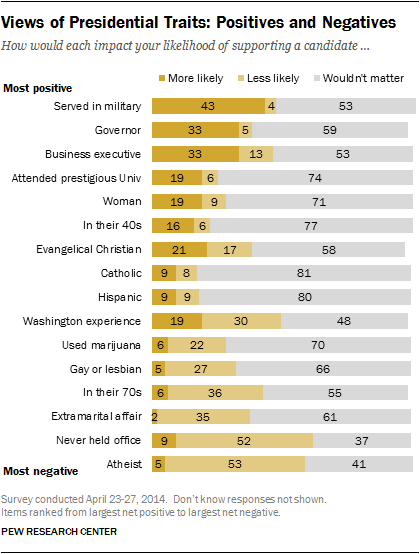
Four years ago, twenty-three economists (mostly conservative) signed a letter to Ben Bernanke warning that the Fed’s quantitative easing policy – adding billions of dollars to the economy – would be disastrous. It would “debase the currency,” create high inflation, distort financial markets, and do nothing to reduce unemployment.
Four years later, it’s clear that they were wrong (as Paul Krugman never tires of reminding us). Have they changed their beliefs?
Of course not.
Bloomberg asked the letter-signers what they now thought about their prophecy. Here’s the headline: “Fed Critics Say ’10 Letter Warning Inflation Still Right.”
This despite the actual low inflation:
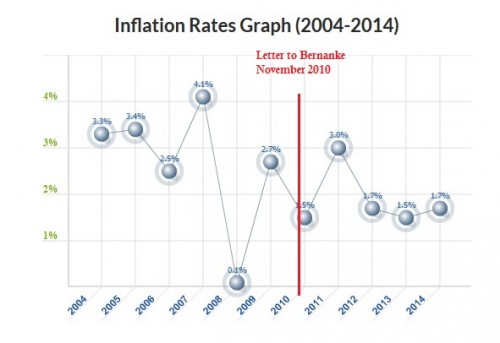
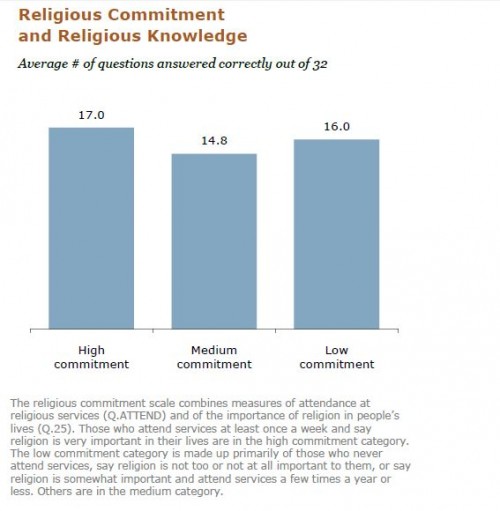
I don’t know why I assume that high-level economists would be more likely than some ordinary people to change their ideas to adjust for new facts. Fifty years ago, in The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, Thomas Kuhn showed that even in areas like chemistry and physics, scientists cling to their paradigms even in the face of accumulated anomalous facts. Why should big-shot economists be any different? It also occurs to me that it’s the most eminent in a profession who will be more resistant to change. After all, it’s the people at the top who have the greatest amount invested in their ideas – publications, reputations, consultantships, and of course ego. Economists call these “sunk costs.”
So how do they maintain their beliefs?
Most of the 23 declined to comment; a few could not be reached (including Ronald McKinnon, who died the previous day). Of those who responded, only one, Peter Wallison at the American Enterprise Institute, came close to saying, “My prediciton was wrong.”
“All of us, I think, who signed the letter have never seen anything like what’s happened here.”
Most of the others preferred denial:
“The letter was correct as stated.” (David Malpass. He worked in Treasury under Reagan and Bush I)
“The letter mentioned several things… and all have happened.” (John Taylor, Stanford)
“I think there’s plenty of inflation — not at the checkout counter, necessarily, but on Wall Street.” (Jim Grant of “Grant’s Interest Rate Observer.” Kinda makes you wonder how closely he’s been observing interest rates.)
Then there was equivocation. After Thursday night’s debacle – Giants 8, Pirates 0, knocking Pittsburgh out of the playoffs– someone reminded me, “Hey, didn’t you tell me that the Pirates would win the World Series?”
“Yes, but I didn’t say when.”
Some of the letter-signers used this same tactic, and just about as convincingly.
“Note that word ‘risk.’ And note the absence of a date.” (Niall Ferguson, Harvard)
“Inflation could come…” (Amity Shlaes, Calvin Coolidge Memorial Foundation)
The 1954 sociology classic When Prophecy Fails describes group built around a prediction that the world would soon be destroyed and that they, the believers, would be saved by flying saucers from outer space. When it didn’t happen, they too faced the problem of cognitive dissonance – dissonance between belief and fact. But because they had been very specific about what would happen and when it would happen, they could not very well use the denial and equivocation favored by the economists. Instead, they first by claimed that what had averted the disaster was their own faith. By meeting and planning and believing so strongly in their extraterrestrial rescuers, they had literally saved the world. The economists, by contrast, could not claim that their warnings saved us from inflation, for their warning – their predictions and prescriptions – had been ignored by Fed. So instead they argue that there actually is, or will be, serious inflation.
The other tactic that the millenarian group seized on was to start proselytizing – trying to convert others and to bring new members into the fold. For the conservative economists, this tactic is practically a given, but it is not necessarily a change. They had already been spreading their faith, as professors and as advisors (to policy makers, political candidates, wealthy investors, et al.). They haven’t necessarily redoubled their efforts, but the evidence has not given them pause. They continue to publish their unreconstructed views to as wide an audience as possible.
That’s the curious thing about cognitive dissonance. The goal is to reduce the dissonance, and it really doesn’t matter how. Of course, you could change your ideas, but letting go of long and deeply held ideas when the facts no longer co-operate is difficult. Apparently it’s easier to change the facts (by denial, equivocation, etc.). Or, equally effective in reducing the dissonance, you can convince others that you are right. That validation is just as effective as a friendly set of facts, especially if it comes from powerful and important people and comes with rewards both social and financial.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.