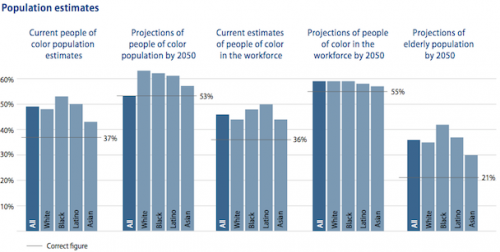
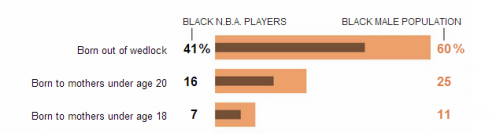
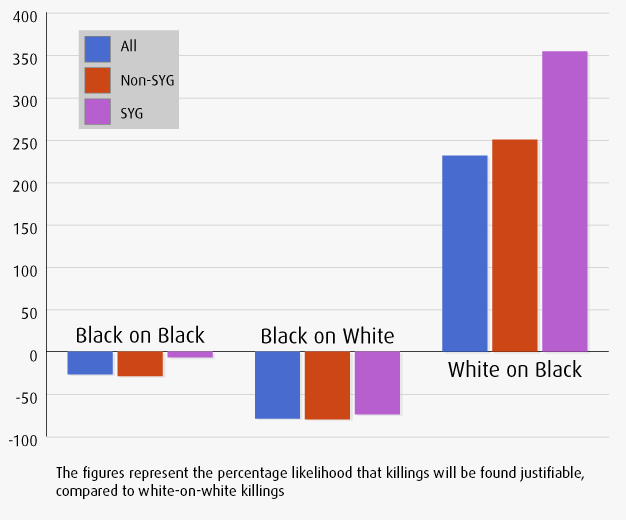
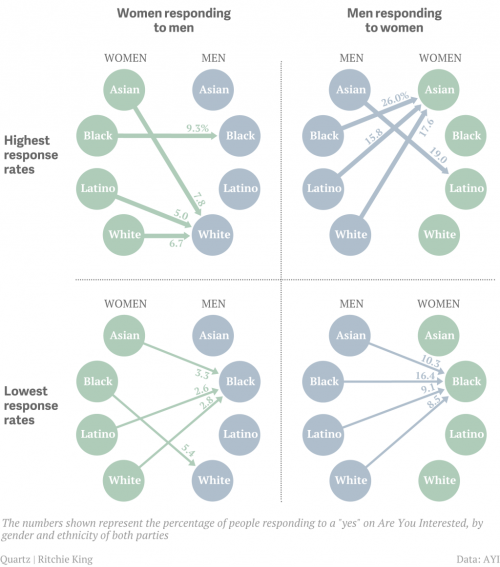
New survey data shows that the average person overestimates the diversity of the American population, both now and in the future. Today, for example, racial minorities make up 37% of the population, but the average guess was 49%.
Many Americans fear rising diversity. Over half worry that more minorities means fewer jobs, nearly half think that it means more crime, and almost two-thirds think these groups strain social services. If people think that minorities are bad for America and overestimate their prevalence, they may be more likely to support draconian and punishing policy designed to minimize their numbers or mitigate the consequences they are believed to bring.
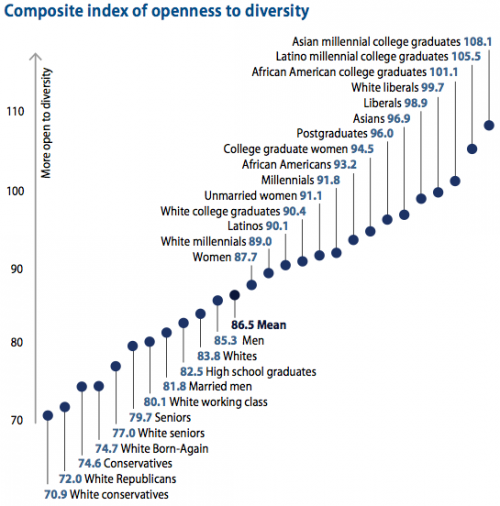
Not all Americans, of course, fear diversity equally. Below are the scores of various groups on an “openness to diversity” measure with a range of 0-160.
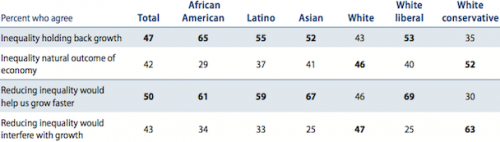
For the future, Americans are still strongly divided as to what to do about diversity and the racialized inequality we currently see.
Via The Atlantic; thanks to @_ettey for the link. Cross-posted at Pacific Standard.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.