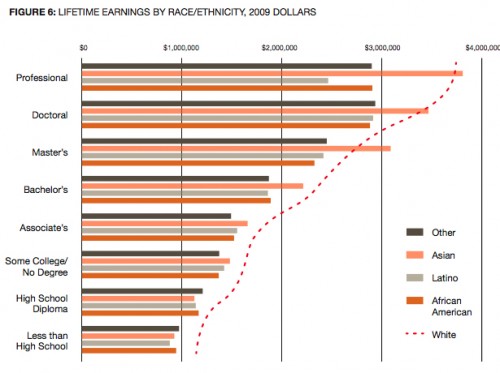
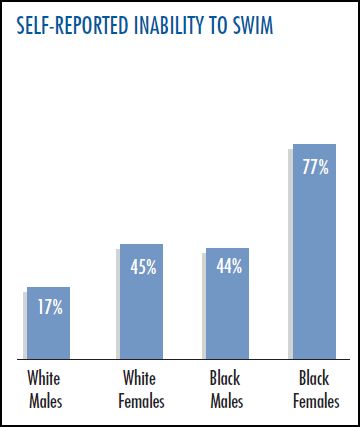
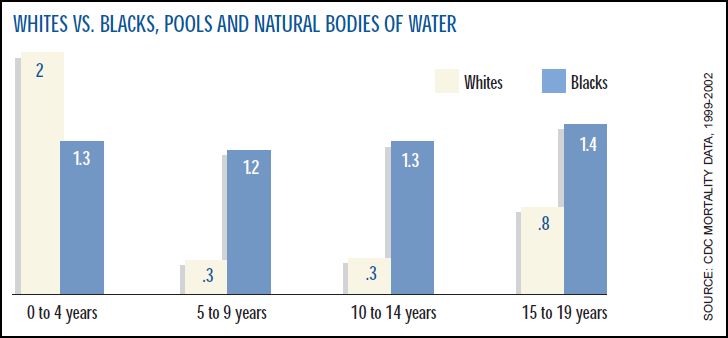
Every once in a while we here at SocImages pick a fight and a couple of years ago we sunk our teeth into satire and didn’t let go. Satirical humor is often used to expose prejudice and bigotry and it can be damn effective, as many viewers of The Colbert Report will testify. But it’s also a risky strategy. It makes fun of by doing; so, for example, it exposes racism by being extremely, over-the-top, no-one-will-ever-believe-we’re-serious racist. Except for… someone might think you’re being serious. In fact, a significant proportion of political conservatives viewing The Colbert Report believe that he is conservative like them. They recognize that he’s trying to be funny, but they don’t think he’s joking.
In our effort to think more critically about satire, we covered Amy Sedaris’ hipster racism, Ellen DeGeneres’ CoverGirl commercial, a New Yorker cover depicting Obama as a Muslim, covers of the National Review featuring Bill Clinton and Sonia Sotomayor, and board games. We also featured Jay Smooth’s commentary on Asher Roth using the phrase “nappy headed hos.”
Now Anita Sarkeesian, of Feminist Frequency, offers another illustration of how satire doesn’t always work the way progressives would like it to. She takes on TV commercials, arguing that ironic racism and sexism is still racism and sexism. Ironic advertising, she argues, allows marketers to “…use all the racist, sexist, misogynist imagery they want, and simultaneously distance themselves from it with a little wink and a nod.” You be the judge:
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.