race relations, such as this 1848 cartoon from Punch [Note: a reader thinks this might be about France, which banned slavery in 1848, but the NYPL has it listed as relevant to U.S. slavery, so there may be so lost context here]:
Enjoy!
[Note: A commenter has expressed concern that I ended this post with “Enjoy!” I apologize for my insensitivity. I meant it in terms of “Enjoy browsing this fascinating archive,” of which racist imagery is only a small part, not, I hope it would be clear, “Enjoy looking at racist cartoons!” I wasn’t thinking about how it might appear immediately after those set of images, and I should have been more careful.]
Justin A. B. drew our attention to a Marie Claire fashion slide show titled “Nude is the New Black.” By “nude” (ironically) they mean, “white-person-color.” Every single picture featured a tan or cream item. Every. Single. One.
We’ve been covering this phenomenon. See our posts on “flesh-colored,” Michelle Obama’s “nude” colored dress, the new in-color, lotion for “normal to darker skin,” and color-assisted medical diagnosis.
NEW! (July ’10): Anna sent in another example, this time an article about Givenchy’s Fall 2010 collection. According to the article (at style.com), “everything was white, flesh-colored, or gold, with a salon dedicated to each shade.” On the Givenchy website, they use the term “nude.” An example of a “flesh-colored/nude” dress:
A group photo that shows the range of colors; the two in the middle are the “nude” dresses:
Also NEW! (July ’10): Juliana B. pointed out that in the May 2010 issue of Esquire an article on haircuts completely ignored Black men, who might not be able to use the suggestions on their hair…but in the June issue, the editor responded to a letter from a reader by acknowledging “he’s right.” They then included a segment on haircuts for Black men:
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.