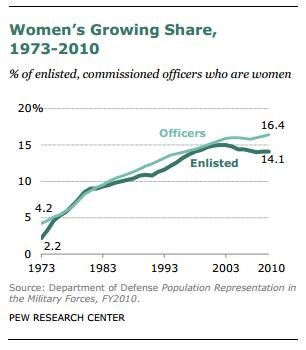
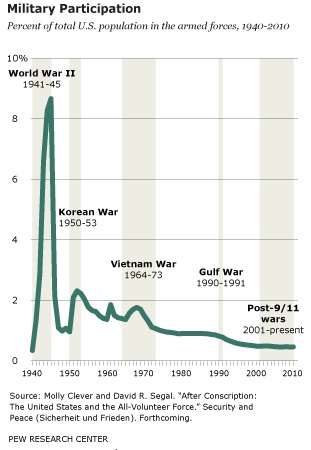
Pew Research Center reports that, as of 2010, women make up about 15% of enlisted soldiers and commissioned officers:
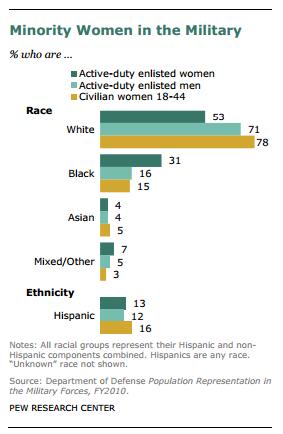
Not all types of women are entering the military at the same rate. Nearly a third of women in the military are Black, about twice their proportion in the general population. In contrast, about half are white, about 2/3rds their proportion among civilian women.
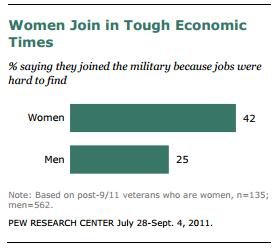
A larger proportion of women, compared to men, said that they joined the military because it was difficult to find a good civilian job:
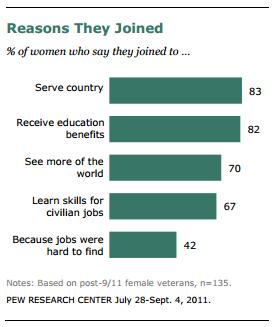
They were just as likely as men, however, to report other more common reasons for joining:
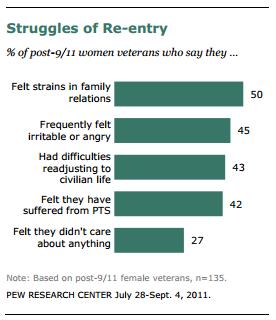
Interestingly, women reported high levels of strain re-entering the civilian population and the majority believe that the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq are not worth fighting:
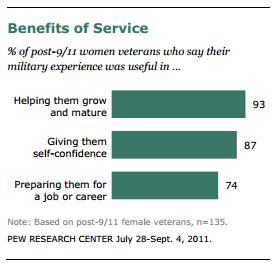
Nevertheless, a large majority felt that entering the military was good for their personal growth and career opportunities:
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.