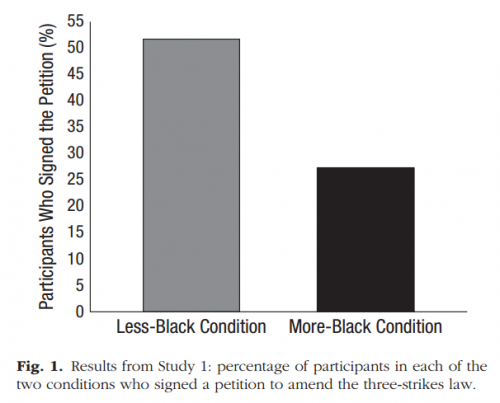
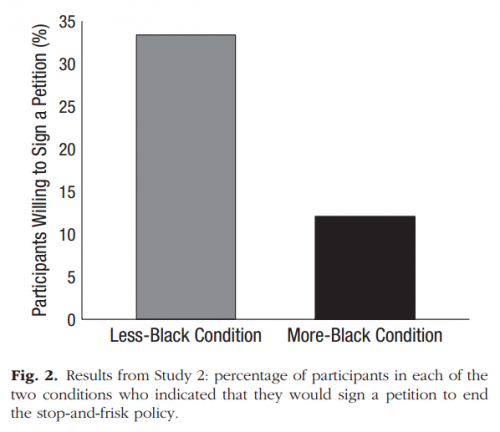
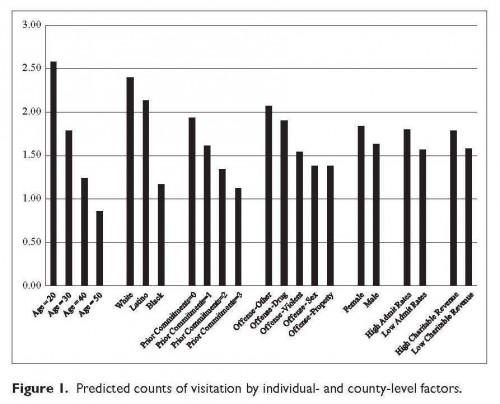
One of the better things about social media is that if you manage to curate social feeds with just the right balance of entertaining spirits and brilliant intellects, it delivers unto you amazing content you would have otherwise missed.
I woke up one of these days — Sunday? Monday? I’m dissertating — to find dozens of messages from social media comrades about John Oliver’s take-down of for-profit colleges. You can watch it here:
It’s very satisfying.
It is particularly satisfying if you’ve experienced what education professor Kevin Kinser rightly points out is the oddly sporadic nature of public interest in a 100 year old institutional practice of selling education for profit. Oliver is one of the best in the entertainment-as-news genre. He reaches people that mainstream media does not. He makes difficult issues palatable for general, concerned audiences.
And if you think about debt, precarity, credentialism, and financial cronyism, like I do, it is gratifying to see someone like Oliver take on an issue most people could care less about until someone they care about borrows $50,000 for a veterinary assistant’s degree. Then they’re emailing you like the roof is on fire.
I do have a greater hope, though, than that something I study benefit from the spotlight of people like Oliver.
I wish we could talk about impoverished educations without ignoring impoverished conditions.
Here’s the thing, for-profit colleges have manipulated a system primed for manipulation. No doubt about that. But eliminating for-profit colleges does not eliminate the conditions that cause people to seek them out.
By and large, none of the people I have interviewed, observed or worked with is an idiot without agency. They have sometimes been lied to and led astray; occasionally they are bamboozled by sparkly advertising and aggressive sales tactics. They do sign documents they do not completely understand and they trust authority that has little incentive to counsel as opposed to sell. All of that is true.
But most students picked up the phone to “call today; start tomorrow” because they have been unemployed, underemployed, marginalized, and otherwise made vulnerable by socio-economic conditions.
So, by all means, crib Oliver’s letter. It’s a doozy.
But maybe keep in mind that moving inequality around isn’t exactly the same as addressing inequality.
Tressie McMillan Cottom is a PhD candidate in the Sociology Department at Emory University in Atlanta, GA. Her doctoral research is a comparative study of the expansion of for-profit colleges. You can follow her on twitter and at her blog, where this post originally appeared.