I took these pictures at a Vons in Los Angeles, CA (Eagle Rock neighborhood):
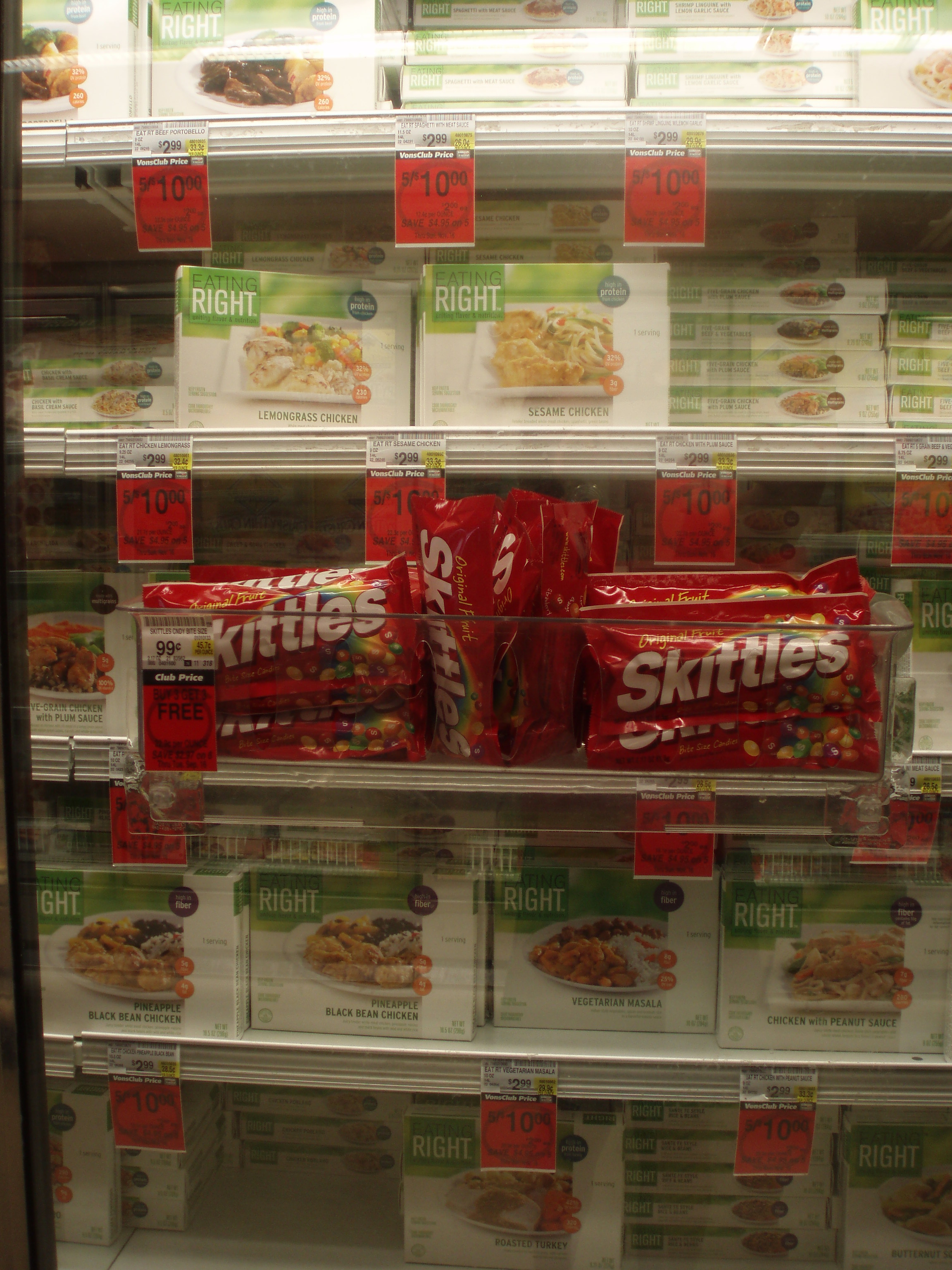
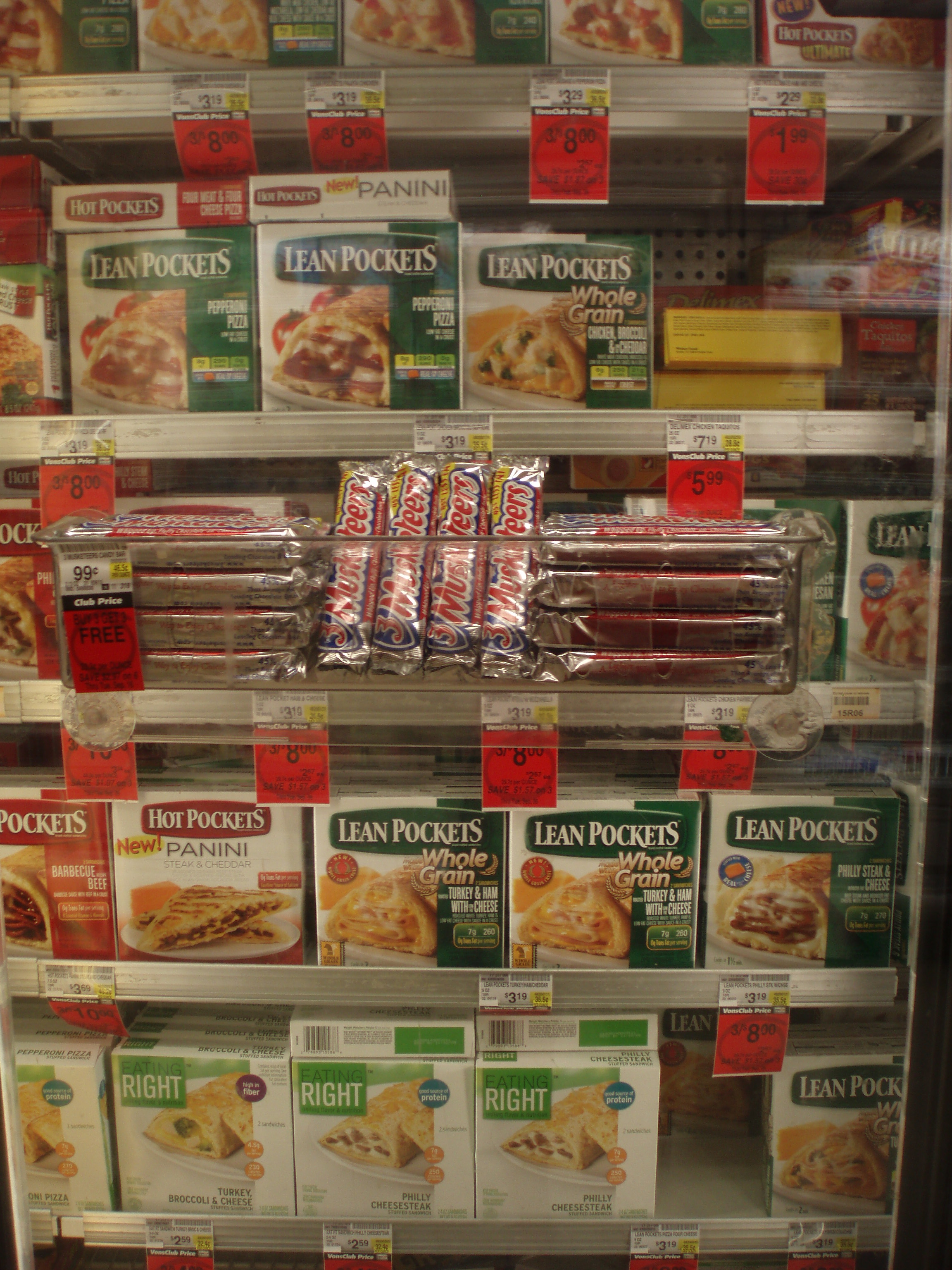
Someone or someones somewhere made a conscious decision to hang candy bars on the outside of the freezer doors leading to the TV dinners marketed as healthy. I think it nicely illustrates how, in American culture, we are subject to incredible temptation and pressure to consume more calories than we need at the same time that we’re encouraged to look as if we do not submit to that temptation. This is good for the economy in that both the food industry and the diet industry are far larger industries than they would be were we to restrict our caloric intake according to need.
NEW (from Gwen): I took the following two photos in my office building at Nevada State College. We don’t have any food service program and there aren’t any places to eat within walking distance, so the only options faculty and students have are the vending machines. The other day my attention was drawn to this sign posted inside one of them:
Now, on the face of it, this seems all good–individuals should take responsibility for their food choices by choosing healthier options, and the vendor is even providing guidelines. How nice!
