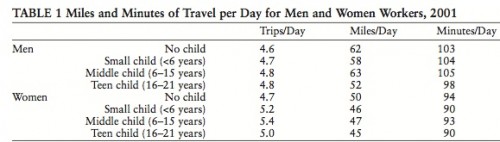
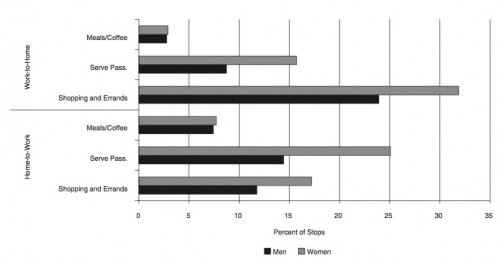
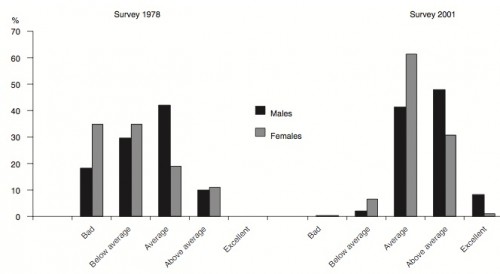
Cross-Posted at BagNewsNotes.
We have posted in the past about how airlines use images of female flight attendants in ads to appeal to customers with promises of caretaking, eye candy, flirtation, and emotion work. Katrin sent in another example. This Cathay Pacific ad, which appeared in the U.K., presents Karina Yau, a flight attendant, to customers as the perfect caretaking woman — one who just wants to listen to you, not talk:
Notice also the passive stance — arms pulled into the body, her face turned away and eyes averted, hand fiddling with her coat sleeve. The text reads:
Karina went from fashion model to flight attendant — and still doesn’t think that life has had any real ups and downs. You can meet her and other members of the Cathay Pacific team at www.cathaypacific.co.uk. And while you’re there, check out our great fares to over 110 destinations worldwide. If you see Karina on your next flight, you might recommend a favourite book — she loves to read.
A post on the Cathay Pacific blog about Yau describes her as “modest.” At Cathay’s website you can “meet the team who go the extra mile to make you feel special.” It includes photos and bios of some employees, and I found Yau’s. The text they chose to highlight reinforces the emotion work she engages in for customers — “of course” she “smiled and apologised immediately.”
The ad and the features present customers with the promise of more than just a flight attendant who will do her job well. This flight attendant is the ideal of femininity: she’s beautiful (a former model), she’s submissive (apologizes immediately!), and she’s interested in you — your thoughts, your taste in books — whoever you are.
I wonder to what degree this draws on a specifically racialized femininity — the stereotypical depiction of Asian women as particularly submissive and docile. But since this ad ran in the U.K., I don’t know if that stereotype is as relevant. Readers, what say you?