Cross posted at Racialicious.
In many places in the midwest the American Indian is very present, but in other places in the U.S., like in California, Disney’s Pocahontas is as close as we get to “Indians.” The idea that American Indians are gone comes, in part, from the ubiquitous representation of them with feathers, buckskins, and moccasins. These anachronisms are everywhere (see, for example, here, here, here, here, and here).
American Indians are as modern as the rest of us, why are representations of American Indians, as they live today, so unusual? And what effect might that have on the psyche of American Indian people?
Via PostSecret.
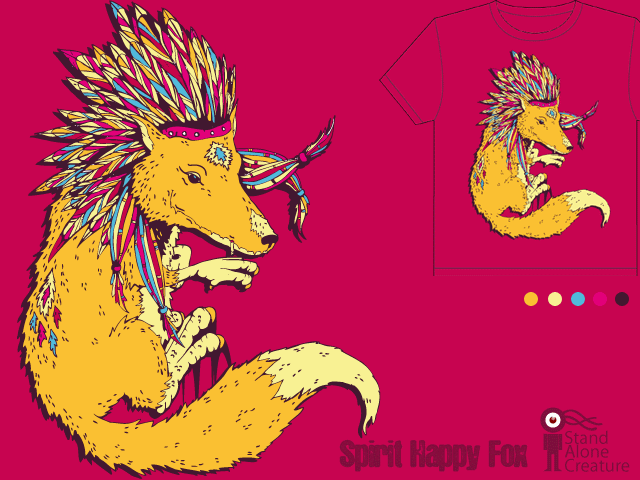
NEW! One of the commenters at Racialicious pointed us to a cartoon that illustrates how anachronistic images of American Indians may shape our ideas of what they are like: