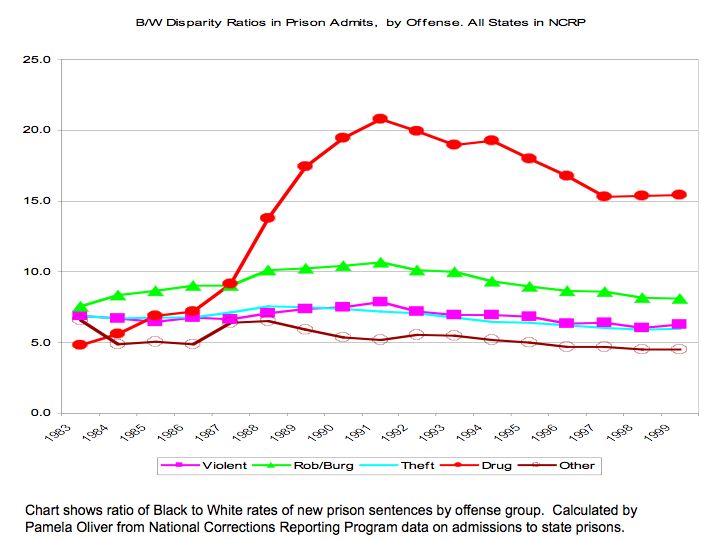
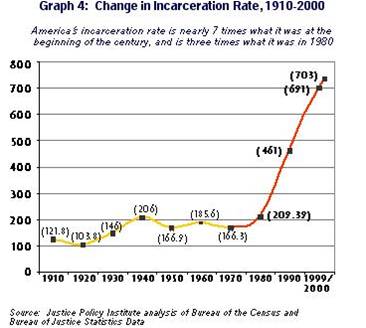
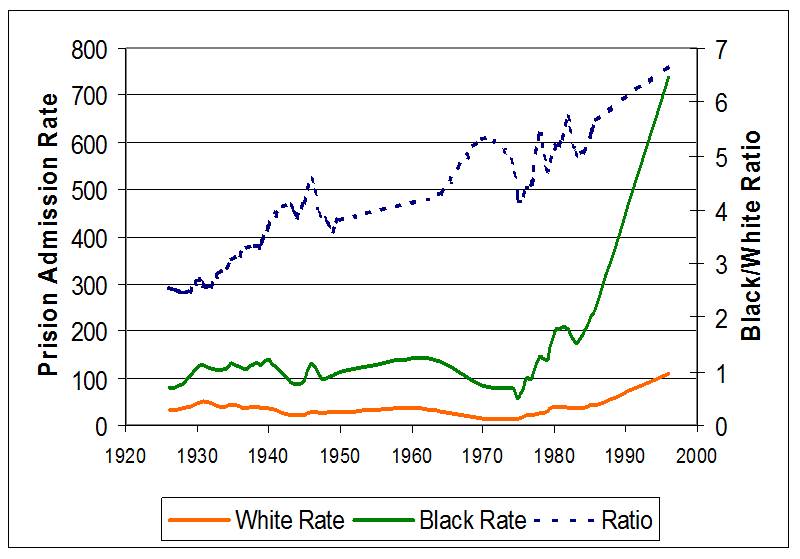
Remember that Trojan ad where men were pigs? Daniel G. sent us another ad portraying men as animals. In this one, men in a bar grow antlers so as to head-butt over a cute girl. Guess which one she goes for? Thanks Daniel!
We consolidated our products-shaped-like-boobs posts and added 17 (yes, 17) new boob-shaped products. Thanks to Stumblng Tumblr and Shakesville.
On a similar theme, we added some additional images of things shaped like women, generally, including a cigarette extinguisher. See them here.
And, still on this theme, we added one more urinal shaped like a woman. We added a second example of a non-American Indian appropriating an American Indian identity and doing conservation work. Click here for Archibald, I mean, Grey Owl.
We added another example of people of color being associated with “spice” and, thus, spicing up the bland world of white people. And this one in a truly misguided pro-diversity ad!
We added to our ad using the idea that Latinas are “hot” and “spicy,” some ads for Rio Casino in which a black woman is used to communicate “passion.” Both demonstrate how women of color are stereotyped as more highly sexual than white women. See it here.
We added a description of a chapter in the book Freakonomics that presents a theory on how baby names become popular to this post about historical trends in baby names, including a link to a website that tracks the popularity of names the Freakonomics authors predict will be most popular by 2015.
We updated this post about an Israeli air conditioner ad that let viewers manipulate a thermostat to make a woman’s nipples get more or less visible. We added a comment from the CEO of the company that he released after protests in Israel forced the company to take the ad down in which he calls people out for being hypocrites for targeting some sexist material but not others. And also says that if they can’t use sexist ads, products would have to actually have a competitive advantage. We thought it was awesome that a CEO would admit they need media images to sell their products because or they’d have to actually make something better or cheaper than what’s already out there.
Eva Longoria was recently accused of being “fat.” We added a pic of her offending body to this post on the scandal over Czech model Karolina Kurkova’s scandalous appearance on the runway and Ali Michael’s fall from grace. Thanks to Elizabeth A. for the tip!
We added an ad for I Can’t Believe It’s Not Butter and one for Skyy vodka to this post about the sexualization of food. Scroll way down.
We added a Snickers commercial in which Mr. T. attacks a man for acting like a sissy (i.e., gay and/or feminine) to our other commecial demonstrating the policing of masculinity. Thanks to Penny R. for alerting us to the commercial!