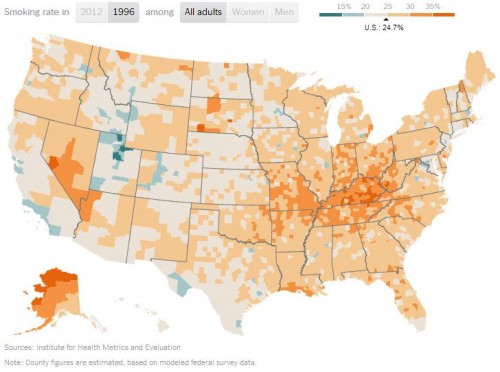
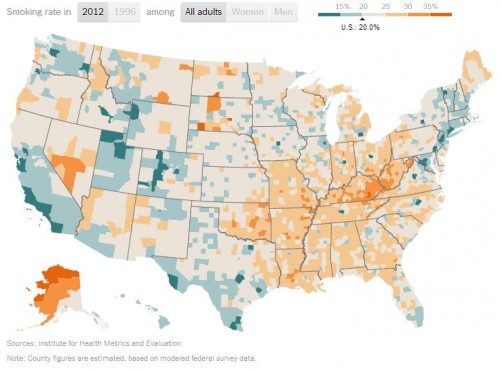
The Pink Lady is 15 oz. gin, 4 dashes of grenadine, and an egg white.
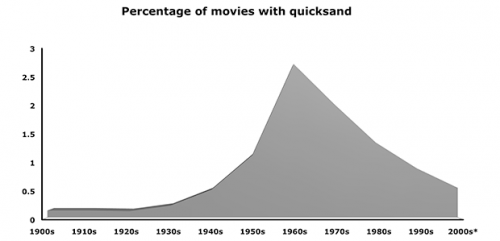
According to Shanna Farrell, the Pink Lady was popularized in the ’50s. Women were believed to have “dainty palates,” and so cocktails for women were designed to disguise any taste of alcohol. In the ’70s, the Pink Lady was surpassed by the Lemon Drop and, in the ’80s, the Cosmopolitan.
Farrell asks “What does it mean to drink like a woman” today? Anecdotally, she finds that bartenders consistently expect her to order something “juicy or sweet” — “It’s pink; you’ll like it” — and respond with a favorable nod when she orders something “spirit forward.”
This is typical for America today: women are expected to perform femininity, but when they perform masculinity, they are admired and rewarded. This is because we still put greater value on men and the things we associate with them.
This phenomenon of valuing masculinity over femininity — what we call “androcentrism” — may be changing how women drink, since everyone likes that nod of approval. Farrell reports that “women account for the fastest-growing segment of worldwide whiskey consumers.” Well hello, Hilary.
I wonder how men will respond to women’s incursion into the whiskey market. Traditionally we’ve seen male flight. As an activity, occupation, or product is increasingly associated with women, men leave. In a society where women keep infiltrating more and more of men’s domains, this is a bad long-term strategy for maintaining dominance (see, for example, the feminization of education). As I ask in my forthcoming sociology of gender textbook: “What will happen when women are sipping from all the bottles?”
Thanks to the super-cool bartender Naomi Schimek for the tip!
Cross-posted at Jezebel and Pacific Standard.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.