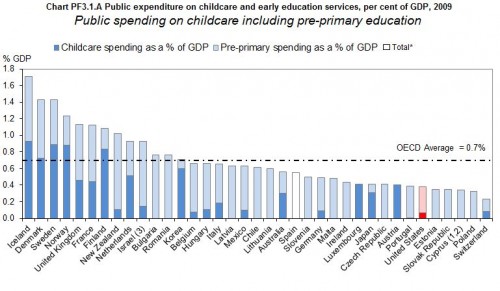
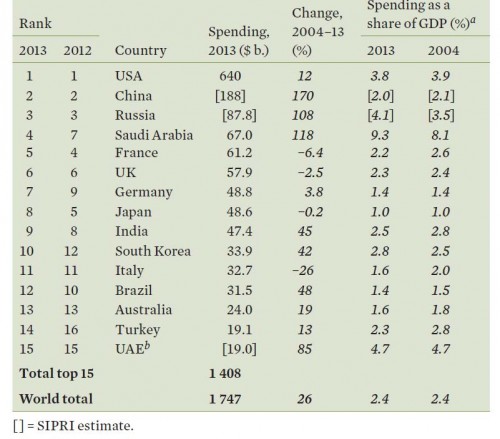
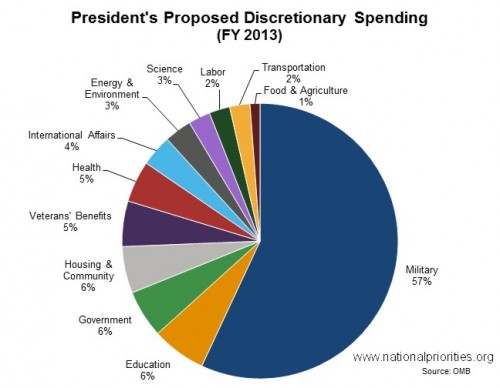
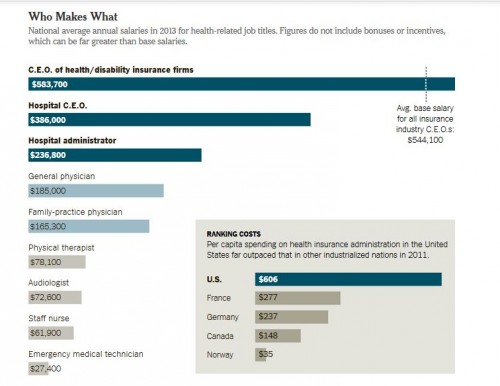
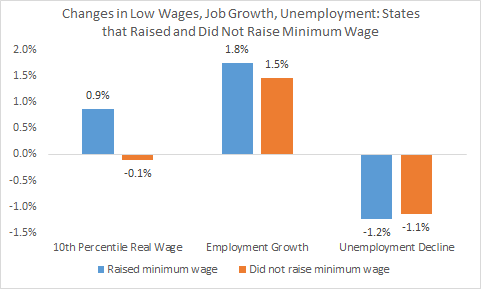As workers battle to raise the minimum wage it is nice to see more evidence that doing so helps both low wage workers and state economies.
Thirteen states raised their respective minimum wages in 2014: AZ, CA, CT, FL, MO, MT, NJ, NY, OH, OR, RI, VT, and WA. Elise Gould, an economist at the Economic Policy Institute, compared labor market changes in these thirteen states with changes in the rest of the states from the first half of 2013 to the first half of 2014.
Economic analyst Jared Bernstein summarizes the results as follows:
[Gould] compares the 10th percentile [lowest earners] wage growth among these thirteen states that increased their minimums with the rest that did not. The results are the first two bars in the figure below.
Real wages for low-wage workers rose by just about 1% over the past year in the states that raised their minimum wages, and were flat (down 0.1%) in the other states.
OK, but did those increases bite into employment growth, as opponents typically insist must be the case? Not according to the other two sets of bars. They show that payroll employment growth was slightly faster in states that raised, and the decline in unemployment, slightly greater.
In short, raising the minimum wage did boost the earnings of those at the bottom of the income distribution. Moreover, workers in states that raised the minimum wage also enjoyed greater employment growth and a greater decline in unemployment than did workers in states that did not.
Martin Hart-Landsberg is a professor of economics at Lewis and Clark College. You can follow him at Reports from the Economic Front.