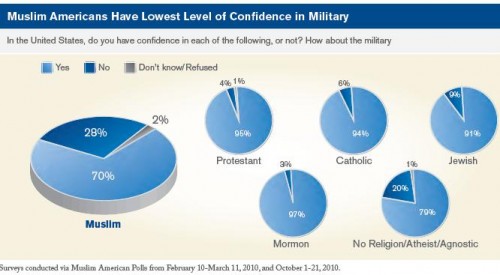
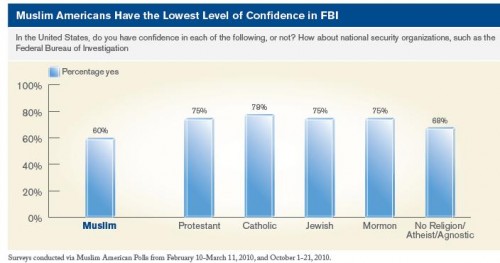
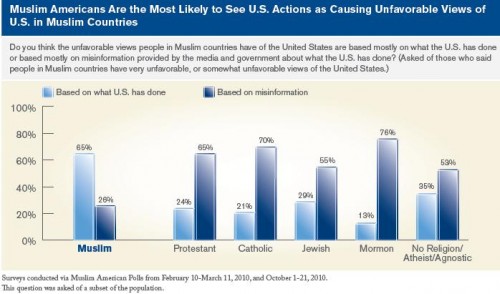
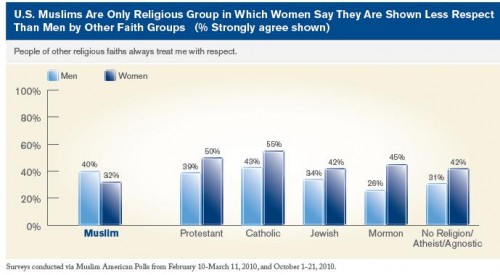
At the intersection of the trivializing of horrific violence aimed at ethnic/religious groups and the pornification of American culture, comes this “Anne Skank” costume:
[APOLOGIES: We were asked to remove the photograph and complied.]
Yes that is, indeed, a woman dressed up like Anne Frank, the Jewish child who hid from the Nazis for two years, only to be discovered and moved to a concentration camp where she died from Typhus. Her companions are dressed up like Nazi soldiers. The Halloween revelers who made the choice to sexualize and laugh at this 15-year-old victim of the holocaust are graduate students in a Creative Writing program.
UPDATE: Comments thread closed.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.