With the college football championship games coming up, Dmitriy T.M. thought it was a good time to highlight the NCAA’s database that provides detailed information on graduation rates of college athletes. For each school, you can select particular sports and years. I decided to look up graduation rates for 2010-2011 at the two schools I attended: University of Oklahoma (undergrad) and University of Wisconsin-Madison (grad school).
The database reports two numbers. The Federal Graduation Rate (FGR) reports numbers for individuals who were first-time college students when they enrolled at the institution (that is, no transfer students are included, and students who transfer count negatively in the rate for their initial school, the equivalent of a drop-out); the FGR indicates how many students graduated from their initial institution within 6 years. The Graduation Success Rate (GSR) takes into account transfer students; as long as they’re in good academic standing when they transfer, they aren’t counted against the initial school’s graduation rate.
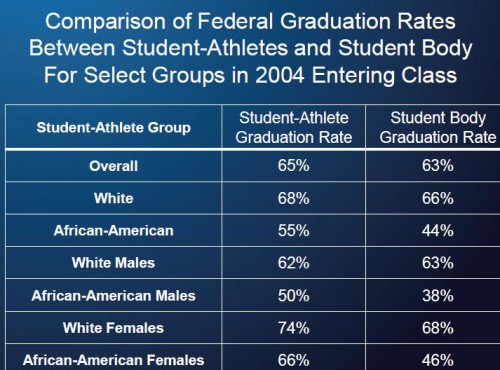
So how are student athletes doing? According to the NCAA’s analysis, if we look at the more restrictive FGR for students who began college in 2004, student athletes actually have higher graduation rates in general, especially for African Americans:
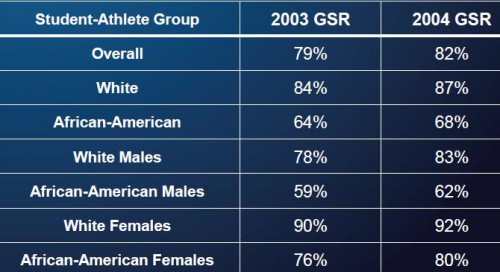
If we switch to looking at the GSR (which, again, drops transfers from the data for the initial school, rather than counting them as non-graduates), for students who began college in 2003 and 2004, overall graduation was pretty high (79 and 82 percent), but we see pretty wide disparities. White student athletes were significantly more likely to graduate than African Americans, and for both races, women were more likely to graduate than men:
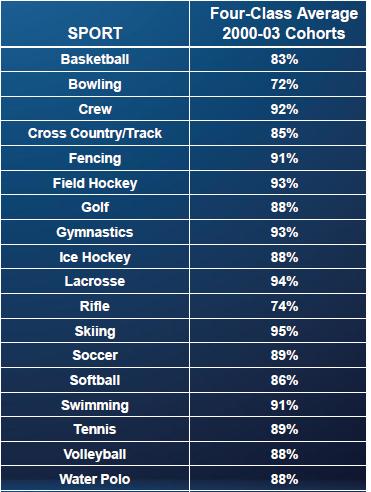
Graduation rates also vary by sport. Here are the averages for male athletes who enrolled between 2000 and 2003; we see basketball and football at the lower end, while lacrosse graduated 88% of its players from that period (the two football #s refer to the different divisions):
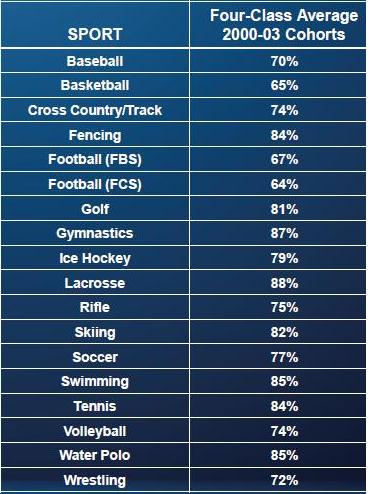
Female athletes from the same cohorts; the only sport where they didn’t have (usually significantly) higher graduation rates than men playing the same sport is rifle:
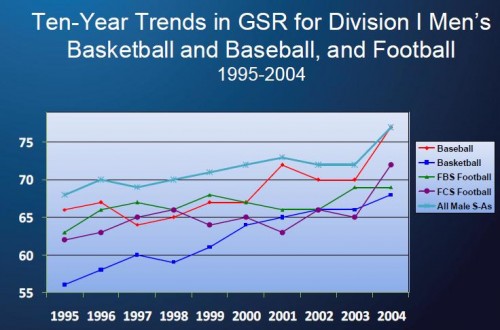
Ten-year trends for men in Division I schools in the “big three” sports:
There’s lots more detailed info available if you click the “Trends in Graduation Success Rates and Federal Graduation Rates at NCAA Division I Institutions” link at the top of the website; you can also get reports for particular schools broken down by sport, race/ethnicity, sex, etc.