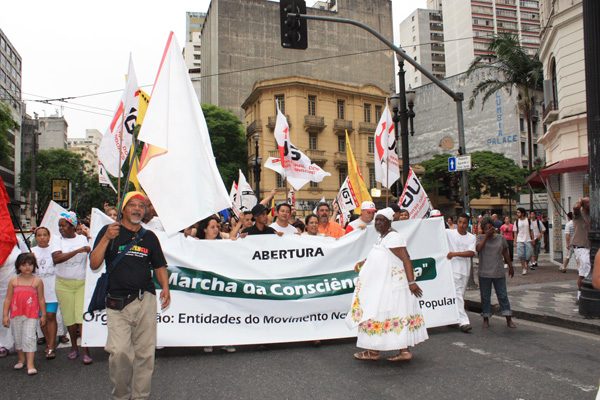
Historically, Brazil had presented itself as a “racial democracy” where interaction between racial groups formed a utopian, raceless society. In the last few decades, Brazil has come to acknowledge its underlying racism and resulting disparities, leading to the 2001 enactment of race-based affirmative action projects. Social scientific research can help us better understand the functions and necessity of these programs, which are likely to be under threat following the election of right-wing candidate Jair Bolsonaro who has been openly critical of Blacks and the LGBT community and the policies that serve them.
In Brazil, skin color has been the defining mechanism for racial categorization and identity in between a black and white binary. Some official methods, however, including the Brazilian Census, recognize multiracial identity and a number of racial categories. Multiple methods of classification can be tricky, and this can obscure deeper and more basic racial inequalities. Though pardos (a mixed-race category used in the census) can face similar social situations as dark-skinned Blacks (sometimes referred to as pretos), recent research finds that pardos actually do experience less disadvantage than pretos, complicating decisions about who receives help from affirmative action programs.
- Stanley R. Bailey. 2009. “Unmixing for Race Making in Brazil.” American Journal of Sociology 114(3): 577-614.
- Mara Loveman, Jeronimo O. Muniz, and Stanley R. Bailey. 2012. “Brazil in Black and White? Race Categories, the Census, and the Study of Inequality.” Ethnic and Racial Studies 35(8): 1466-1483.
Given this complexity, determining who is Black and a possible beneficiary of the racial quota program has differed. Some universities have required applicants to be of African descent to qualify for racial quotas, which has caused complications since many Brazilians could claim African ancestry even though they may have light skin or are not seen as “Black.” In other cases, verification committees at different universities confirm whether an applicant should be considered Black and a beneficiary of the racial quota system. The quota program has now significantly broadened to include applicants from low-income families as well as Indigenous peoples. Independent of skin color or racial group, support for affirmative action programs and race-targeted public policies is strong. Research suggests, however, that the more education someone has, the less likely they are to support racial quotas. It is important to consider what factors affect support and execution of these policies as opponents such as President-elect Bolsonaro attempt to dismantle it.
- Stanley R. Bailey, Fabrício Fialho, and Michelle Peria. 2015. “Support for Race-Targeted Affirmative Action in Brazil.” Ethnicities 1-34.
- Edward Telles. 2014. Pigmentocracies: Ethnicity, Race, and Color in Latin America. The University of North Carolina Press.