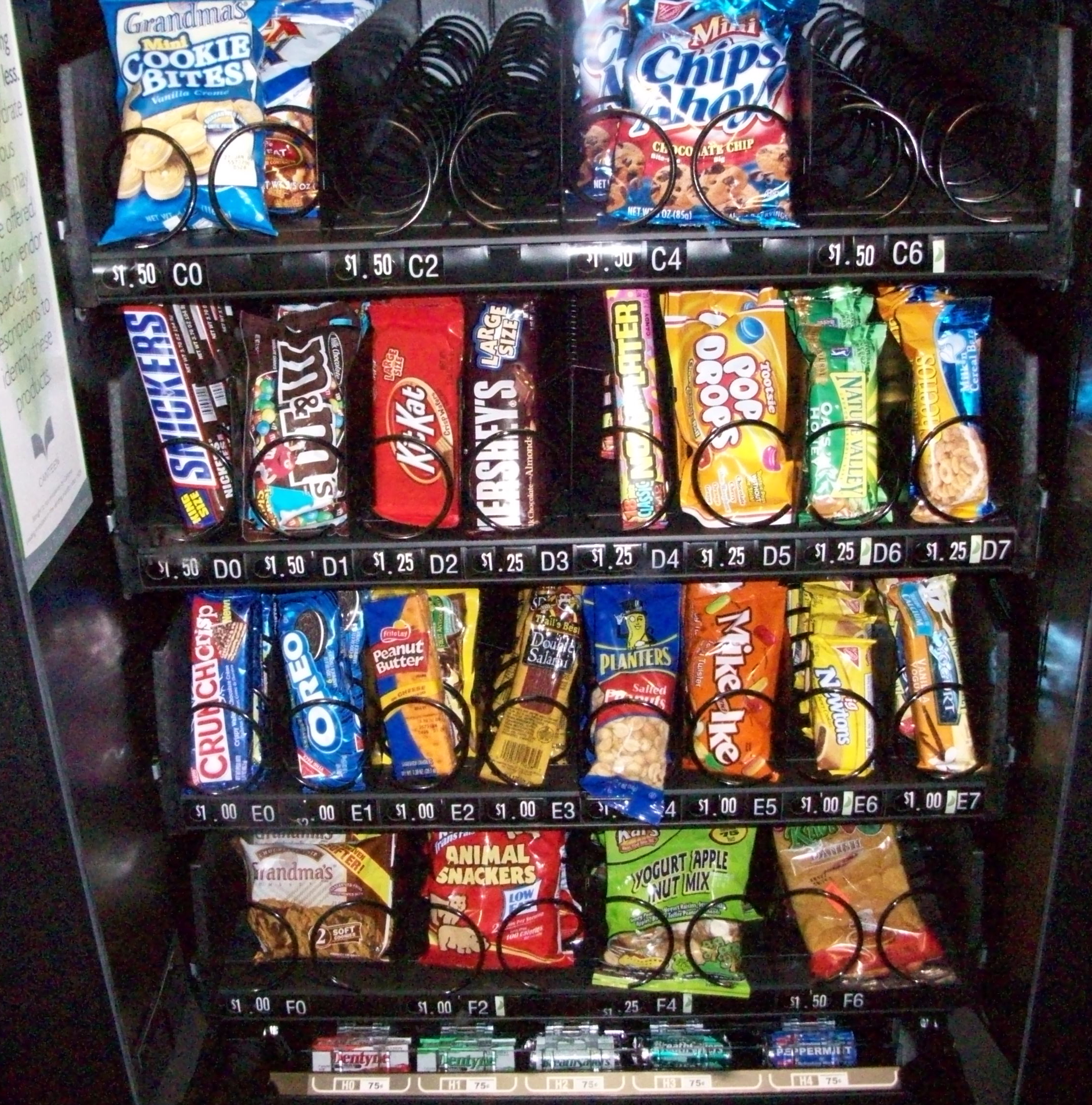
But then I stood back and looked at the products for sale in that same vending machine (there were a couple of rows of chips at the top that got cut off in the photo):
None of these products had nutritional information in view, so I couldn’t actually see how many of them fell within the guidelines helpfully posted along the side. I know, from looking at similarly-sized packages at a convenience store later, that all the chips had over 350 calories.
My guess would be that most people would choose the “yogurt apple nut mix” on the next-to-last row as the healthiest item, but I’ve found that mixes like that often have surprisingly high fat and calorie contents, particularly because they often come in multiple-serving packages. But without access to more information, the consumer is left to try to guess what would be healthiest and what might have lots of hidden calories (like those yogurt-covered nuts might).
I thought it was a great example of how concerns about unhealthy eating habits and obesity are often framed as failures of individual responsibility–people just eat too much and make bad decisions about food. The food industry likes this explanation because it takes the focus off of the types of products it makes available or the responsibility food companies might have for producing healthier options…or at least telling us more openly about what we’re eating. But this framing of the issue ignores the fact that it’s often very difficult to make better eating decisions; nutritional information is often lacking (I have on several occasions asked for nutritional information at restaurants, just out of interest, and usually found that employees have difficulty locating it; in one case they eventually found it posted on a chart hidden by a fake plant), and in other cases there simply aren’t better options (or they’re more expensive than the unhealthy ones). Providing platitudes about “making balanced choices” isn’t that helpful in the absence of specific information about and access to foods that are, you know…balanced.