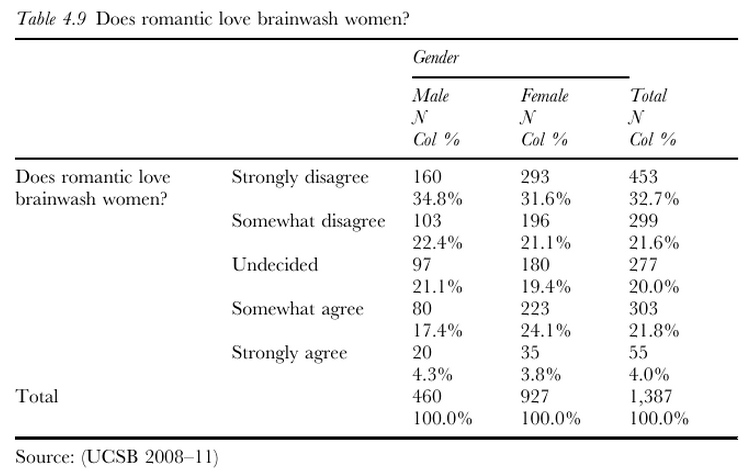
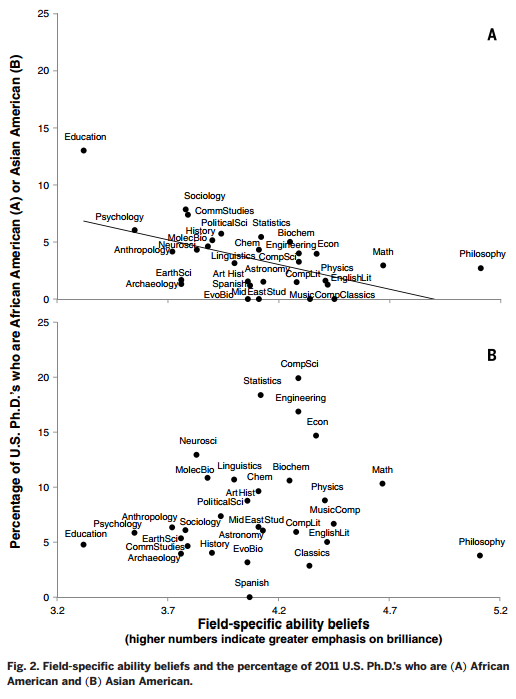
In 1975, Mulvey conceptualized the gaze as the power derived by the viewer when they cast their glance upon a hierarchized, usually female, body. This idea perfectly captures the way a subject on film is both frozen in a time and space, and consumed. I want to turn that around, in a more kyriarchal and postmodern fashion, and allot power to the subject.
Refinery 29 has a series of photographs by Blaise Cepis. Through them, women discuss and display their body hair. In a beautifully hued array, these women speak of personal choice, empowerment and acceptance in ways that act as a counternarrative to the Brazilian-plucked-chicken-prepubescent-non-mammal-landscaping construct that is currently in vogue.
And yet. Yet. Among this abundance of hairy joy – there is no direct gaze. Among the 21 slides there are faces in profile, lower portions of faces, averted glances with pupils looking away. There is only one woman directly glancing at the viewer, and even as her defiant brows dominate her face she is neither fully seen nor subsequently fully known. Also, nowhere in the 21 slides does the women’s whole body occupy the visual frame. The pictures show a bushy underarm with barely a chest wall or breast, a lushly forested pudenda without whole legs or torso, or a lightly furred arm without a hand attached.
Counter this power and gaze conundrum with Kim Kardashian’s photoessay for Paper’s Winter issue where she appears, full frontal, body hair free, and fully faced. With the hashtag #breaktheinternet, the intent of the shoot is clear. Neither during the photoshoot’s extended video interview or the accompanying print piece does Kardashian invoke feminism’s ideals of choice, power or acceptance. Yet, in her direct gaze and whole body there is a definitive power of being fully present in the visual medium.
Censored to be safe for work, but you can see the original here: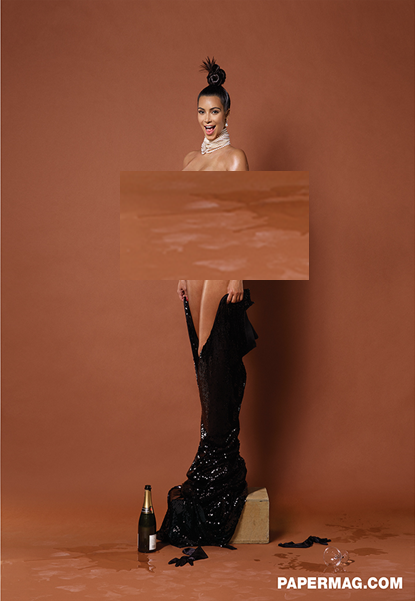
In his classic Disidentifications, Munoz interrogates the intersections between queer theory and life as performance to illustrate the ways hegemony is constructed. All the women in the photoessay above are performing: to disrupt a gaze by capturing the consumer; to deliver through visual imagery a counternarrative to normed assumptions; to shine a spotlight upon their bodies so that other stories can be told about them that subsequently reflect the world. These are all photos of “naked women”, but they are not equal in power.
Make no mistake, Kardashian’s photoshoot does not aspire to be anything but performance – a denuded spectacle that we can believe – illustrating her power to create reverberating social narratives. But the theme of empowered, hirsuit women who embrace the social, sexual, and personal repercussions of their decision is undercut by the disembodied visual presentation. The power of these women has no whole body in which to reside. They are intended to be read as both brave and everyday, but they are visually reduced to decontextualized hair clumps; the performances of pride do not ring true because the viewer does not witness the incorporation of their body pride into a fully human landscape. Frankly, if women are going to “grow hair there” – we need to fully embody it.
Cross-posted at Pacific Standard.
Kerrita K. Mayfield, PhD is an experienced social justice oriented educator and teacher trainer, with over 20 years working in urban and rural classrooms and alternative educational settings. Currently teaching ESL at UMass Amherst to liminal non-benefitted workers, she was the first student to earn a graduate minor in Women’s Studies at the University of Wyoming.