The Equal Justice Initiative just released a report about racial bias in jury selection, particularly in the South. I first heard about it on NPR. Racial discrimination in jury selection is illegal, but evidence suggests it’s still quite common, particularly through the use of peremptory challenges (the ability of attorneys to exclude a certain number of potential jurors without having to say why or justify it).
The results are striking; for instance, “…in Houston County, Alabama, 80% of African Americans qualified for jury service have been struck by prosecutors in death penalty cases” (p. 4 of the report).
Here’s a short video about one case:
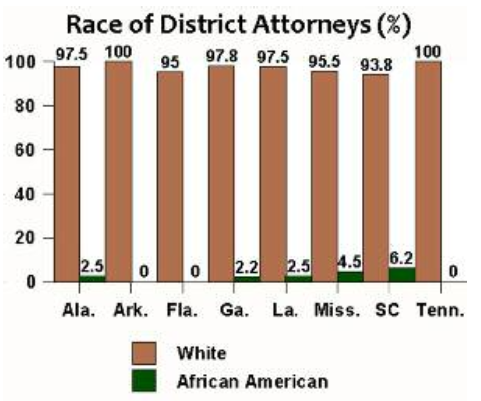
The report doesn’t have as many informational images as I’d like, but here’s one showing the race of District Attorneys in several Southern states:
This video gives a historical overview, though it’s maybe not the most captivating description you’ll ever encounter:
And with that, dear readers, I’m off to court, as I got a jury summons and now must find out if I’ll end up on an actual jury. I’m taking lots of reading material.