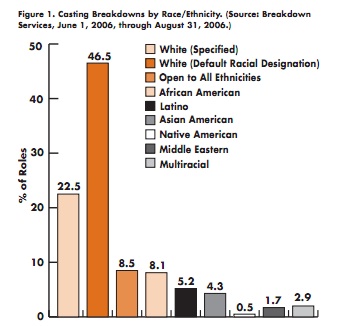
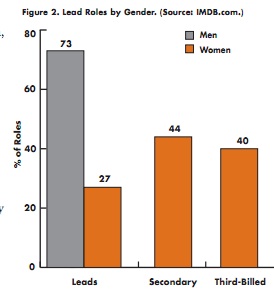
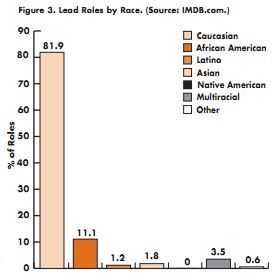
Christie W. sent in an idea that inspired me to revive our pointlessly gendered products post. It’s a fun one. I’ve added Christie’s submission — a super-pink for-her version of a continuous positive airway pressure machine for people with sleep apnea.
————————
At this point, the gendering of things like phones doesn’t surprise me, such as this set, sent in by Ben C.:
But really…pink ear plugs?
We seriously need our own earplugs that are “silky soft”? Starchy G., who sent them in, says:
I’ve been told that these things have the extra-feminine side effect of dying one’s earwax pink.
Lovely.
Feminist Philosophers found this delightfully marketed pair of earplugs for, um, I’m gonna guess working class men:

Gendered tape, also from Feminist Philosophers:

Lee D.-T. found these sandwich bags for sale at a Safeway store in Melbourne, Australia. Sandwich bags, people!

Original Will sent in this image of pink computer cables, found at boing boing:
NEW! (Mar. ’10): Marjolaine N. found pink and blue chocolate Easter bunnies:
Michelle at The Red Pill Survival Guide took this photograph of gendered lollipops. But not just any lollies: “Girls Enchanted” and “Boys Adventure” mixes. Sigh:
Em wanted to download Style XP to customize Windows XP, but had to decide between men’s and ladies’ versions:
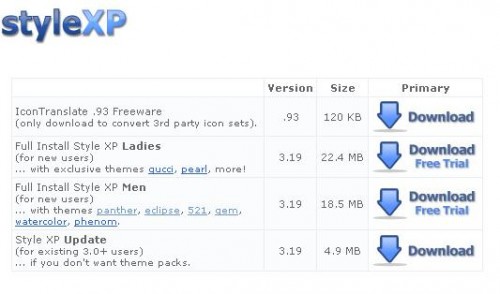
Em says,
The Man theme “gem” and the Lady theme “gucci” look pretty much the same. Still I’m glad it’s called “gucci” so I know it’s for me. Me and my lady friends are going to giggle about it then go online shoe shopping together. I just hope they’ve added extra-easy installation instructions to that version.
Christie W. sent in a pink version of a continuous positive airway pressure machine, and related items, for people, er women, with sleep apnea:
Over a dozen more ridiculous examples, after the jump.