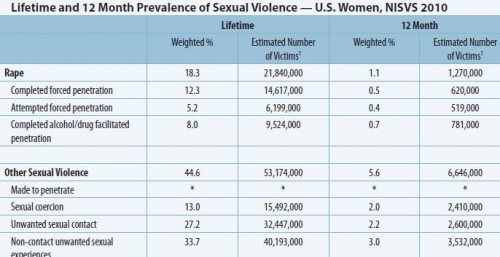
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control recently released a report on domestic violence and sexual assault in the U.S. The National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey 2010 Summary Report presents the results of phone surveys (targeting both landlines and cells) of 18,049 randomly-selected adults conducted in 2010. The results are predictably depressing: 18.3% adult women have experienced rape (defined as attempted or completed forced penetration) in their lifetimes (for men, it’s 1.4%):
Undermining the stranger rapist myth, the report found that the vast majority of perpetrators were acquaintances or partners of their victims.
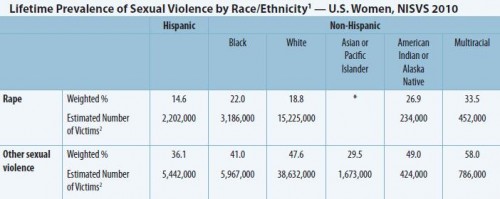
As has been found in other studies, Native American women are more at risk than other racial group for sexual assault; in this study, those identifying multiracial had the highest rates of all:
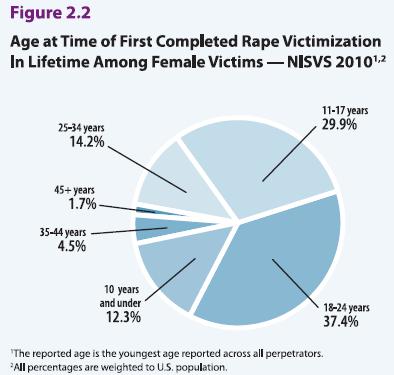
Almost a third of women who are raped are victimized before they’re 18, while over a third are young adults aged 18-24:
Risk of rape varies significantly by state, though in no state did fewer than 10% of women report being raped. Virginia had the lowest levels of victimization of women, at 11.4%; other states on the low end include Tennessee, Delaware, and Rhode Island. Worst was Alaska, at 29.2%, with Oregon not far behind at 27.2% and Nevada at 26.1%.
The report also include information on stalking and domestic violence; 16.2% of women and 5.2% of men report at least one incident, overwhelmingly from an intimate partner, while over 30% of women and 25% of men have been slapped, shoved, or pushed by a partner.
It is a singularly depressing read about the state of men’s and women’s intimate lives.